Diese Erfindung betrifft eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug und insbesondere eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug, welches eine Regeneration durchführen kann unter Verwendung einer Bremsbetätigung oder Erfüllung einer vorherbestimmten Bedingung als einem Auslöser und eine Batterie mit durch die Regeneration erzeugten Energie laden kann.This invention relates to a regenerative control apparatus for a motor vehicle and, more particularly, to a regenerative control apparatus for a motor vehicle which can perform regeneration using a brake operation or fulfillment of a predetermined condition as a trigger and a battery by regeneration can generate generated energy.
Eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1 ist aus der JP H09-254 861 A bekannt.A regenerative control apparatus according to the preamble of claim 1 is known from JP H09-254 861 A known.
Die DE 697 01 586 T2 offenbart eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug, bei der die Notwendigkeit einer Regenerierung auf der Basis einer Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit und einer Druckkraft auf ein Pedal bewertet wird und dann, wenn die Druckkraft für die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zu gering ist, der Motor in einen Regenerierungszustand geschaltet wird, um als Generator elektrische Energie zu erzeugen und eine Batterie mit erzeugter elektrischer Energie zu regenerieren, um hierdurch den Energieverbrauch der Batterie zu senken und die Fahrt komfortabel zu halten.The DE 697 01 586 T2 discloses a regenerative control apparatus for a motor vehicle in which the need for regeneration is evaluated on the basis of a vehicle speed and a pressing force on a pedal, and when the vehicle speed pressing force is too low, the engine is switched to a regeneration state is to generate electrical energy as a generator and to regenerate a battery with generated electrical energy, thereby reducing the energy consumption of the battery and to keep the ride comfortable.
Bei einem motorbetriebenen Fahrzeug (einschließlich eines Fahrzeugs, welches menschliche Kraft durch Motorkraft unterstützt) wird manchmal eine Regeneration durchgeführt, wenn das motorbetriebene Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt oder durch Trägheit oder dgl. fährt, sodass eine Batterie mit durch die Regeneration erzeugten Energie geladen wird, um die Entladung der Batterie zu unterdrücken, um die Strecke auszudehnen, die das Fahrzeug mit einem einzigen Ladevorgang fahren kann. Beispielsweise ist in der amtlichen Veröffentlichung des offengelegten japanischen Gebrauchsmusters Nr. JP H05-75086 U ein Fahrrad mit einer Hilfsantriebsvorrichtung offenbart, in welcher eine Regeneration unter Verwendung einer Betätigung eines Bremshebels als einem Auslöser (Trigger) durchgeführt wird. Mittlerweile ist in der amtlichen Veröffentlichung des offengelegten japanischen Patents Nr. JP 2001-30 974 A ein motorunterstütztes Fahrrad offenbart, in welchem ein Auslöser für eine Regenerative-Steuerung/Regelung aus einer Ausgabe eines Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeitssensors und Betätigungen eines Bremsschalters und eines manuellen Schalters erhalten wird.In a motor vehicle (including a vehicle that supports human power by engine power), regeneration is sometimes performed when the engine-driven vehicle is traveling on a downhill slope or driving by inertia or the like, so that a battery is charged with energy generated by the regeneration, to suppress the discharge of the battery to extend the distance that the vehicle can drive with a single charge. For example, in the official publication of Japanese Utility Model Laid-Open No. JP H05-75086 U discloses a bicycle having an auxiliary drive device in which regeneration is performed using operation of a brake lever as a trigger. Meanwhile, in the official publication of Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. JP 2001-30974A discloses a motor assisted bicycle in which a trigger for regenerative control is obtained from an output of a vehicle speed sensor and operations of a brake switch and a manual switch.
Bei einer Regenerativ-Steuerung/Regelung von herkömmlichen motorbetriebenen Fahrzeugen wird ein Regenerationsbetrag in der Regel in Antwort auf die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zu einem Zeitpunkt, wenn eine Bremsbetätigung durchgeführt wird, bestimmt und wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zu dem Zeitpunkt der Bremsbetätigung dieselbe ist, dann wird ein festgelegter Regenerationsbetrag ungeachtet der Geschwindigkeit der Betätigung des Bremshebels erzeugt, d. h. ungeachtet davon, ob die Bremsung dann eine harte Bremsung ist oder nicht. Folglich wird ein Verzögerungsgefühl des Fahrzeugs durch eine Regenerative-Steuerung/Regelung im Wesentlichen ungeachtet eines Wunsches nach einer harten oder weichen Bremsung festgelegt.In regenerative control of conventional motor-driven vehicles, a regeneration amount is usually determined in response to the vehicle speed at a time when a brake operation is performed, and when the vehicle speed is the same at the time of the brake operation, then a set regeneration amount regardless of the speed of operation of the brake lever, d. H. regardless of whether the braking is then a hard braking or not. Thus, a deceleration feeling of the vehicle is determined by regenerative control substantially regardless of a desire for hard or soft braking.
Ferner besteht ein Bedarf, selbst wenn die Betätigungsgeschwindigkeit der Bremse gleich ist, die Bremskraft zur Geschwindigkeit des Fahrzeugs dann durch eine Regeneration insbesondere bei einer niedrigen Geschwindigkeit zu erhöhen. Ferner besteht ein Bedarf, eine regenerative Bremsung bzw. Regenerativ-Bremsung nicht nur durch eine Ausgabe eines Bremsschalters, sondern auch durch Einstellen von Bedingungen, welche für ein Abwärtsgefälle geeignet sind, zu erreichen, damit ein Benutzer ein komfortables Fahrgefühl auf einem Abwärtsgefälle hat.Further, even if the operating speed of the brake is equal, there is a need to increase the braking force to the speed of the vehicle by regeneration, particularly at a low speed. Further, there is a need to achieve regenerative braking not only by outputting a brake switch, but also by setting conditions suitable for a downward slope so that a user has a comfortable ride feeling on a downhill slope.
Es ist die Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug bereitzustellen, bei der eine Verzögerung durch eine Regeneration abhängig davon, ob eine Bremsbetätigung hart oder weich ist, variiert werden kann.It is the object of the present invention to provide a regenerative control apparatus for a motor vehicle in which a delay through regeneration can be varied depending on whether a brake operation is hard or soft.
Diese Aufgabe wird durch eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug mit den Merkmalen des Anspruchs 1 gelöst. Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen enthalten die abhängigen Unteransprüche.This object is achieved by a regenerative control device for a motor vehicle with the features of claim 1. Advantageous embodiments include the dependent subclaims.
Die erfindungsgemäße Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung umfasst einen Motor zum Antreiben des Fahrzeugs, ein Bremsmittel zum Bremsen des Fahrzeugs mit einer einem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag entsprechenden variablen Bremskraft, ein Umschaltmittel zum Umschalten des Motors in einen Regenerationsbetrieb, einen Bremsschalter zur Ausgabe eines den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag repräsentierenden Bremssignals, und ein Regenerationsbetragbestimmungsmittel zur Bestimmung eines Regenerationsbetrags in Antwort auf einen Veränderungsbetrag des basierend auf dem Bremssignal erkannten Bremsbetätigungsbetrags, wobei das Umschaltmittel den Motor in Antwort auf eine basierend auf dem Bremssignal erkannte Betätigung des Bremsmittels in den Regenerationsbetrieb umschaltet, und wobei die Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeitserfassungsmittel umfasst und das Regenerationsbetragbestimmungsmittel den Regenerationsbetrag als eine Funktion des Veränderungsbetrags des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit derart einstellt, dass eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer, welche den Regenerationsbetrag bestimmt, bei gleichem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags in einem niedrigen Geschwindigkeitsbereich, in welchem die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit niedriger als 10 km/h ist, zunimmt, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zunimmt, und in einem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich, in welchem die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit von 10 km/h bis 20 km/h reicht, abnimmt, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zunimmt.The regenerative control apparatus according to the present invention comprises a motor for driving the vehicle, braking means for braking the vehicle with a variable braking force corresponding to a brake operation amount, switching means for switching the engine to a regeneration mode, a brake switch for outputting a brake signal representing the brake operation amount, and a regeneration amount determination means for determining a regeneration amount in response to a change amount of the brake operation amount detected based on the brake signal, the switching means switching the engine to the regeneration mode in response to an operation of the brake means detected based on the brake signal, and wherein the regenerative control apparatus is vehicle speed detecting means and the regeneration amount determination means comprises the regeneration amount as a function of the amount of change of the brake operation amount set gs and the vehicle speed such that a regenerative duty, which determines the regeneration amount, with the same change amount of the brake operation amount in a low speed range in which the vehicle speed is lower than 10 km / h, increases as the vehicle speed increases, and decreases in a middle speed range in which the vehicle speed ranges from 10 km / h to 20 km / h, as the vehicle speed increases ,
Die Regenerationsbetragbestimmungsmittel können derart konfiguriert sein, wie nachstehend in (a) bis (e) angegeben:
- (a) Dass der Regenerationsbetrag mittels eines Korrekturkoeffizienten korrigiert wird, welcher so bestimmt wird, dass er den Regenerationsbetrag senkt, wenn die Batteriespannung höher wird, basierend auf der Batteriespannung der Batterie, welche durch regenerativen Strom geladen wird, und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit;
- (b) Dass der bestimmte Regenerationsbetrag erhöht wird, wenn der Bremsbetätigungsbetrag oder der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags zunimmt;
- (c) Dass die Differenz zwischen den Regenerationsbeträgen, welche großen und kleinen Werten des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags oder dem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags entsprechen, in einem niederen Geschwindigkeitsbereich der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit größer ist als in einem hohen Geschwindigkeitsbereich der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit;
- (d) Dass die Differenz zwischen den Regenerationsbeträgen, welche großen und kleinen Werten des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags oder dem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags entsprechen, in einem hohen Geschwindigkeitsbereich der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit allmählich verkleinert wird; und
- (e) Dass dann, wenn erkannt wird, dass das Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt, ein vorbestimmter Regenerationsbetrag ungeachtet des Vorhandenseins oder Fehlens einer Bremsbetätigung ausgegeben wird.
