JP2005195604A - Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery - Google Patents
Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005195604A JP2005195604A JP2005026432A JP2005026432A JP2005195604A JP 2005195604 A JP2005195604 A JP 2005195604A JP 2005026432 A JP2005026432 A JP 2005026432A JP 2005026432 A JP2005026432 A JP 2005026432A JP 2005195604 A JP2005195604 A JP 2005195604A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- abnormality
- abnormality determination
- assembled battery
- deviation
- battery
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Current Or Voltage (AREA)
- Tests Of Electric Status Of Batteries (AREA)
- Secondary Cells (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、組電池の異常判定装置に関し、詳しくは、複数の電池を直列に接続してなる組電池の異常を判定する異常判定装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an assembled battery abnormality determination device, and more particularly to an abnormality determination device that determines an abnormality of an assembled battery formed by connecting a plurality of batteries in series.
従来、この種の組電池の異常判定装置としては、単位電池毎にあるいは複数の単位電池からなるブロック毎に電池の内部抵抗を算出し、その値の大きさに基づいて異常を判定するものが提案されている。単位電池は、その構成に依存する内部抵抗が存在するから、その内部抵抗を計算し、その値に基づいて異常を判定することができる。 Conventionally, as an abnormality determination device for this type of assembled battery, there is an apparatus for calculating an internal resistance of a battery for each unit battery or for each block composed of a plurality of unit batteries and determining an abnormality based on the magnitude of the value. Proposed. Since the unit battery has an internal resistance depending on its configuration, it is possible to calculate the internal resistance and determine abnormality based on the value.
しかしながら、こうした内部抵抗を算出しその値の大きさに基づいて異常を判定する装置では、充放電のパターンによっては正確に判定することが困難であるという問題があった。充放電のパターンによっては組電池の起電力が変動する。内部抵抗は電池の起電圧が変動しなければ正確に算出できるが、ある内部抵抗値が充放電のパターンによって正常な値となったり、異常な値となってしまう。また、電池の起電圧は、電池の温度によっても変化するから、上述の問題は更にクローズアップされる。さらに、単位電池毎やブロック毎に内部抵抗を算出すると、その計算処理が膨大なものとなるため、その計算に高性能なコンピュータを必要とする。 However, an apparatus that calculates the internal resistance and determines an abnormality based on the magnitude of the value has a problem that it is difficult to accurately determine depending on the charge / discharge pattern. The electromotive force of the assembled battery varies depending on the charge / discharge pattern. Although the internal resistance can be calculated accurately if the electromotive voltage of the battery does not fluctuate, a certain internal resistance value becomes a normal value or an abnormal value depending on the charge / discharge pattern. Moreover, since the electromotive voltage of a battery also changes depending on the temperature of the battery, the above problem is further highlighted. Furthermore, if the internal resistance is calculated for each unit battery or block, the calculation process becomes enormous, and a high-performance computer is required for the calculation.
本発明の異常判定装置は、こうした問題を解決し、充放電のパターンや温度が変化したときでも正確に組電池の異常を判定することを目的の一つとする。また、本発明の異常判定装置は、こうした異常の判定を簡易な計算で行なうことを目的の一つとする。 An object of the abnormality determination device of the present invention is to solve such problems and accurately determine abnormality of a battery pack even when a charge / discharge pattern or temperature changes. Another object of the abnormality determination device of the present invention is to perform such abnormality determination by simple calculation.
本発明の異常判定装置は、上述の目的の少なくとも一部を達成するために以下の手段を採った。 The abnormality determination apparatus of the present invention employs the following means in order to achieve at least a part of the above-described object.
本発明の組電池の異常判定装置は、複数の電池を直列に接続してなる組電池の異常を判定する異常判定装置であって、前記複数の電池の各々の電圧を所定のタイミングで計測する電圧計測手段と、前記組電池を流れる電流を該タイミングで計測する電流計測手段と、前記電圧計測手段により計測された前記各々の電圧を入力し、該入力した各々の電圧のうちの最大値と最小値との偏差を演算する偏差演算手段と、前記電流計測手段により計測された電流と、前記偏差演算手段により演算された偏差と、を対の値として複数記憶する記憶手段と、該タイミングで計測され、記憶された複数の対の値に基づいて前記組電池の異常を判定する異常判定手段と、を備えることを要旨とする。さらに、前記偏差演算手段は、前記組電池が充電状態であるか、放電状態であるかに分けて偏差を演算する。 An abnormality determination apparatus for an assembled battery according to the present invention is an abnormality determination apparatus for determining an abnormality of an assembled battery formed by connecting a plurality of batteries in series, and measures the voltage of each of the plurality of batteries at a predetermined timing. Voltage measuring means; current measuring means for measuring the current flowing through the assembled battery at the timing; and the respective voltages measured by the voltage measuring means are input, and the maximum value of the input voltages is Deviation calculating means for calculating a deviation from the minimum value; storage means for storing a plurality of currents measured by the current measuring means and deviations calculated by the deviation calculating means as a pair of values; The present invention includes an abnormality determination unit that determines abnormality of the assembled battery based on a plurality of pairs of measured and stored values. Further, the deviation calculating means calculates the deviation according to whether the assembled battery is in a charged state or a discharged state.
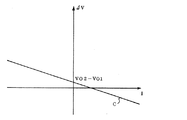
ここで、各々の電圧の最大値と最小値との偏差と組電池を流れる電流とからなる対の値を複数用いることによって組電池の異常を判定できる原理について説明する。電池の電圧(V)は、電池が正常であるか否かに拘わらず、次式(1)に示すように、起電力(V0)から電池を流れる電流(I)と内部抵抗(R)との積を減じたものとして表わされる。 Here, the principle by which the abnormality of the assembled battery can be determined by using a plurality of pairs of values consisting of the deviation between the maximum value and the minimum value of each voltage and the current flowing through the assembled battery will be described. Regardless of whether or not the battery is normal, the voltage (V) of the battery is represented by the following equation (1): current (I) flowing through the battery from the electromotive force (V0) and internal resistance (R) It is expressed as the product of.
V=V0−R・I (1)
いま、正常な電池と異常な電池とを直列に接続した組電池を考える。正常な電池が示す電圧も異常な電池が示す電圧も上式(1)によって表わされ、それぞれ次式(2)および(3)となる。正常な電池と異常な電池を直列に接続して組電池を構成している場合を考えているから各電池に流れる電流(I)は同じ値となる。
V = V0−R · I (1)
Consider an assembled battery in which a normal battery and an abnormal battery are connected in series. The voltage indicated by the normal battery and the voltage indicated by the abnormal battery are expressed by the above equation (1), and are expressed by the following equations (2) and (3), respectively. Since the case where a normal battery and an abnormal battery are connected in series to form an assembled battery is considered, the current (I) flowing through each battery has the same value.
V1=V01−R1・I (2)
V2=V02−R2・I (3)
上式(3)から上式(2)を減じれば、次式(4)となり、左辺は電圧の偏差(ΔV)となる。
V1 = V01−R1 · I (2)
V2 = V02−R2 · I (3)
When the above equation (2) is subtracted from the above equation (3), the following equation (4) is obtained, and the left side is the voltage deviation (ΔV).
ΔV=V2−V1=(V02−V01)−(R2−R1)・I (4)
各電池の電圧と組電池を電流が計測できるものであれば、電圧の偏差(ΔV)と電流(I)とは既知のものとして取り扱うことができるから、未知数は起電力の偏差と内部抵抗の偏差の二つとなる。したがって、電圧の偏差と電流とを対の値としたとき2以上の対の値を用いれば起電力の偏差と内部抵抗の偏差とを求めることができる。一般に、電池の異常は内部抵抗に現われるから、内部抵抗の偏差によって電池の異常は判定できるのである。すなわち一方の電池が正常であれば、複数の対の値に基づいて、すなわち複数の対の値から内部抵抗の偏差に相当するものを求めることにより他方の電池が正常であるか否かを判定できるのである。
ΔV = V2−V1 = (V02−V01) − (R2−R1) · I (4)
Since the voltage deviation (ΔV) and the current (I) can be treated as known if the voltage of each battery and the assembled battery can be measured, the unknown is the difference between the electromotive force and the internal resistance. There are two deviations. Therefore, when the voltage deviation and the current are taken as a pair value, the electromotive force deviation and the internal resistance deviation can be obtained by using two or more pairs of values. In general, a battery abnormality appears in the internal resistance, so that the battery abnormality can be determined by the deviation of the internal resistance. That is, if one battery is normal, it is determined whether or not the other battery is normal based on the values of a plurality of pairs, that is, by obtaining a value corresponding to the deviation of the internal resistance from the values of the plurality of pairs. It can be done.