The regeneration amount determination means may be configured as indicated in (a) to (e) below: - (a) that the regeneration amount is corrected by means of a correction coefficient which is determined to lower the regeneration amount as the battery voltage becomes higher, based on the battery voltage of the battery charged by regenerative current and the vehicle speed;
- (b) that the determined regeneration amount is increased as the brake operation amount or the change amount of the brake operation amount increases;
- (c) that the difference between the regeneration amounts corresponding to large and small values of the brake operation amount or the amount of change of the brake operation amount is greater in a lower speed range of the vehicle speed than in a high speed range of the vehicle speed;
- (d) That the difference between the regeneration amounts, which correspond to large and small values of the brake operation amount or the amount of change of the brake operation amount, is gradually decreased in a high speed range of the vehicle speed; and
- (e) That, when it is detected that the vehicle is traveling on a downward slope, a predetermined regeneration amount is output regardless of the presence or absence of a brake operation.
Ferner kann vorgesehen sein, dass ein Regenerationsbetrag basierend auf der Batteriespannung und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit so bestimmt wird, dass der Regenerationsbetrag abnimmt, wenn die Batteriespannung höher wird, und der Regenerationsbetrag in Antwort auf den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag korrigiert wird, welcher basierend auf dem Bremssignal erkannt wird, oder dem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags.Further, it may be provided that a regeneration amount based on the battery voltage and the vehicle speed is determined so that the regeneration amount decreases as the battery voltage becomes higher, and the regeneration amount is corrected in response to the brake operation amount detected based on the brake signal, or the change amount of the brake operation amount.
Gemäß den oben beschriebenen Charakteristika kann, da ein Regenerationsbetrag gemäß beispielsweise der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit gesetzt werden kann, eine für eine Anwendung oder eine Charakteristik des Fahrzeugs geeignete Regeneration erreicht werden. Da ferner ein großer Regenerationsbetrag erhalten wird, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit verhältnismäßig niedrig ist, kann ein großer Regenerationsbetrag in einer solchen Fahrsituation erhalten werden, in welcher es nicht wahrscheinlich ist, dass die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit hoch wird, da Stoppen und Starten häufig wiederholt werden. Wenn ferner das Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt, kann selbst dann, wenn eine Bremsbetätigung nicht durchgeführt wird, eine komfortable Fahrt und Energieerzeugung durch regeneratives Bremsen bewirkt werden. Ferner wird der Regenerationsbetrag in Antwort auf die Batteriespannung gesteuert/geregelt, d. h. die Restkapazität der Batterie, sodass der Regenerationsbetrag kleiner wird, wenn die Batterie-Restkapazität höher wird.According to the characteristics described above, since a regeneration amount can be set according to, for example, the vehicle speed, regeneration suitable for an application or a characteristic of the vehicle can be achieved. Further, since a large regeneration amount is obtained when the vehicle speed is relatively low, a large regeneration amount can be obtained in such a driving situation in which the vehicle speed is not likely to be high because stopping and starting are frequently repeated. Further, when the vehicle is traveling on a downhill slope, even if a brake operation is not performed, comfortable driving and power generation by regenerative braking can be effected. Further, the regeneration amount is controlled in response to the battery voltage, i. H. the remaining capacity of the battery, so that the amount of regeneration becomes smaller as the battery remaining capacity becomes higher.
Kurze Beschreibung der Zeichnungen:Brief description of the drawings:
1 ist ein Blockdiagramm, welches Funktionen von wesentlichen Teilen einer Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung gemäß einer Ausführungsform der vorliegenden Erfindung zeigt. 1 Fig. 10 is a block diagram showing functions of essential parts of a regenerative control apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
2 ist eine Seitenaufrissansicht eines motorunterstützten Fahrrads. 2 is a side elevational view of a motor-assisted bicycle.
3 ist eine Draufsicht eines Lenkers, welcher einen Bremsschalter umfasst. 3 is a plan view of a handlebar, which includes a brake switch.
4 ist eine Ansicht längs der Linie B-B der 3. 4 is a view along the line BB 3 ,
5 ist eine Schnittansicht eines wesentlichen Teils einer Kraftunterstützungseinheit. 5 is a sectional view of an essential part of a power assist unit.
6 ist eine Schnittansicht längs der Linie A-A der 5. 6 is a sectional view taken along the line AA of 5 ,
7 ist eine Draufsicht, welche ein Beispiel eines Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitts zeigt. 7 FIG. 10 is a plan view showing an example of a power supply switching section. FIG.
8 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Tretkrafthistorie zeigt, welche einen Unterstützungsabschaltzustand veranschaulicht. 8th FIG. 12 is a view showing a pedaling history illustrating a backup off state. FIG.
9 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Tretkrafthistorie zeigt, welche einen Startzustand eines Unterstützungsbetriebs veranschaulicht. 9 FIG. 13 is a view showing a pedaling force illustrating a start state of a backup operation. FIG.
10 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Tretkrafthistorie zeigt, welche einen Unterstützungsbetriebstarterfüllungszustand bei einer Mehrzahl von Tretniveaus veranschaulicht. 10 FIG. 13 is a view showing a pedaling history illustrating a backup mode starter fill state at a plurality of tread levels. FIG.
11 ist ein Flussdiagramm (Teil 1) eines wesentlichen Teils eines Verfahrens in einem Ökomodus. 11 Fig. 10 is a flowchart (part 1) of an essential part of a method in an eco mode.
12 ist ein Flussdiagramm (Teil 2) eines wesentlichen Teils des Verfahrens im Ökomodus. 12 Fig. 10 is a flowchart (part 2) of an essential part of the method in the eco mode.
13 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zeigt, welche einem Bremsbetätigungsbetragveränderungsbetrag und einer Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit entspricht. 13 FIG. 15 is a view showing an example of a regenerative duty corresponding to a brake operation amount change amount and a vehicle speed. FIG.
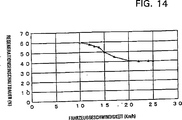
14 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer beim Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle zeigt, wo die Tretkraft im Wesentlichen ”0” ist. 14 FIG. 13 is a view showing an example of a regenerative duty in running on a downslope where the treading force is substantially "0".
15 ist ein Flussdiagramm (Teil 1) einer Regenerativsteuerung/regelung gemäß einer Modifikation beim Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle. 15 FIG. 10 is a flowchart (part 1) of regenerative control according to a modification when driving on a downhill slope. FIG.
16 ist ein Flussdiagramm (Teil 2) der Regenerativsteuerung/regelung gemäß der Modifikation beim Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle. 16 FIG. 10 is a flowchart (part 2) of the regenerative control according to the modification when driving on a downhill slope. FIG.
17 ist ein Blockdiagramm einer Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung, in welcher ein Motor mit einer Bürste verwendet wird. 17 Fig. 10 is a block diagram of a regenerative control apparatus in which a motor with a brush is used.
18 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zeigt, welche einem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag und einer Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit entspricht. 18 FIG. 12 is a view showing an example of a regenerative duty corresponding to a brake operation amount and a vehicle speed. FIG.
19 ist ein Blockdiagramm eines wesentlichen Teils einer Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung, welche eine Funktion zur Bestimmung einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer in Antwort auf eine Batteriespannung umfasst. 19 FIG. 10 is a block diagram of an essential part of a regenerative control device including a function of determining a regenerative duty in response to a battery voltage.
20 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel eines Hilfskennfelds zeigt. 20 Fig. 10 is a view showing an example of an auxiliary map.
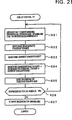
21 ist ein Flussdiagramm einer Regenerativsteuerung/regelung, welche eine Batteriespannung und eine Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit berücksichtigt. 21 FIG. 10 is a flowchart of regenerative control taking into account a battery voltage and a vehicle speed. FIG.
22 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel eines Kennfelds zeigt, welches so ausgebildet ist, dass eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer als eine Funktion einer Batteriespannung und einer Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit ausgegeben wird. 22 FIG. 12 is a view showing an example of a map configured to output a regenerative duty as a function of a battery voltage and a vehicle speed.
Nachfolgend werden Ausführungsformen der vorliegenden Erfindung unter Bezugnahme auf die Zeichnungen beschrieben. 2 ist eine Seitenaufrissansicht eines motorunterstützten Fahrrads als einem motorbetriebenen Fahrzeug, welches eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung gemäß einer Ausführungsform der vorliegenden Erfindung umfasst. Ein Körperrahmen 2 des motorunterstützten Fahrrads umfasst ein Kopfrohr 21, welches an einem vorderen Abschnitt eines Fahrzeugkörpers angeordnet ist, ein Abwärtsrohr 22, das sich von dem Kopfrohr 21 nach unten und nach hinten erstreckt, und eine Sitzstütze 23, welche sich von einem Abschnitt in der Nähe eines Anschlussendes des Abwärtsrohrs 22 nach oben erstreckt. Ein Kupplungsabschnitt zwischen dem Abwärtsrohr 22 und der Sitzstütze 23 und Randabschnitte sind mit einer Kunstharzabdeckung 33 abgedeckt, welche in zwei obere und untere Abschnitte geteilt ist, die lösbar miteinander gekuppelt sind. Ein Lenker (nachfolgend einfach als ”Lenker” bezeichnet) 27 ist für eine Schwenkbewegung an einem oberen Abschnitt des Kopfrohrs 21 durch eine Lenkerstange 27A befestigt und eine vordere Gabel 26, welche mit der Lenkerstange 27A verbunden ist, ist an einem unteren Abschnitt des Kopfrohrs 21 abgestützt. Ein Vorderrad WF ist zur Drehung an einem unteren Ende der vorderen Gabel 26 abgestützt.Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. 2 FIG. 10 is a side elevational view of a motor assisted bicycle as a powered vehicle including a regenerative control device according to one embodiment of the present invention. FIG. A body frame 2 of the motor-assisted bicycle includes a head pipe 21 , which is arranged on a front portion of a vehicle body, a down tube 22 that is different from the head pipe 21 extends down and to the rear, and a seat support 23 extending from a portion near a terminal end of the down tube 22 extends upwards. A coupling section between the down tube 22 and the seat support 23 and edge portions are covered with a synthetic resin cover 33 covered, which is divided into two upper and lower portions which are detachably coupled together. A handlebar (hereinafter simply referred to as "handlebar") 27 is for a pivoting movement on an upper portion of the head pipe 21 through a handlebar 27A attached and a front fork 26 , which with the handlebar 27A is connected to a lower portion of the head pipe 21 supported. A front wheel WF is for rotation at a lower end of the front fork 26 supported.
Eine Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 als eine Antriebsvorrichtung einschließlich eines Elektromotors (nachfolgend beschrieben) für eine Tretkraftunterstützung ist an einem unteren Abschnitt des Körperrahmens 2 aufgehängt. Insbesondere ist die Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 an drei Orten angeschraubt und aufgehängt einschließlich eines Verbindungsabschnitts 92 an einem unteren Ende des Abwärtsrohrs 22, einem Verbindungsabschnitt 90, der an einem hinteren Abschnitt eines Batterieträgers vorgesehen ist, welcher an der Sitzstütze 23 durch Schweißen oder dgl. befestigt ist, und einem Verbindungsabschnitt, der an einem vorderen Abschnitt des Batterieträgers (nicht gezeigt) vorgesehen ist. Eine Hinterradgabel 25 ist zusammen mit der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 an dem Verbindungsabschnitt 90 befestigt.An engine support unit 1 as a drive device including an electric motor (described below) for pedaling assistance is at a lower portion of the body frame 2 suspended. In particular, the engine assistance unit 1 bolted and hung in three places including a connecting section 92 at a lower end of the down tube 22 , a connecting section 90 which is provided on a rear portion of a battery tray, which on the seat support 23 by welding or the like, and a connecting portion provided at a front portion of the battery tray (not shown). A rear fork 25 is together with the engine support unit 1 at the connecting portion 90 attached.
Ein Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitt 29 der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 ist an dem Abwärtsrohr 22 in der Nähe des Kopfrohrs 21 vorgesehen. Von dem Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitt 29 aus ist es möglich, die Energiezufuhr anzuschalten und einen Ökomodus (dessen Details nachfolgend beschrieben werden) auszuwählen, um einen Energieverbrauch durch eine Schlüsselbetätigung zu unterdrücken. Ein Anschalten der Energiezufuhr kann anderenfalls beispielsweise mittels eines Fernsteuerungsschalters unter Verwendung eines Infrarotsignals erfolgen. In diesem Fall ist der Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitt 29 mit einem Empfänger versehen, um ein von dem Fernsteuerungsschalter signalisiertes Infrarotsignal zu empfangen.A power supply switching section 29 the engine support unit 1 is on the down pipe 22 near the head pipe 21 intended. From the power supply switching section 29 For example, it is possible to turn on the power supply and select an eco mode (the details of which will be described later) to suppress power consumption by a key operation. Otherwise, the power supply can be turned on by, for example, a remote control switch using an infrared signal. In this case, the power supply switching section is 29 provided with a receiver to receive an infrared signal signaled by the remote control switch.
Die Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 umfasst ein Antriebskettenrad 13 und die Drehung einer Kurbelwelle 101 wird von dem Antriebskettenrad 13 zu einem hinteren Kettenrad 14 durch eine Kette 6 übertragen. Ein Bremshebel 27B ist an dem Lenker 27 vorgesehen und eine Betätigung des Bremshebels 27B wird zu einer Bremsvorrichtung (nicht gezeigt) für ein Hinterrad WR durch eine Bremsleitung 39 übertragen. Ferner ist ein Bremsschalter (dessen Details nachfolgend beschrieben sind) für den Bremshebel 27B vorgesehen und umfasst einen Hubsensor, welcher, wenn der Bremshebel 27B betätigt wird, ein Bremssignal ausgibt, das den Betätigungsbetrag (Hub) des Bremshebels 27B repräsentiert. In Antwort auf das Bremssignal werden die Tatsache, dass der Lenker 27 bedient wird und der Betätigungsbetrag des Bremshebels 27B erfasst.The engine support unit 1 includes a drive sprocket 13 and the rotation of a crankshaft 101 is from the drive sprocket 13 to a rear sprocket 14 through a chain 6 transfer. A brake lever 27B is on the handlebars 27 provided and an actuation of the brake lever 27B is supplied to a brake device (not shown) for a rear wheel WR through a brake pipe 39 transfer. Further, a brake switch (the details of which are described below) for the brake lever 27B provided and includes one Lift sensor, which when the brake lever 27B is actuated, outputs a brake signal representing the amount of operation (stroke) of the brake lever 27B represents. In response to the brake signal are the fact that the handlebar 27 is operated and the amount of operation of the brake lever 27B detected.
Die Kurbelwelle 101 ist zur Drehung an der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 abgestützt und ein Paar von Pedalen 12 sind zur Drehung an den gegenüberliegenden linken und rechten Enden der Kurbelwelle 101 durch eine Kurbel 11 abgestützt. Das Hinterrad WR, welches als ein Antriebsrad dient, ist zur Drehung zwischen Anschlussenden eines Paars von linken und rechten Hinterradgabeln 25 abgestützt, welche sich von der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 nach hinten erstrecken. Ein Paar von linken und rechten Sitzstreben 24 ist zwischen einem oberen Abschnitt der Sitzstütze 23 und den Anschlussenden der zwei Hinterradgabeln 27 vorgesehen. Ein Sitzrohr 31 mit einem an einem oberen Ende davon vorgesehenen Sitz 30 ist zur Schiebebewegung an der Sitzstütze 23 so befestigt, dass die Höhe des Sitzes eingestellt werden kann.The crankshaft 101 is for rotation on the engine support unit 1 supported and a pair of pedals 12 are for rotation at the opposite left and right ends of the crankshaft 101 through a crank 11 supported. The rear wheel WR, which serves as a drive wheel, is for rotation between terminal ends of a pair of left and right rear wheel forks 25 supported, which differ from the engine support unit 1 extend to the rear. A pair of left and right seatstays 24 is between an upper section of the seat support 23 and the connection ends of the two rear wheel forks 27 intended. A seat tube 31 with a seat provided at an upper end thereof 30 is for sliding movement on the seat support 23 fixed so that the height of the seat can be adjusted.
Eine Batterie 4 ist an einem hinteren Abschnitt der Sitzstütze 23 unter dem Sitz 30 angebracht. Die Batterie 4 ist in einem Aufnahmegehäuse untergebracht und an der Sitzstütze 23 durch eine Batteriehalterung angebracht. Die Batterie 4 umfasst eine Mehrzahl von Batteriezellen und ist längs der Sitzstütze 23 so angeordnet, dass die Längsrichtung davon eine im wesentlichen nach oben und unten verlaufende Richtung sein kann.A battery 4 is at a rear section of the seat post 23 under the seat 30 appropriate. The battery 4 is housed in a receiving housing and on the seat support 23 attached by a battery holder. The battery 4 includes a plurality of battery cells and is along the seat support 23 arranged so that the longitudinal direction thereof may be a substantially up and down direction.
3 ist eine Draufsicht des Lenkers, welcher den Bremsschalter umfasst, und 4 ist eine Schnittansicht längs der Linie B-B der 3. Auf die zwei Figuren Bezug nehmend ist der Bremshebel 27B in der Nähe eines Lenkergriffs 27B durch eine Hebelhalterung 27C abgestützt. Die Hebelhalterung 27C ist eine in zwei Elemente in einer Längsrichtung des Fahrzeugkörpers geteilte Baugruppe und eine Schwenkwelle 27E ist an einer vorderen Hälfte 27CF vorgesehen und der Bremshebel 27B ist für eine Schwenkbewegung an der Schwenkwelle 27E vorgesehen. Ein Bremsschalter 51 ist in der vorderen Hälfte 27CF untergebracht. Der Bremsschalter 51 ist ein Hubsensor, dessen Widerstandswert in Antwort auf den Versatzbetrag eines Tauchkerns variiert und ein Ende des Tauchkerns 51A ist mit einem Längsabschnitt im Eingriff, welcher an einem Endabschnitt des Bremshebels 27B ausgebildet ist. 3 is a plan view of the handlebar, which includes the brake switch, and 4 is a sectional view taken along the line BB of 3 , Referring to the two figures, the brake lever is 27B near a handlebar grip 27B through a lever bracket 27C supported. The lever bracket 27C is a split into two elements in a longitudinal direction of the vehicle body assembly and a pivot shaft 27E is at a front half 27CF provided and the brake lever 27B is for a pivoting movement on the pivot shaft 27E intended. A brake switch 51 is in the front half 27CF accommodated. The brake switch 51 is a stroke sensor whose resistance value varies in response to the displacement amount of a plunger and an end of the plunger core 51A is engaged with a longitudinal portion which at an end portion of the brake lever 27B is trained.