上述の原理の説明では、一方の電池が正常であるものとして他方の電池の異常を判定している。本発明の組電池の異常判定装置では、各々の電池の電圧の最大値と最小値との偏差を演算することにより、電圧が最大の電池を正常な電池と仮定すると共に電圧が最小の電池を異常のおそれがある電池と仮定し、電圧が最小の電池を判定することによって組電池の異常を判定するのである。 In the above description of the principle, it is determined that one battery is normal and the other battery is abnormal. In the battery pack abnormality determination device of the present invention, by calculating the deviation between the maximum value and the minimum value of the voltage of each battery, the battery having the maximum voltage is assumed to be a normal battery and the battery having the minimum voltage is determined. It is assumed that the battery is likely to be abnormal, and the abnormality of the assembled battery is determined by determining the battery having the minimum voltage.
こうした本発明の組電池の異常判定装置によれば、各々の電池の電圧の最大値と最小値との偏差と組電池を流れる電流とに基づいて組電池の異常を判定することができる。しかも、起電圧の変動は差を算出することにより打ち消されるから、充放電のパターンや温度の変化に異常の判定が左右されることがない。 According to the assembled battery abnormality determination device of the present invention, it is possible to determine the abnormality of the assembled battery based on the deviation between the maximum value and the minimum value of the voltage of each battery and the current flowing through the assembled battery. Moreover, since fluctuations in the electromotive voltage are canceled by calculating the difference, the determination of abnormality does not depend on the charge / discharge pattern or temperature change.
こうした本発明の組電池の異常判定装置において、前記異常判定手段は前記記憶手段により記憶された複数の対の値が所定対数となったときに異常を判定する手段であるものとしたり、前記異常判定手段は前記記憶手段により記憶された複数の対の値のうちの前記電流の値が所定範囲を越えて分布したときに異常を判定する手段であるものとすることもできる。このように複数の対の値を所定対数のものを使ったり、所定範囲を越えた分布のものを使って異常を判定することにより、より正確に組電池の異常を判定することができる。 In such an assembled battery abnormality determination device of the present invention, the abnormality determination means is means for determining abnormality when a plurality of pairs of values stored in the storage means reaches a predetermined logarithm, or the abnormality The determination means may be means for determining an abnormality when the current values of a plurality of pairs of values stored by the storage means are distributed beyond a predetermined range. As described above, by using a plurality of pairs of values having a predetermined logarithm or by using a distribution having a distribution exceeding a predetermined range, it is possible to determine the abnormality of the assembled battery more accurately.
また、本発明の組電池の異常判定装置において、前記異常判定手段は、前記複数の対の値を用いて最小二乗法により少なくとも傾きを演算し、該傾きに基づいて異常を判定するものとすることもできる。上式(4)は直線の式をなしており、内部抵抗の偏差はこの直線の傾きをなすから、直線近似の手法として最小二乗法を用いて傾きを求め、これにより組電池の異常を判定することができる。こうした傾きにより判定をする組電池の異常判定装置において、前記異常判定手段は、前記傾きの絶対値が所定値より大きいときに異常と判定する手段であるものとすることもできる。さらに、本発明に係る異常判定方法は、複数の電池を直列に接続してなる組電池の異常を判定する異常判定方法であって、前記複数の電池の各々の電圧を所定のタイミングで計測する電圧計測工程と、前記組電池を流れる電流を該タイミングで計測する電流計測工程と、前記電圧計測工程により計測された前記各々の電圧を入力し、該入力した各々の電圧のうちの最大値と最小値との偏差を演算する偏差演算工程と、前記電流計測工程により計測された電流と、前記偏差演算工程により読み込まれた前記各々の電圧から演算された偏差と、を対の値として複数記憶する記憶工程と、該タイミングで計測され、記憶された複数の対の値に基づいて前記組電池の異常を判定する異常判定工程と、を含んでいる。 Further, in the battery pack abnormality determination device of the present invention, the abnormality determination means calculates at least an inclination by a least square method using the plurality of pairs of values, and determines an abnormality based on the inclination. You can also. The above equation (4) is a straight line equation, and the deviation of the internal resistance makes the slope of this straight line. Therefore, the slope is obtained using the least squares method as a linear approximation method, and the abnormality of the assembled battery is judged by this. can do. In the battery pack abnormality determination device that makes a determination based on such an inclination, the abnormality determination unit may be a unit that determines an abnormality when the absolute value of the inclination is greater than a predetermined value. Furthermore, the abnormality determination method according to the present invention is an abnormality determination method for determining an abnormality of an assembled battery formed by connecting a plurality of batteries in series, and measures each voltage of the plurality of batteries at a predetermined timing. A voltage measurement step, a current measurement step of measuring the current flowing through the assembled battery at the timing, the respective voltages measured by the voltage measurement step are input, and the maximum value of the input voltages is A plurality of deviation calculation steps for calculating a deviation from the minimum value, a current measured by the current measurement step, and a deviation calculated from each of the voltages read by the deviation calculation step are stored as a pair of values. And an abnormality determination step of determining abnormality of the assembled battery based on a plurality of pairs of values measured and stored at the timing.