Wenn der Bremshebel 27B zum Lenkergriff 27D hingezogen wird (d. h. wenn eine Bremsbetätigung durchgeführt wird), dann ragt der Tauchkern 51A aus einem Körper des Bremsschalters 51 hervor, aber wenn der Bremshebel 27B von dem Lenkergriff 27D wegbewegt wird, dann wird der Tauchkern 51A in den Körper des Bremsschalters 51 hineingedrückt. Wenn folglich eine Schaltung zur Erfassung des Widerstandswerts (Bremssignal) des Bremsschalters 51, welcher sich in Antwort auf die Bewegung des Tauchkerns 51A verändert, geprüft wird, dann kann das Vorhandensein oder Fehlen einer Bremsbetätigung und der Betätigungsbetrag (Betätigungshub) erfasst werden basierend auf einer Ausgabe der Schaltung. Es wird angenommen, dass die Bremsstärke zunimmt, wenn der Betätigungsbetrag zunimmt. Es ist zu bemerken, dass in der folgenden Beschreibung die Ausgabe der Schaltung zur Erfassung des Widerstandswerts als ein Äquivalent zu der Ausgabe (Bremssignal) des Bremsschalters 51 angesehen wird, um eine komplizierte Beschreibung auszuschließen.When the brake lever 27B to the handlebar grip 27D is pulled (ie, when a brake operation is performed), then protrudes the plunger 51A from a body of the brake switch 51 but if the brake lever 27B from the handlebar grip 27D is moved away, then the diving core 51A in the body of the brake switch 51 pushed. Consequently, when a circuit for detecting the resistance value (brake signal) of the brake switch 51 which is in response to the movement of the diving core 51A is changed, the presence or absence of a brake operation and the operation amount (operation stroke) can be detected based on an output of the circuit. It is assumed that the braking strength increases as the amount of operation increases. It should be noted that in the following description, the output of the resistor value detection circuit is equivalent to the output (brake signal) of the brake switch 51 is considered to exclude a complicated description.
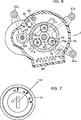
5 ist eine Schnittansicht der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 und 6 ist eine Schnittansicht längs der Linie A-A. Ein Gehäuse der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 umfasst einen Körper 70 und eine linke Abdeckung 70L und eine rechte Abdeckung 70R, welche an den gegenüberliegenden Seitenflächen des Körpers 70 angebracht sind. Das Gehäuse 70, die linke Abdeckung 70L und die rechte Abdeckung 70R sind vorzugsweise aus geformten Kunstharzteilen ausgebildet, um eine Gewichtsverringerung zu erreichen. Aufhängungen 90a, 91a und 92a zum Anbringen an den oben erwähnten Verbindungsabschnitten 90, 91 bzw. 92 sind um den Gehäusekörper 70 herum ausgebildet. Ein Lager 71 ist an dem Körper 70 vorgesehen und ein weiteres Lager 72 ist an der rechten Abdeckung 70R vorgesehen. Die Kurbelwelle 101 ist in einen inneren Laufring des Lagers 71 eingeprägt und eine koaxial zur Kurbelwelle 101 für eine Schiebebewegung in einer Außenumfangsrichtung bezüglich der Kurbelwelle 101 vorgesehene Hülse 73 ist in einen inneren Laufring des Lagers 72 eingeprägt. Mit anderen Worten ist die Kurbelwelle 101 durch das Lager 71 und das Lager 72 abgestützt. 5 is a sectional view of the engine support unit 1 and 6 is a sectional view taken along the line AA. A housing of the engine support unit 1 includes a body 70 and a left cover 70L and a right cover 70R which are on the opposite side surfaces of the body 70 are attached. The housing 70 , the left cover 70L and the right cover 70R are preferably formed from molded synthetic resin parts to achieve weight reduction. suspensions 90a . 91a and 92a for attachment to the above-mentioned connecting portions 90 . 91 respectively. 92 are around the case body 70 trained around. A warehouse 71 is on the body 70 provided and another camp 72 is on the right cover 70R intended. The crankshaft 101 is in an inner race of the bearing 71 stamped and a coaxial to the crankshaft 101 for a sliding movement in an outer circumferential direction with respect to the crankshaft 101 provided sleeve 73 is in an inner race of the bearing 72 imprinted. In other words, the crankshaft 101 through the camp 71 and the camp 72 supported.
Eine Nabe 74 ist an der Hülse 73 befestigt und ein Hilfszahnrad 76 ist an einem Außenumfang der Nabe 74 durch eine Einwegkupplung 75 vorgesehen, welche beispielsweise aus einem Sperrklinkenmechanismus ausgebildet ist. Das Hilfszahnrad 76 besteht vorzugsweise aus Kunstharz im Hinblick auf eine Gewichtsreduzierung und ist vorzugsweise aus einem Schrägzahnrad im Hinblick auf die Geräuschlosigkeit usw. ausgebildet.A hub 74 is on the sleeve 73 attached and an auxiliary gear 76 is on an outer circumference of the hub 74 through a one-way clutch 75 provided, which is formed for example of a pawl mechanism. The auxiliary gear 76 is preferably made of synthetic resin in view of weight reduction, and is preferably formed of a helical gear in view of quietness, etc.
Ein Zahnrad 73a ist an einem Endabschnitt der Hülse 73 ausgebildet und drei Planetenräder 77 sind an einem äußeren Umfang des Zahnrads 73a so angeordnet, dass das Zahnrad 73a als ein Sonnenrad dient. Die Planetenräder 77 sind an einer Welle 77a abgestützt, welche aufrecht an einer Lagerplatte 102 vorgesehen ist, welche an der Kurbelwelle 101 durch eine Einwegkupplung 78 abgestützt ist. Die Planetenräder 77 sind mit einem an einem inneren Umfang eines Tretkrafterfassungsrings 79 ausgebildeten Innenrad im Eingriff. Das Antriebskettenrad 13 ist an einem Endabschnitt der Hülse 73 (einem Endabschnitt, an welchem kein Zahnrad ausgebildet ist) befestigt und mit dem hinteren Kettenrad 14 über die Kette 6 verbunden.A gear 73a is at an end portion of the sleeve 73 trained and three planet gears 77 are on an outer circumference of the gear 73a so arranged that the gear 73a serves as a sun wheel. The planet wheels 77 are on a wave 77a supported, which upright on a bearing plate 102 is provided, which on the crankshaft 101 through a one-way clutch 78 is supported. The planetary gears 77 are with one on an inner circumference of a pedaling force detection ring 79 trained inner wheel engaged. The drive sprocket 13 is at an end portion of the sleeve 73 (an end portion on which no gear is formed) attached and with the rear sprocket 14 over the chain 6 connected.
Der Tretkrafterfassungsring 79 weist ein Paar Arme 79a und 79b auf, welche sich von einem äußeren Rand desselben nach außen erstrecken. Die Arme 79a und 79b sind in einer Richtung (in der Richtung im Uhrzeigersinn in 6) entgegengesetzt zu der Drehrichtung der Kurbelwelle 101 beim Fahren vorgespannt durch eine Zugfeder 80, welche sich zwischen dem Arm 79a und dem Körper 70 erstreckt, und eine Druckfeder 81, welche sich zwischen dem Arm 79b und dem Körper 70 erstreckt. Die Druckfeder 81 ist vorgesehen, um ein Spiel des Tretkrafterfassungsrings 79 zu verhindern. Ein Potenziometer 82 zur Erfassung eines Versatzes des Tretkrafterfassungsrings 79 in der Drehrichtung ist für den Arm 79b vorgesehen.The pedaling force detection ring 79 has a pair of arms 79a and 79b which extend outwardly from an outer edge thereof. The poor 79a and 79b are in one direction (in the clockwise direction in 6 ) opposite to the direction of rotation of the crankshaft 101 biased while driving by a tension spring 80 which is between the arm 79a and the body 70 extends, and a compression spring 81 which is between the arm 79b and the body 70 extends. The compression spring 81 is intended to be a game of pedaling detection ring 79 to prevent. A potentiometer 82 for detecting an offset of the pedaling force detection ring 79 in the direction of rotation is for the arm 79b intended.
Eine Kupplungsplatte 86 für eine Regenerierung ist in einer benachbarten Beziehung mit dem Hilfszahnrad 76 angeordnet, wobei ein Federring 85 dazwischen angeordnet ist, und eine Druckplatte 87, um die Kupplungsplatte 86 zum Hilfszahnrad 76 hin gegen den Federring zu pressen, ist in einer benachbarten Beziehung mit der Kupplungsplatte 86 angeordnet. Die Kupplungsplatte 86 und die Druckplatte 87 sind in einer axialen Richtung der Hülse 73 bezüglich der Hülse 73 verschiebbar beweglich.A coupling plate 86 for a regeneration is in an adjacent relationship with the auxiliary gear 76 arranged, with a spring washer 85 interposed therebetween, and a pressure plate 87 to the coupling plate 86 to the auxiliary gear 76 towards pressing against the spring ring is in an adjacent relationship with the coupling plate 86 arranged. The coupling plate 86 and the pressure plate 87 are in an axial direction of the sleeve 73 with respect to the sleeve 73 movable movable.
Die Druckplatte 87 ist zur Kupplungsplatte 86 hin durch einen Nocken 88 vorgespannt, welcher eine geneigte Fläche kontaktiert, die an einem Nabenabschnitt der Druckplatte 87 ausgebildet ist. Der Nocken 88 ist an einer Welle 89 befestigt, welche zur Drehung an der rechten Abdeckung 70R abgestützt ist. Ein Stellantrieb 7 zum Drehen der Welle 89 ist sicher an einem Endabschnitt der Welle 89 befestigt, d. h. einem Abschnitt der Welle 89, welcher von der rechten Abdeckung 70R nach außen hin vorsteht. Der Stellantrieb 7 kann von einem Motor oder einem Solenoid gebildet sein. Der Stellantrieb 7 wird in Antwort auf ein Bremssignal des Bremsschalters 51 bei einer Bremsbetätigung mit Strom versorgt. Wenn der Stellantrieb 7 in Antwort auf ein Bremssignal dreht, wird die Welle 89 gedreht, um den Nocken 88 zu drehen.The printing plate 87 is to the clutch plate 86 through a cam 88 biased, which contacts a sloped surface, which at a hub portion of the pressure plate 87 is trained. The cam 88 is on a wave 89 attached, which for rotation on the right cover 70R is supported. An actuator 7 for turning the shaft 89 is safe at one end of the shaft 89 attached, ie a portion of the shaft 89 , which from the right cover 70R protrudes outwards. The actuator 7 may be formed by a motor or a solenoid. The actuator 7 is in response to a brake signal from the brake switch 51 energized during a brake application. When the actuator 7 turns in response to a brake signal, the shaft becomes 89 turned to the cam 88 to turn.
Ein an einer Welle eines Motors M befestigtes Ritzel 83 ist mit dem Hilfszahnrad 76 im Eingriff. Der Motor M ist ein bürstenloser Dreiphasenmotor und umfasst einen Rotor 111 mit Magnetpolen 110 aus einem Neodym (Nd-Fe-B-Typ) Magneten, Statorspulen 112, welche an einem äußeren Rand des Rotors 111 vorgesehen sind, einen Gummimagnetring 113 (einen Ring, an welchem Nordpole und Südpole abwechselnd angeordnet sind) für einen Magnetpolsensor, welcher an einer Seitenfläche des Rotors 111 vorgesehen ist, ein Hall-IC 115, welches in einer gegenüberliegenden Beziehung zu dem Gummimagnetring 113 angeordnet und an einer Leiterplatte 114 angebracht ist, und eine Welle 116 für den Rotor 111. Die Welle 116 ist durch ein Lager 98 abgestützt, das an der linken Abdeckung 70L vorgesehen ist, und ein weiteres Lager 99, das an dem Gehäusekörper 70 vorgesehen ist.An attached to a shaft of a motor M pinion 83 is with the auxiliary gear 76 engaged. The motor M is a three-phase brushless motor and includes a rotor 111 with magnetic poles 110 Neodymium (Nd-Fe-B type) magnets, stator coils 112 , which on an outer edge of the rotor 111 are provided, a rubber magnet ring 113 (A ring on which north poles and south poles are alternately arranged) for a magnetic pole sensor which is attached to a side surface of the rotor 111 is provided, a Hall IC 115 which is in opposite relation to the rubber magnet ring 113 arranged and on a circuit board 114 attached, and a shaft 116 for the rotor 111 , The wave 116 is through a warehouse 98 supported on the left cover 70L is provided, and another camp 99 attached to the housing body 70 is provided.
Eine Steuer/Regeleinrichtung 100, welche ein Treiber-FET und einen Kondensator umfasst zur Steuerung/Regelung des Motors M, ist an einem Abschnitt des Gehäusekörpers 70 vorgesehen, ziemlich nahe zur Vorderseite des Fahrzeugkörpers und die Statorspulen 112 werden durch den FET gespeist. Die Steuer/Regeleinrichtung 100 steuert/regelt den Motor M zur Betätigung in Antwort auf eine Tretkraft, welche von dem Potenziometer 82 erfasst wird, welches als ein Tretkraftsensor dient, um eine Hilfskraft bzw. Unterstützungskraft zu erzeugen, und versorgt bei einer Bremsbetätigung den Stellantrieb 7 mit Strom, um eine Regeneration zu ermöglichen. Ferner steuert/regelt die Steuer/Regeleinrichtung 100 den Treiber für den Motor M, sodass ein Regenerationsbetrag, welcher einem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags entspricht, erzeugt werden kann (Details werden nachfolgend beschrieben).A control device 100 which comprises a driver FET and a capacitor for controlling the motor M, is at a portion of the case body 70 provided, quite close to the front of the vehicle body and the stator coils 112 are fed by the FET. The control device 100 controls the motor M for actuation in response to a treading force applied by the potentiometer 82 which serves as a pedaling force sensor to generate an assisting force, and supplies the actuator in a braking operation 7 with electricity to allow regeneration. Further, the controller controls 100 the driver for the motor M, so that a regeneration amount corresponding to a change amount of the brake operation amount can be generated (details will be described below).
Während der Gehäusekörper 70 und die Abdeckungen 70L und 70R vorzugsweise aus geformten Kunstharzteilen im Hinblick auf eine Gewichtsreduzierung ausgebildet sind, ist es notwendig, die Festigkeit von Abschnitten von ihnen um die Lager herum zu erhöhen. In der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 der vorliegenden Ausführungsform sind Metallverstärkungselemente 105, 106 und 107 aus Eisen, Aluminium, Aluminiumlegierung, Kupferlegierung oder dgl. um die Lager herum angeordnet. Da insbesondere die an dem Gehäusekörper 70 angeordneten Verstärkungselemente Abschnitte verstärken, an welchen eine hohe Last voraussichtlich ausgeübt wird, wie z. B. das Lager 71 für die Kurbelwelle 101, das Lager 99 für die Welle 116 und die Aufhängungen 90a, 91a und 92a, welche als Befestigungselemente für den Körper dienen, wobei die Verstärkungselemente an den Abschnitten miteinander verbunden sind, um eine einheitliche Verstärkungsplatte 105 auszubilden. Durch die Verstärkungsplatte 105 arbeiten die Verstärkungselemente, welche um die Lager herum angeordnet sind, und die Aufhängungen miteinander zusammen, wodurch der Verstärkungseffekt weiter erhöht wird.While the case body 70 and the covers 70L and 70R preferably formed of molded synthetic resin parts with a view to weight reduction, it is necessary to increase the strength of portions of them around the bearings. In the engine support unit 1 In the present embodiment, metal reinforcing elements 105 . 106 and 107 made of iron, aluminum, aluminum alloy, copper alloy or the like arranged around the bearings. Since in particular the on the housing body 70 arranged reinforcing members reinforce portions at which a high load is expected to be exerted, such. B. the camp 71 for the crankshaft 101 , the warehouse 99 for the wave 116 and the suspensions 90a . 91a and 92a , which serve as fastening elements for the body, wherein the reinforcing elements are connected to each other at the sections to a uniform reinforcing plate 105 train. Through the reinforcement plate 105 For example, the reinforcing members disposed around the bearings and the suspensions cooperate with each other, thereby further increasing the reinforcing effect.
Die Verstärkungsplatte 105 ist nicht auf eine Verstärkungsplatte beschränkt, welche alle Verstärkungselemente um das Lager 71 und das Lager 99 wie auch die Aufhängungen 90a, 91a und 92a verbindet, sondern kann im Übrigen eine andere Verstärkungsplatte sein, welche jene der Verstärkungselemente miteinander verbindet, welche einander benachbart sind oder beispielsweise das Verstärkungselement um die Aufhängung 90a und das Verstärkungselement um das Lager 99 miteinander verbindet, oder außerdem das Verstärkungselement um das Lager 71 und das Verstärkungselement um das Lager 99 oder eine der Aufhängungen 90a, 91a und 92a miteinander verbinden. Zu bemerken ist, das die Verstärkungselemente 105, 106 und 107 vorzugsweise integral mit dem Gehäuse 70 und/oder den Abdeckungen 70L und 70R beim Kunstharz-Formen ausgebildet werden.The reinforcement plate 105 is not limited to a reinforcing plate, which all reinforcing elements around the bearing 71 and the camp 99 as well as the suspensions 90a . 91a and 92a Incidentally, it may be another reinforcing plate connecting those of the reinforcing members which are adjacent to each other or, for example, the reinforcing member around the suspension 90a and the reinforcing element around the bearing 99 connects together, or also the reinforcing element around the bearing 71 and the reinforcing element around the bearing 99 or one of the suspensions 90a . 91a and 92a connect with each other. It should be noted that the reinforcing elements 105 . 106 and 107 preferably integral with the housing 70 and / or the covers 70L and 70R be formed in the resin molds.
Wenn bei der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 mit der oben beschriebenen Konfiguration eine Tretkraft auf die Kurbelwelle 101 durch die Kurbel 11 ausgeübt wird, dann wird die Kurbelwelle 101 gedreht. Die Drehung der Kurbelwelle 101 wird zu der Lagerplatte 102 durch die Einwegkupplung 78 übertragen, um die Wellen 77a der Planetenräder 77 um das Sonnenrad 73a so zu drehen, dass das Sonnenrad 73a durch die Planetenräder 77 gedreht wird. Wenn das Sonnenrad 73a dreht, wird das an der Hülse 73 sicher befestigte Antriebskettenrad 13 gedreht.If at the engine support unit 1 with the configuration described above, a pedaling force on the crankshaft 101 through the crank 11 is exercised, then the crankshaft 101 turned. The rotation of the crankshaft 101 becomes the bearing plate 102 through the one-way clutch 78 transferred to the waves 77a the planet wheels 77 around the sun wheel 73a to turn that sun gear 73a through the planet wheels 77 is turned. When the sun wheel 73a it turns on the sleeve 73 securely fastened drive sprocket 13 turned.