次に、本発明の実施の形態を実施例を用いて説明する。図1は、本発明の一実施例である組電池の異常判定装置40の構成の概略を例示する概略構成図である。図示するように、実施例の組電池の異常判定装置40は、n個の単位電池を直列に接続してなる組電池20に取り付けられており、組電池20には、組電池20の充放電により動作する負荷30が接続されている。
Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described using examples. FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram illustrating an outline of the configuration of an assembled battery
実施例の異常判定装置40は、組電池20の各単位電池の電圧V1〜Vnを計測する複数の電圧計からなる電圧計測器42、組電池20に流れる電流Iを計測する電流計44、異常判定装置40全体を制御すると共に組電池20の異常の判定処理を行なう電子処理装置50、所定タイミング毎(例えば、10ms毎)に電子処理装置50にクロック信号CLを出力するクロック発振回路60、異常判定装置40の各部に必要な電力を供給する図示しない電源回路などを備える。
The
電子処理装置50は、CPU52を中心として構成された1チップマイクロコンピュータであり、その内部には処理プログラムを予め記憶した内部ROM54と、データを一時的に記憶する内部RAM56と、各種入力ポートおよび出力ポートとが備えられている。入力ポートには、電圧計測器42により計測された組電池20の各単電池の電圧V1〜Vnや電流計44により計測された電流I,クロック発振回路60から出力されるクロック信号CLなどが入力されており、出力ポートからは、異常判定装置40による組電池20の異常の判定結果をLCD70や他の装置(例えば組電池20の運転を制御する図示しないコンピュータや負荷30の運転を制御する図示しないコンピュータなど)に出力する異常判定信号J,Kが出力されている。
The
こうして構成された実施例の異常判定装置40は、内部ROM54に予め記憶された図2に例示する異常判定ルーチンを所定時間毎(例えば、10ms毎)に繰り返し実行することによって組電池20に異常がないか否かを監視している。なお、図示する異常判定ルーチンを実行するタイミングは、クロック発振回路60から入力されるクロック信号CLをカウントすることによって計られている。以下、この異常判定ルーチンに基づいて異常判定装置40による組電池20の異常の判定について説明する。
The
異常判定ルーチンが実行されると、CPU52は、まず電流計44により計測される電流Iと電圧計測器42により計測される組電池20の各単位電池の電圧V1〜Vnを同タイミングで読み込む処理を実行する(ステップS100)。次に、読み込んだ電流Iが値0より大きいか否か判定し(ステップS110)、電流Iが値0より大きいときには読み込んだ電圧V1〜Vnのうちの最小値から最大値を減じて電圧偏差ΔVを算出し(ステップS120)、電流Iが値0以下のときには逆に電圧V1〜Vnのうちの最大値から最小値を減じて電圧偏差ΔVを算出する(ステップS130)。ここで、電流Iの値により電圧偏差ΔVの符号を変えるのは、電流Iが値0より大きいときの状態、即ち組電池20からの放電により負荷30で電力を消費している状態と、電流Iが値0以下のときの状態、即ち負荷30により供給される電力により組電池20を充電している状態とを考慮し、いずれの状態でも電圧偏差ΔVを同様に扱うためである。
When the abnormality determination routine is executed, the
次に、CPU52は、こうして算出された電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとを対の値として内部RAM56に一時的に記憶する(ステップS140)。そして、カウンタNをインクリメントし(ステップS150)、カウンタNの値が閾値Nrefより大きいか否かを判定する(ステップS160)。カウンタNは、電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとからなる対の値を幾つ内部RAM56に記憶したかをカウントするものであり、異常判定装置40の電源が投入されたときに実行される図示しない初期化ルーチンにより初期値として値0が設定されるものである。また、閾値Nrefは、組電池20を判定するのに十分な対の値の数として設定されるものであり、組電池20に要求される安定性の程度や組電池20を構成する単位電池の数あるいは単位電池の製品のばらつきなどにより定められる。カウンタNが閾値Nref以下のときには、組電池20の異常を判定するのに十分な数の対の値を記憶していないと判断し本ルーチンを終了する。
Next, the
一方、カウンタNが閾値Nrefより大きいときには、記憶したN個の対の値を用いて最小二乗法による演算により傾きΔRを算出すると共に(ステップS170)、N個の電流Iよりその分散σIを算出する(ステップS180)。最小二乗法による傾きΔRの算出および電流Iの分散σIの算出の手法については一般的な数値計算法によるため、その計算手法についての説明は省略する。 On the other hand, when the counter N is larger than the threshold value Nref, the slope ΔR is calculated by the operation of the least square method using the stored N pairs of values (step S170), and the variance σI is calculated from the N currents I. (Step S180). Since the method of calculating the slope ΔR by the least square method and the calculation of the variance σI of the current I is based on a general numerical calculation method, the description of the calculation method is omitted.
次に、算出した電流Iの分散σIが閾値σrefより大きいか否かを判定する(ステップS190)。電流Iの分散σIを考慮するのは、カウンタNを閾値Nrefと比較することにより組電池20の異常を判定するのに十分な数の対の値を記憶していると判定されても、最小二乗法によって求められる傾きΔRの精度が電流Iの分散σIによって左右されるからである。電流Iの分散σIが閾値σref以下のときには、十分な精度の傾きΔRが得られず組電池20の異常を十分な精度で判定できないと判断して、本ルーチンを終了する。 Next, it is determined whether or not the calculated variance σI of the current I is larger than the threshold value σref (step S190). The variance σI of the current I is taken into consideration even if it is determined that a sufficient number of pairs of values for determining an abnormality of the battery pack 20 is stored by comparing the counter N with the threshold value Nref. This is because the accuracy of the slope ΔR obtained by the square method depends on the variance σI of the current I. When the variance σI of the current I is equal to or less than the threshold σref, it is determined that the slope ΔR with sufficient accuracy cannot be obtained and the abnormality of the assembled battery 20 cannot be determined with sufficient accuracy, and this routine is terminated.
電流Iの分散σIが閾値σrefより大きいときには、傾きΔRを閾値Rrefと比較する(ステップS200)。本発明の原理で説明したように、電池の異常はその内部抵抗に現われるから、実施例の組電池20の場合には、内部抵抗の偏差、即ち傾きΔRに基づいて組電池20の異常を判定することができる。実施例では、正常な単位電池の電圧と電流との関係および異常な単位電池の電圧と電流との関係は共に直線関係にあり、電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとの関係も直線関係にあると考えることにより、内部抵抗の偏差を傾きΔRとして求めている。図3に正常な単位電池および異常な単位電池の電圧と電流との関係を例示する。図中直線状の線Aは正常な単位電池の電圧と電流との関係であり、直線状の線Bは異常な単位電池の電圧と電流との関係である。図示するように、それぞれの関係は上述した式(2)および式(3)に示したような直線状のものとなる。したがって、電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとの関係も図4に例示するように直線状のものとなる。いま、組電池20を構成する単位電池のすべてが正常であれば、いずれの単位電池も図3中の線Aに近い特性を示すから、傾きΔRは値0に近いものとなる。組電池20を構成する単位電池のうちのいずれかが異常であれば、その単位電池の特性は起電力V02は異なるものの図3中の線Bのように線Aとは異なる傾きの直線状になるから、傾きΔRは値0に比して大きな値となる。このような理由から、傾きΔRを閾値Rrefと比較することによって組電池20の異常を判定できるのである。なお、閾値Rrefの値は、組電池20を構成する単位電池の特性やその製品のばらつきなどによって定められるものである。
When the variance σI of the current I is larger than the threshold value σref, the slope ΔR is compared with the threshold value Rref (step S200). As described in the principle of the present invention, the abnormality of the battery appears in its internal resistance. In the case of the assembled battery 20 of the embodiment, the abnormality of the assembled battery 20 is determined based on the deviation of the internal resistance, that is, the slope ΔR. can do. In the embodiment, the relationship between the voltage and current of a normal unit cell and the relationship between the voltage and current of an abnormal unit cell are both linear, and the relationship between the voltage deviation ΔV and the current I is also linear. Thus, the deviation of the internal resistance is obtained as the slope ΔR. FIG. 3 illustrates the relationship between the voltage and current of normal unit cells and abnormal unit cells. In the figure, the straight line A is the relationship between the voltage and current of a normal unit cell, and the straight line B is the relationship between the voltage and current of an abnormal unit cell. As shown in the figure, the respective relationships are linear as shown in the above-described equations (2) and (3). Therefore, the relationship between the voltage deviation ΔV and the current I is also linear as illustrated in FIG. If all the unit batteries constituting the assembled battery 20 are normal, all the unit batteries exhibit characteristics close to the line A in FIG. 3, and the slope ΔR is close to the