Wenn eine Last auf das Hinterrad WR ausgeübt wird, dann wird der Tretkrafterfassungsring 79 in Antwort auf die Größe der Last gedreht und der Betrag der Drehung von dem Potenziometer 82 erfasst. Wenn eine Ausgabe des Potenziometers 82, d. h. eine Ausgabe, welche der Last entspricht, höher als ein vorbestimmter Wert ist, wird der Motor M mit Strom versorgt in Antwort auf das Ausmaß der Last, um eine Hilfskraft zu erzeugen. Die Hilfskraft wird mit dem Antriebsdrehmoment kombiniert, welches durch die von der Kurbelwelle 101 eingegebenen menschlichen Kraft ausgeübt wird und zu dem Antriebskettenrad 13 übertragen.When a load is applied to the rear wheel WR, the pedaling detection ring becomes 79 rotated in response to the size of the load and the amount of rotation from the potentiometer 82 detected. If an output of the potentiometer 82 That is, an output corresponding to the load is higher than a predetermined value, the motor M is energized in response to the amount of load to generate an assist power. The auxiliary power is combined with the drive torque, which by that of the crankshaft 101 input human force and to the drive sprocket 13 transfer.
Wenn eine Bremsbetätigung durchgeführt wird, um das Fahrzeug während der Fahrt zu verzögern, dann wird der Bremsschalter 51 angeschaltet (ein Bremssignal, welches ein Kriterium für die Bremsbetätigung übersteigt, wird ausgegeben) und der Stellantrieb 7 wird angetrieben, um die Welle 89 zu drehen, woraufhin die Druckplatte 87 die Kupplungsplatte 86 drückt. Dann wird die Kupplungsplatte 86 zu der Seite des Hilfszahnrads 76 versetzt, um die Nabe 74 mit dem Hilfszahnrad 76 zusammenzukuppeln, sodass die Drehung der Nabe 74 zu dem Hilfszahnrad 76 übertragen wird. Folglich wird die Drehung des Antriebskettenrads 13 während des Bremsens zu dem Ritzel 83 durch die Hülse 73, Nabe 74 und Hilfszahnrad 76 übertragen. Wenn das Ritzel 83 dreht, wird eine elektromotorische Kraft durch eine Regeneration in den Statorspulen 112 erzeugt. Der durch die Regeneration erzeugte Strom wird der Batterie 4 durch die Steuer/Regeleinrichtung 100 zugeführt, um die Batterie 4 zu laden.When a brake operation is performed to decelerate the vehicle while driving, then the brake switch becomes 51 is turned on (a brake signal exceeding a criterion for the brake operation is output) and the actuator 7 is driven to the shaft 89 to turn, whereupon the pressure plate 87 the coupling plate 86 suppressed. Then the clutch plate 86 to the side of the auxiliary gear 76 staggered to the hub 74 with the auxiliary gear 76 Couple together so that the rotation of the hub 74 to the auxiliary gear 76 is transmitted. As a result, the rotation of the drive sprocket becomes 13 during braking to the pinion 83 through the sleeve 73 , Hub 74 and auxiliary gear 76 transfer. If the pinion 83 turns, an electromotive force by a regeneration in the stator coils 112 generated. The electricity generated by the regeneration becomes the battery 4 through the control / regulation device 100 fed to the battery 4 to load.
In der vorliegenden Ausführungsform wird in einem Ökomodus gefahren, wenn ein vorbestimmtes Steuer/Regelkriterium während des Fahrens auf einer flachen Straße oder dgl. erfüllt ist. Wenn in dem Ökomodus ein vorbestimmtes Steuer/Regelkriterium erfüllt ist, wird der Unterstützungsbetrieb unterbrochen, aber wenn ein anderes vorbestimmtes Steuer/Regelkriterium erfüllt ist, wird der Unterstützungsbetrieb wieder aufgenommen. Wenn ferner der Bremsschalter 51 an bzw. ein ist, wird eine regenerative Ladung durchgeführt. Der Ökomodus kann durch eine Betätigung des Fahrers ausgewählt werden. 7 ist eine Draufsicht, welche ein Beispiel des Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitts 29 zeigt.In the present embodiment, driving is in an eco mode when a predetermined control criterion is satisfied while traveling on a flat road or the like. If a predetermined control criterion is met in the economy mode, the assist operation is suspended, but if another predetermined control criterion is satisfied, the assist operation is resumed. Further, when the brake switch 51 is on or a, a regenerative charge is performed. The eco mode can be selected by an operation of the driver. 7 FIG. 10 is a plan view showing an example of the power supply switching section. FIG 29 shows.
Auf 7 Bezug nehmend kann ein Modus durch Einsetzen eines nicht gezeigten Schlüssels in ein Schlüsselloch 32 und Drehen des Schlüssels ausgewählt werden. Wenn der Schlüssel in der Position ”AUS” ist, dann ist die Energiezufuhr zur Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 aus und die Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 wird nicht von der Batterie 4 gespeist. Wenn der Schlüssel zu der Position ”EIN” gedreht wird, dann kann die Energie der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 zugeführt werden und der Motor M wird so gesteuert/geregelt, dass er dann, wenn die Tretkraft ein vorbestimmtes Niveau übersteigt, eine Hilfskraft gemäß einem Verhältnis (Unterstützungsverhältnis) zwischen einer Hilfskraft, welche aus einem Kennfeld ausgelesen wird, das im Voraus eingestellt ist, und der Tretkraft ausübt. Wenn ferner der Schlüssel zur Position ”ÖKO” gestellt wird, dann ist der ”Ökomodus” ausgewählt, in welchem eine solche Steuerung/Regelung durchgeführt werden kann, dass ein Unterstützungsbetrieb gemäß vorbestimmtem Steuer/Regelkriterium, wie nachfolgend detailliert beschrieben, gestartet oder gestoppt wird. In dem Ökomodus wird auch eine Regenerativ-Bremsung durchgeführt. Zu bemerken ist, dass der Energieversorgungsschaltabschnitt 29 vorzugsweise an dem Fahrzeugkörper so angebracht ist, dass die Position von ”EIN” in die Fahrtrichtung des Fahrzeugkörpers gerichtet ist.On 7 Referring to a mode, by inserting a key (not shown) into a keyhole 32 and turning the key. If the key is in the "OFF" position, then the power is supplied to the engine support unit 1 off and the engine support unit 1 is not from the battery 4 fed. If the key is turned to the "ON" position, then the power of the motor assist unit may be 1 and the motor M is controlled so that, when the treading force exceeds a predetermined level, an auxiliary force according to a ratio (assist ratio) between an auxiliary power read out from a map set in advance, and the pedaling force. Further, if the key is set to the "ECO" position, then the "eco mode" is selected in which such control can be performed that a support operation is started or stopped according to a predetermined control criterion as described in detail below. In eco mode, regenerative braking is also performed. It should be noted that the power supply switching section 29 is preferably attached to the vehicle body so that the position of "ON" is directed in the direction of travel of the vehicle body.
Nachfolgend wird ein Unterstützungsbetrieb, ein Unterstützungsabschaltbetrieb und eine Regenerative-Steuerung/Regelung in dem Ökomodus beschrieben. In dem Ökomodus wird eine Tretkrafthistorie erfasst und ein Unterstützungsabschaltbetrieb wird durchgeführt, wenn erkannt wird, dass die Tretkraft in der Nähe eines keine Unterstützung benötigenden Niveaus bleibt (nachfolgend als ”Unterstützungsabschaltniveau” bezeichnet), welches unter einem vorbestimmten Wert liegt.Hereinafter, a support operation, a backup shutoff operation, and a regenerative control in the eco mode will be described. In the eco mode, a pedaling history is detected, and a backup cutoff operation is performed when it is detected that the treading force remains near a non-assistance-required level (hereinafter referred to as "assist cut-off level") which is below a predetermined value.
8 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Tretkrafthistorie zeigt, welche eine Bedingung zur Unterstützungsabschaltung veranschaulicht und zusätzlich einen Zählerwert CNTBT eines Zählers veranschaulicht, welcher abhängig von der Höhe der Tretkraft aktualisiert wird. Die Tretkraft verändert sich periodisch entsprechend der Periode der Drehung der Kurbel. Auf 8 Bezug nehmend werden ein oberer Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP und ein unterer Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT eingestellt (gesetzt). Der obere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP wird beispielsweise in einen Bereich von 15 bis 20 kgf eingestellt und der untere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT wird beispielsweise in einen anderen Bereich von 13 bis 15 kgf eingestellt. Die Tretkraft wird in einer Unterbrechungsverarbeitung beispielsweise alle 10 ms erfasst. 8th FIG. 13 is a view showing a pedaling history illustrating a condition for assistive shutdown, and in addition. FIG illustrates a counter value CNTBT of a counter, which is updated depending on the height of the pedaling force. The treading force changes periodically according to the period of rotation of the crank. On 8th Referring to FIG. 14, an upper pedaling force limit TRQUP and a lower pedaling force limit TRQBT are set (set). For example, the upper pedaling threshold TRQUP is set in a range of 15 to 20 kgf, and the lower pedaling threshold TRQBT is set in another range of 13 to 15 kgf, for example. The treading force is detected in an interrupt processing every 10 ms, for example.