こうして傾きΔRと閾値Rrefとを比較し、傾きΔRが閾値Rrefより大きいときには、組電池20を構成する単位電池のうちのいずれかが異常な状態となり組電池20に異常が発生したと判定して異常判定フラグFに値1をセットし(ステップS210)、カウンタNを値0にリセットして(ステップS230)、本ルーチンを終了する。一方、傾きΔRが閾値Rref以下のときには、組電池20を構成するいずれの単位電池も正常な状態にあると判定して異常判定フラグFに値0をセットし(ステップS220)、カウンタNを値0にリセットして(ステップS230)、本ルーチンを終了する。実施例の異常判定装置40では、このようにセットされた異常判定フラグFの値を異常判定信号J,KとしてLCD70や他の装置に出力する。
Thus, the inclination ΔR is compared with the threshold value Rref, and when the inclination ΔR is larger than the threshold value Rref, it is determined that one of the unit batteries constituting the assembled battery 20 is in an abnormal state and an abnormality has occurred in the assembled battery 20. The abnormality determination flag F is set to 1 (step S210), the counter N is reset to 0 (step S230), and this routine is terminated. On the other hand, when the slope ΔR is equal to or smaller than the threshold value Rref, it is determined that any unit battery constituting the assembled battery 20 is in a normal state, the
以上説明した実施例の組電池の異常判定装置40によれば、組電池20を構成する各単位電池の電圧V1〜Vnのうちの最大値と最小値との偏差である電圧偏差ΔVと組電池20に流れる電流Iとからなる対の値に基づいて組電池20の異常を判定することができる。しかも、電流Iの分散σIを考慮して種々の充放電のパターン等が含まれるようにするから、充放電のパターンに拘わらずより正確に組電池20の異常を判定することができる。また、組電池20に温度変化が生じることにより正常な単位電池も異常な単位電池もその特性を変化させるが、電圧の偏差である電圧偏差ΔVを用いて特性の変化を相殺するから、組電池20に温度変化が生じたときでも組電池20の異常を正確に判定することができる。さらに、最小二乗法による演算で傾きΔRを算出するだけで組電池20の異常を判定するから、組電池20を構成する各単位電池の内部抵抗をすべて計算して異常を判定するものや複数個の単位電池により構成される電池ブロックの各内部抵抗を計算して異常を判定するものに比して簡易な計算により異常を判定することができる。
According to the assembled battery
実施例の組電池の異常判定装置40では、電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとからなる対の値が閾値Nrefより多く、しかも電流Iの分散σIが閾値σrefより大きいときに組電池20の異常を判定するものとしたが、電流Iの分散σIは考慮せずに電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとからなる対の値が閾値Nrefより大きいときに組電池20の異常を判定するものとしたり、カウンタNを用いずに単に電流Iの分散σIが閾値σIより大きくなったときに組電池20の異常を判定するものとしても差し支えない。
In the battery pack
また、実施例の組電池の異常判定装置40では、正常な電池か否かに拘わらずその電圧と電流との関係を直線関係として捉え、最小二乗法による直線近似の手法で内部抵抗の偏差である傾きΔRを求めて組電池20の異常を判定したが、電池と電流との関係を直線以外の関係(例えば3次関数曲線やベゼー曲線など)として捉えると共に電圧偏差ΔVと電流Iとの関係も直線以外の関係として捉え、その関係における単位電池の内部抵抗に基づいて構成される項に着目し、これにより異常を判定するものとしてもよい。
In addition, in the battery pack
以上、本発明の実施の形態について実施例を用いて説明したが、本発明はこうした実施例に何等限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において、種々なる形態で実施し得ることは勿論である。 The embodiments of the present invention have been described using the embodiments. However, the present invention is not limited to these embodiments, and can be implemented in various forms without departing from the gist of the present invention. Of course you get.
20 組電池、30 負荷、40 異常判定装置、42 電圧計測器、44 電流計、50 電子処理装置、52 CPU、54 内部ROM、56 内部RAM、60 クロック発振回路。 20 assembled battery, 30 load, 40 abnormality determination device, 42 voltage measuring device, 44 ammeter, 50 electronic processing device, 52 CPU, 54 internal ROM, 56 internal RAM, 60 clock oscillation circuit.
Claims (7)
前記複数の電池の各々の電圧を所定のタイミングで計測する電圧計測手段と、
前記組電池を流れる電流を該タイミングで計測する電流計測手段と、
前記電圧計測手段により計測された前記各々の電圧を入力し、該入力した各々の電圧のうちの最大値と最小値との偏差を演算する偏差演算手段と、
前記電流計測手段により計測された電流と、前記偏差演算手段により演算された偏差と、を対の値として複数記憶する記憶手段と、
該タイミングで計測され、記憶された複数の対の値に基づいて前記組電池の異常を判定する異常判定手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする異常判定装置。 An abnormality determination device for determining abnormality of an assembled battery formed by connecting a plurality of batteries in series,
Voltage measuring means for measuring each voltage of the plurality of batteries at a predetermined timing;
Current measuring means for measuring the current flowing through the assembled battery at the timing;
Deviation calculating means for inputting each of the voltages measured by the voltage measuring means and calculating a deviation between the maximum value and the minimum value of the input voltages;
Storage means for storing a plurality of currents measured by the current measurement means and deviations calculated by the deviation calculation means as a pair of values;
An abnormality determining means for determining an abnormality of the assembled battery based on a plurality of pairs of values measured and stored at the timing;
An abnormality determination device comprising:
前記複数の電池の各々の電圧を所定のタイミングで計測する電圧計測工程と、
前記組電池を流れる電流を該タイミングで計測する電流計測工程と、
前記電圧計測工程により計測された前記各々の電圧を入力し、該入力した各々の電圧のうちの最大値と最小値との偏差を演算する偏差演算工程と、
前記電流計測工程により計測された電流と、前記偏差演算工程により読み込まれた前記各々の電圧から演算された偏差と、を対の値として複数記憶する記憶工程と、
該タイミングで計測され、記憶された複数の対の値に基づいて前記組電池の異常を判定する異常判定工程と、
を含むことを特徴とする異常判定方法。 An abnormality determination method for determining abnormality of an assembled battery formed by connecting a plurality of batteries in series,
A voltage measuring step of measuring the voltage of each of the plurality of batteries at a predetermined timing;
A current measurement step of measuring the current flowing through the assembled battery at the timing;
A deviation calculating step of inputting each of the voltages measured in the voltage measuring step and calculating a deviation between the maximum value and the minimum value of the input voltages;
A storage step of storing a plurality of currents measured by the current measurement step and deviations calculated from the respective voltages read by the deviation calculation step as a pair of values;
An abnormality determination step of determining abnormality of the assembled battery based on a plurality of pairs of values measured and stored at the timing;
The abnormality determination method characterized by including.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005026432A JP2005195604A (en) | 2005-02-02 | 2005-02-02 | Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005026432A JP2005195604A (en) | 2005-02-02 | 2005-02-02 | Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP06622299A Division JP4030217B2 (en) | 1999-03-12 | 1999-03-12 | Abnormality determination device and abnormality determination method for battery pack |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005195604A true JP2005195604A (en) | 2005-07-21 |
Family
ID=34824716
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005026432A Withdrawn JP2005195604A (en) | 2005-02-02 | 2005-02-02 | Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005195604A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008014152A (en) * | 2006-07-03 | 2008-01-24 | Denso Corp | Learning method of injection characteristic and fuel injection control device |
| WO2008096771A1 (en) | 2007-02-08 | 2008-08-14 | Panasonic Ev Energy Co., Ltd. | Device and method for detecting abnormality of electric storage device |
| EP2088445A1 (en) * | 2006-11-27 | 2009-08-12 | Panasonic Corporation | Accumulator failure detecting device, accumulator failure detecting method, accumulator failure detecting program, and computer-readable recording medium containing the accumulator failure detecting program |
| JP2011076746A (en) * | 2009-09-29 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Abnormality prediction system for secondary battery |
| KR20140013759A (en) * | 2012-07-27 | 2014-02-05 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Method for vehicle battery pack management using module-impedance |
| EP2518522A4 (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2017-06-28 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Abnormality detection device for assembled battery |
| KR20210007247A (en) * | 2019-07-10 | 2021-01-20 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Apparatus and method for diagnosing cooling requirement for battery module |
| CN113533979A (en) * | 2021-07-15 | 2021-10-22 | 合肥力高动力科技有限公司 | Method for judging abnormal battery cell of battery pack |
| CN114361617A (en) * | 2021-12-31 | 2022-04-15 | 重庆长安新能源汽车科技有限公司 | Power battery thermal runaway risk early warning method and early warning system |
| WO2022098096A1 (en) * | 2020-11-05 | 2022-05-12 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Battery diagnostic device and method |
-
2005
- 2005-02-02 JP JP2005026432A patent/JP2005195604A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4682935B2 (en) * | 2006-07-03 | 2011-05-11 | 株式会社デンソー | Injection characteristic learning method and fuel injection control device |
| JP2008014152A (en) * | 2006-07-03 | 2008-01-24 | Denso Corp | Learning method of injection characteristic and fuel injection control device |