Wenn die Tretkraft TRQA niedriger als der untere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT ist, wird der Zählerwert CNTBT erhöht (+1), aber wenn die Tretkraft TRQA gleich oder höher als der obere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP ist, wird der Zählerwert CNTBT vermindert (–1). Wenn die Tretkraft TRQA gleich oder höher als der untere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT ist, aber niedriger als der obere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP ist, wird der Zählerwert CNTBT nicht verändert. Wenn der Zählerwert CNTBT einen Referenzwert (Unterstützungsabschaltbestimmungsreferenzwert) TTED übersteigt, wird bestimmt, dass die Tretkraft TRQA um das Unterstützungsabschaltniveau bleibt und eine Unterstützungsabschaltbetätigung wird durchgeführt.If the pedaling force TRQA is lower than the bottom pedaling threshold TRQBT, the counter value CNTBT is incremented (+1), but if the pedaling force TRQA is equal to or higher than the upper pedaling threshold TRQUP, the counter value CNTBT is decreased (-1). If the treading force TRQA is equal to or higher than the lower treadle threshold TRQBT but lower than the upper treadle threshold TRQUP, the counter CNTBT is not changed. When the counter value CNTBT exceeds a reference value (assistance cutoff determination reference value) TTED, it is determined that the treading force TRQA remains around the assist cutoff level, and a support cutoff operation is performed.
Zu bemerken ist, dass der Zählerwert CNTBT zurückgesetzt werden kann, wenn die Tretkraft TRQA ein Rücksetzniveau RESET übersteigt, welches höher als der obere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP eingestellt ist oder wenn eine Unterstützungsstartbedingung erfüllt ist, welche nachfolgend beschrieben wird.It should be noted that the counter value CNTBT may be reset when the pedaling force TRQA exceeds a reset level RESET set higher than the upper pedaling threshold TRQUP or when an assist start condition is satisfied, which will be described below.
Nachfolgend wird eine Steuerung/Regelung zum Start eines Unterstützungsvorgangs in dem Ökomodus beschrieben. Ein Unterstützungsvorgang wird durchgeführt, wenn eine Tretkrafthistorie erfasst wird und es erkannt wird, dass das Tretkraftniveau in ein Niveau (nachfolgend als ”Unterstützungsniveau” bezeichnet) ist, in welchem eine Hilfskraft benötigt wird, basierend auf einem Unterstützungsverhältnis, welches dem Niveau entspricht. 9 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Trethistorie zeigt, welche einen Unterstützungsvorgangstartzustand veranschaulicht und zusätzlich einen Zählerwert CNTASL zeigt, welcher jedes Mal aktualisiert wird, wenn die Tretkraft einen Referenzwert übersteigt. Auf 9 Bezug nehmend wird ein Referenzwert TRQASL für die Tretkraft, welcher ein Faktor zur Erkennung des Startens eines Unterstützungsvorgangs ist, und die Häufigkeit, mit welcher ein Höchstwert der Tretkraft TRQA, welcher sich verändert, den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt, als der Zählerwert CNTASL für den Unterstützungsstartzähler gesetzt. Hier ist der Zählerwert CNTASL so konfiguriert, dass er vermindert wird (–1) jedes Mal, wenn ein Höchstwert der Tretkraft TRQA den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt und wenn der Zählerwert CNTASL ”0” ist und die Tretkraft TRQA den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt, wird erkannt, dass die Tretkraft in dem Unterstützung benötigenden Niveau ist und die Unterstützungsstartbedingung ist erfüllt.Hereinafter, a control for starting a assisting operation in the eco mode will be described. A supporting operation is performed when a pedaling force history is detected and it is recognized that the treading level is in a level (hereinafter referred to as "assisting level") in which an assisting force is needed based on an assist ratio corresponding to the level. 9 FIG. 12 is a view showing a trethistory illustrating an assist process start state and additionally showing a counter value CNTASL which is updated each time the treading force exceeds a reference value. On 9 Referring to FIG. 14, a reference value TRQASL for the treading force, which is a factor for detecting the start of an assistance operation, and the number of times a maximum value of the treading force TRQA which exceeds the reference value TRQASL is set as the count value CNTASL for the assistance start counter , Here, the counter value CNTASL is configured to decrease (-1) every time a maximum value of the treading force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL, and when the counter value CNTASL is "0" and the treading force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL, that the treading force is in the support-requiring level and the assist start condition is satisfied.
Insbesondere ist ein Beispiel, in welchem der Anfangswert des Zählerwerts CNTASL ”3” ist, in 9 gezeigt. Auf 9 Bezug nehmend übersteigt zu den Zeitpunkten t1 und t2 ein Höchstwert der Tretkraft TRQA den Referenzwert TRQASL und der Zählerwert CNTASL wird zwei Mal vermindert. Da jedoch der Höchstwert in der nächsten Veränderungsperiode nicht den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt, wird der Zählerwert CNTASL zurückgesetzt auf den Anfangswert ”3” zu einem Zeitpunkt t3. Danach wird der Zählerwert CNTASL zu den Zeitpunkten t4, t5 und t6 vermindert und wird somit gleich ”0”. Wenn ferner die Tretkraft TRQA den Referenzwert TRQASL zu einem Zeitpunkt t7 übersteigt, ist die Unterstützungsstartbedingung erfüllt und ein Unterstützungsvorgang wird begonnen.In particular, an example in which the initial value of the counter value CNTASL is " 3 " 9 shown. On 9 Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, a maximum value of the treading force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL, and the counter value CNTASL is decreased twice. However, since the maximum value in the next change period does not exceed the reference value TRQASL, the counter value CNTASL is reset to the initial value "3" at a time t3. Thereafter, the counter value CNTASL is decreased at the times t4, t5 and t6 and thus becomes equal to "0". Further, when the treading force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL at a time t7, the assist start condition is satisfied and a assist operation is started.
Für den Referenzwert TRQASL können eine Mehrzahl von Niveaus gesetzt werden und für jedes der Niveaus kann ein Zählerwert CNTASL, welcher sich von denen der anderen Niveaus unterscheidet, gesetzt werden. 10 ist eine Ansicht, welche eine Tretkrafthistorie veranschaulicht, welche für Unterstützungsvorgangstarterfüllungsbedingungen für unterschiedliche Referenzwerte zu verwenden ist, wenn eine Mehrzahl von Referenzwerten TRQASL gesetzt sind. Auf 10 Bezug nehmend entspricht der Referenzwert TRQASL1 der Tretkraft, wenn das motorunterstützte Fahrrad allmählich beschleunigt, während es auf einer flachen Straße fährt und wird auf beispielsweise 20 kgf eingestellt. Der Referenzwert TRQASL2 entspricht der Tretkraft, wenn das motorunterstützte Fahrrad an eine Aufwärtssteigung mit einer geneigten Fläche kommt und wird auf beispielsweise 30 kgf eingestellt. Ferner entspricht der Referenzwert TRQASL3 der Tretkraft, wenn das motorunterstützte Fahrrad anfährt oder auf einer steilen Aufwärtssteigung fährt oder während des Fahrens plötzlich anders beschleunigt und wird beispielsweise auf 35 kgf eingestellt. Ferner wird der Zählerwert CNTASL1, welcher dem Referenzwert TRQASL1 entspricht, auf ”5” gesetzt, der Zählerwert CNTASL2, welcher dem Referenzwert TRQASL2 entspricht, wird auf ”3” gesetzt und der Zählerwert CNTASL3, welcher dem Referenzwert TRQASL3 entspricht, wird auf ”2” gesetzt. Die gesetzten Werte können anderenfalls willkürlich gemäß dem Charakter (Anwendung, Funktion oder dgl.) des Fahrzeugs oder dem Geschmack des Benutzers eingestellt werden.For the reference value TRQASL, a plurality of levels may be set, and for each of the levels, a counter value CNTASL different from those of the other levels may be set. 10 FIG. 14 is a view illustrating a pedaling history to be used for assisting operation starter filling conditions for different reference values when a plurality of reference values TRQASL are set. On 10 Referring to FIG. 9, the reference value TRQASL1 corresponds to the treading force when the motor-assisted bicycle gradually accelerates while traveling on a flat road and is set to, for example, 20 kgf. The reference value TRQASL2 corresponds to the treading force when the motor-assisted bicycle comes to an upward slope with an inclined surface and is set to, for example, 30 kgf. Further, the reference value TRQASL3 corresponds to the treading force when the motor-assisted bicycle starts or runs on a steep upward slope or suddenly accelerates differently during driving and is set to, for example, 35 kgf. Further, the counter value CNTASL1 corresponding to the reference value TRQASL1 is set to "5", the counter value CNTASL2 corresponding to the reference value TRQASL2 is set to "3", and the counter value CNTASL3 corresponding to the reference value TRQASL3 is set to "2". set. Otherwise, the set values may be arbitrarily set according to the character (application, function or the like) of the vehicle or the taste of the user.
Auf 10 Bezug nehmend, wird mit derart eingestellten Werten, wie den oben angegebenen, dann, wenn das motorunterstützte Fahrzeug während des Fahrens auf einer flachen Straße allmählich beschleunigt wird, zu einem Zeitpunkt t10 der Zählerwert CNTASL1 ”0” und die Tretkraft TRQA übersteigt den Referenzwert TRQASL1. Daher wird ein Unterstützungsvorgang mit einem Verhältnis (Unterstützungsverhältnis) der Tretkraft, welches dem Referenzwert TRQASL1 entspricht, begonnen. Wenn ferner das motorunterstützte Fahrrad an eine Aufwärtssteigung mit einer geneigten Fläche kommt, ist zum Zeitpunkt t11 der Zählerwert CNTASL2 ”0” und die Tretkraft TRQA übersteigt den Referenzwert TRQASL2. Folglich wird der Unterstützungsvorgang zu einem Unterstützungsbetrieb mit einem Unterstützungsverhältnis, welches dem Referenzwert TRQASL2 entspricht, gewechselt. Ferner wird beim Starten zu einem Zeitpunkt t13 nach einem kurzen Zeitintervall von einem Anfahrstartzeitpunkt t12 an der Zählerwert CNTASL3 ”0” und die Tretkraft TRQA übersteigt den Referenzwert TRQASL3. Folglich wird ein Unterstützungsvorgang mit einem Unterstützungsverhältnis entsprechend dem Referenzwert TRQASL3 begonnen. On 10 Referring to such set values as those mentioned above, when the motor-assisted vehicle is gradually accelerated while traveling on a flat road, at a time t10, the counter value CNTASL1 becomes "0" and the pedaling force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL1. Therefore, a assist operation is started with a ratio (assist ratio) of the pedaling force corresponding to the reference value TRQASL1. Further, when the motor-assisted bicycle comes to an upward slope with an inclined surface, the counter value CNTASL2 is "0" at the time t11, and the treading force TRQA exceeds the reference value TRQASL2. Consequently, the assist operation is changed to a support operation with an assist ratio corresponding to the reference value TRQASL2. Further, at the time of starting at a time t13, after a short time interval from a startup start time t12 to the counter value CNTASL3, "0" and the treading force TRQA exceed the reference value TRQASL3. Consequently, a supporting operation is started with an assist ratio corresponding to the reference value TRQASL3.