| EP2088445A1 (en) * | 2006-11-27 | 2009-08-12 | Panasonic Corporation | Accumulator failure detecting device, accumulator failure detecting method, accumulator failure detecting program, and computer-readable recording medium containing the accumulator failure detecting program |
| EP2088445A4 (en) * | 2006-11-27 | 2013-03-06 | Panasonic Corp | Accumulator failure detecting device, accumulator failure detecting method, accumulator failure detecting program, and computer-readable recording medium containing the accumulator failure detecting program |
| WO2008096771A1 (en) | 2007-02-08 | 2008-08-14 | Panasonic Ev Energy Co., Ltd. | Device and method for detecting abnormality of electric storage device |
| US8463562B2 (en) | 2007-02-08 | 2013-06-11 | Panasonic Ev Energy Co., Ltd. | Device and method for detecting abnormality of electric storage device |
| CN101622547B (en) * | 2007-02-08 | 2014-07-30 | 松下电动车辆能源股份有限公司 | Device and method for detecting abnormality of electric storage device |
| JP2011076746A (en) * | 2009-09-29 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Abnormality prediction system for secondary battery |
| US8463564B2 (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2013-06-11 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Abnormality prediction system for secondary batteries |
| EP2518522A4 (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2017-06-28 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Abnormality detection device for assembled battery |
| KR20140013759A (en) * | 2012-07-27 | 2014-02-05 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Method for vehicle battery pack management using module-impedance |
| KR101930088B1 (en) * | 2012-07-27 | 2018-12-17 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Method for vehicle battery pack management using module-impedance |
| KR20210007247A (en) * | 2019-07-10 | 2021-01-20 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Apparatus and method for diagnosing cooling requirement for battery module |
| KR102679707B1 (en) | 2019-07-10 | 2024-06-27 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Apparatus and method for diagnosing cooling requirement for battery module |
| WO2022098096A1 (en) * | 2020-11-05 | 2022-05-12 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Battery diagnostic device and method |
| CN113533979A (en) * | 2021-07-15 | 2021-10-22 | 合肥力高动力科技有限公司 | Method for judging abnormal battery cell of battery pack |
| CN113533979B (en) * | 2021-07-15 | 2022-09-23 | 合肥力高动力科技有限公司 | Method for judging abnormal battery cell of battery pack |
| CN114361617A (en) * | 2021-12-31 | 2022-04-15 | 重庆长安新能源汽车科技有限公司 | Power battery thermal runaway risk early warning method and early warning system |
| CN114361617B (en) * | 2021-12-31 | 2023-07-21 | 深蓝汽车科技有限公司 | Power battery thermal runaway risk early warning method and early warning system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4030217B2 (en) | Abnormality determination device and abnormality determination method for battery pack | |
| KR100615371B1 (en) | Apparatus for judging state of assembled battery | |
| EP3160003B1 (en) | Battery charge indication method and rechargeable battery system | |
| Remmlinger et al. | State-of-health monitoring of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles by on-board internal resistance estimation | |
| JP6012447B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, battery pack, and electronic device | |
| US8332169B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for estimating state of health of battery based on battery voltage variation pattern | |
| CN105974316B (en) | Battery remaining power prediction device and battery pack | |
| JP7141012B2 (en) | Secondary battery system | |
| JP6509725B2 (en) | Estimating the state of charge of the battery | |
| TWI669521B (en) | Battery residual prediction device and battery pack | |
| CN103797375A (en) | A system and a method for determining a state of charge of a battery | |
| TWI705261B (en) | Battery residual capacity prediction device and battery pack | |
| EP1989563A1 (en) | System and method for determining both an estimated battery state vector and an estimated battery parameter vector | |
| CN105634051B (en) | Remaining battery level predicting device and battery pack | |
| JP5812968B2 (en) | Current sensor failure detection device, battery system, and current sensor failure detection method | |
| KR20190111963A (en) | Monitoring system for series connected battery cells | |
| JP2005195604A (en) | Abnormality deciding device and abnormality deciding method of group battery | |
| WO2020026509A1 (en) | Cell state estimation device and cell control device | |
| WO2022049804A1 (en) | Determination device relating to plurality of batteries, electricity storage system, determination method and determination program | |
| JP6541412B2 (en) | Charging rate calculation method and charging rate calculation device | |
| EP3605123A1 (en) | Storage battery control device and control method | |
| CN113748438A (en) | Electric quantity prediction method and device | |
| JP3305403B2 (en) | Battery capacity testing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050526 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20070831 |