Die Zählerwerte CNTASL1 bis CNTASL3 werden beim Stoppen eines Unterstützungsvorgangs und beim Rücksetzen einer CPU initialisiert.The counter values CNTASL1 to CNTASL3 are initialized upon stopping a support operation and resetting a CPU.
Die 11 und 12 sind Flussdiagramme, welche einen wesentlichen Teil eines Verfahrens in einem Ökomodus einschließlich eines Unterstützungsvorgangs und eines Unterstützungsabschaltvorgangs zeigen, welche oben unter Bezugnahme auf die 8 und 9 beschrieben wurden. Im Schritt S1 der 11 wird erkannt, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht. Wenn die Erkennungsergebnisse negativ sind, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S2 weiter, aber wenn die Erkennungsergebnisse positiv sind, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S12 weiter (12). Ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht, wird abhängig davon erkannt, ob eine Ausgabe Vbr des Bremsschalters 51 höher als ein Referenzwert (beispielsweise 0,5 V) für eine An-Aus-Unterscheidung ist oder nicht. Im Schritt S2 wird die Tretkraft TRQA erfasst. Im Schritt S3 wird ein Höchstwert der Tretkraft TRQA erfasst und wenn der Höchstwert den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt, wird der Zählerwert CNTASL vermindert. Im Schritt S4 wird erkannt, ob der Zählerwert CNTASL ”0” ist oder nicht, um zu erkennen, ob das Unterstützungsniveau ein Unterstützungsniveau ist, welches dem Referenzwert TRQASL entspricht oder nicht. Im Schritt S5 wird erkannt, ob die Tretkraft TRQA (Ist-Wert) den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt oder nicht.The 11 and 12 FIG. 10 are flowcharts showing an essential part of a method in an eco mode including an assisting operation and a assisting shutoff operation, which are described above with reference to FIGS 8th and 9 have been described. In step S1 of 11 it detects if the brake switch 51 is on or not. If the recognition results are negative, then the processing proceeds to step S2, but if the recognition results are positive, then the processing proceeds to step S12 ( 12 ). Whether the brake switch 51 whether or not is detected depending on whether or not there is an output Vbr of the brake switch 51 is higher than a reference value (for example, 0.5 V) for on-off discrimination or not. In step S2, the pedaling force TRQA is detected. In step S3, a maximum value of the treading force TRQA is detected, and if the maximum value exceeds the reference value TRQASL, the counter value CNTASL is decreased. In step S4, it is recognized whether or not the counter value CNTASL is "0" to recognize whether or not the assistance level is a support level corresponding to the reference value TRQASL. In step S5, it is detected whether or not the treading force TRQA (actual value) exceeds the reference value TRQASL.
Wenn die Unterscheidung im Schritt S5 positiv ist, d. h. wenn die Tretkraft das vorbestimmte Niveau besitzt und die Tretkraft TRQA gegenwärtig den Referenzwert TRQASL übersteigt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S6 weiter, in welchem ein Unterstützungsvorgang erlaubt wird. Bei dem gegenwärtigen Unterstützungsbetrieb wird eine Hilfskraft basierend auf einem Unterstützungsverhältnis, welches von einem Referenzwert TRQASL für die Tretkraft bestimmt wird, und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit berechnet und die Ausgangsleistung des Motors M wird so gesteuert/geregelt, dass die Hilfskraft erhalten werden kann.If the discrimination in step S5 is affirmative, i. H. if the treading force has the predetermined level and the treading force TRQA currently exceeds the reference value TRQASL, then the processing proceeds to step S6 in which a supporting operation is permitted. In the present assist operation, an assist power is calculated based on an assist ratio determined by a reference value TRQASL for the pedaling force and the vehicle speed, and the output of the motor M is controlled so that the assist power can be obtained.
Im Schritt S7 wird aus einer Größenbeziehung der Tretkraft TRQA zu dem oberen Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP und dem unteren Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT unterschieden, ob das Tretkraftniveau ein Unterstützungsabschaltniveau ist oder nicht. Gemäß einem Ergebnis der Unterscheidung im Schritt S7 wird im Schritt S8 der Zählerwert CNTBT +1 erhöht, wenn die Tretkraft dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau entspricht, aber im Schritt S9 wird der Zählerwert CNTBT –1 vermindert, wenn die Tretkraft dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau entspricht. Wenn die Tretkraft dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau ”0” entspricht, geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S10 weiter. Es ist andererseits möglich, den Zählerwert CNTBT umgekehrt zu vermindern, wenn die Tretkraft dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau entspricht, jedoch den Zählerwert CNTBT zu erhöhen, wenn die Tretkraft nicht dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau entspricht.In step S7, it is discriminated whether or not the treading force level is a support cut-off level from a magnitude relation of the treading force TRQA to the upper treadmill threshold TRQUP and the lower treadmill threshold TRQBT. According to a result of the discrimination in step S7, in step S8, the counter value CNTBT +1 is incremented when the treading force corresponds to the assist cutoff level, but in step S9, the counter value CNTBT -1 is decremented when the treading force corresponds to the assist cutoff level. If the treading force corresponds to the assisting shutoff level "0", the processing proceeds to step S10. On the other hand, it is possible to reverse the counter value CNTBT conversely when the treading force corresponds to the assist cut-off level, but to increase the counter value CNTBT when the treading force does not correspond to the assist cut-off level.
Im Schritt S10 wird erkannt, ob der Zählerwert CNTBT gleich dem Unterstützungsabschaltbestimmungsreferenzwert TTED ist oder nicht, um zu erkennen, ob die Tretkraft TRQA auf einem niedrigen Niveau bleibt oder nicht, d. h. um das Unterstützungsabschaltniveau herum bleibt. In der Konfiguration, wo der Zählerwert CNTBT vermindert wird, wenn die Tretkraft dem Unterstützungsabschaltniveau entspricht, wird der Anfangswert auf den Unterstützungsabschaltbestimmungsreferenzwert TTED gesetzt und es wird erkannt, ob der Zählerwert CNTBT ”0” ist oder nicht, um zu erkennen, ob die Tretkraft um das Unterstützungsabschaltniveau herum bleibt oder nicht. Wenn erkannt wird, dass die Tretkraft um das Unterstützungsabschaltniveau herum bleibt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S11 weiter, in welchem ein Unterstützungsabschaltvorgang durchgeführt wird.In step S10, it is judged whether or not the counter value CNTBT is equal to the assist cut determination reference value TTED, to see whether or not the treading force TRQA remains at a low level, that is. H. stays around the backup shutdown level. In the configuration where the counter value CNTBT is decremented when the treading force corresponds to the assist cut-off level, the initial value is set to the assistance cutoff determination reference value TTED, and it is recognized whether or not the counter value CNTBT is "0" to see if the treading force is over the backup shutdown level stays around or not. If it is detected that the treading force remains around the assisting shutdown level, then the processing proceeds to step S11, in which a assisting shutoff operation is performed.
Auf 12 Bezug nehmend werden im Schritt S12 die Ausgabe Vbr des Bremsschalters 51, die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und die Tretkraft TRQA erfasst. Im Schritt S13 wird erkannt, ob die Differenz (Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags) zwischen dem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag Vbr – 1 in dem vorangegangenen Zyklus und der Bremsbetätigungsbetrag Vbr0 zur jetzigen Zeit größer als ein Veränderungsbetragreferenzwert (beispielsweise 0,5 V) ist oder nicht. Wenn die Unterscheidung positiv ist, d. h. wenn die Veränderung des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags groß ist, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S14 weiter, in welchem eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer bzw. Betriebsart, welche den Regenerationsbetrag oder regenerativen Sollstromwert (wo eine Rückkopplung verwendet wird) (nachfolgend beschrieben) bestimmt, korrigiert und ausgegeben wird. Beispielsweise wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer, welche basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit oder dem regenerativen Stromwert bestimmt wird, mit 1,1 multipliziert. Zu bemerken ist, dass in der folgenden Beschreibung die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer oder der regenerative Sollstromwert im Allgemeinen als Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer bezeichnet wird.On 12 Referring to step S12, the output Vbr of the brake switch becomes 51 which detects vehicle speed V and treading force TRQA. In step S13, it is recognized whether or not the difference (change amount ΔVbr of the brake operation amount) between the brake operation amount Vbr-1 in the previous cycle and the brake operation amount Vbr0 at the present time is greater than a change amount reference value (for example, 0.5V). If the Discrimination is positive, that is, when the change of the braking operation amount is large, the processing proceeds to step S14, in which a regenerative duty determining the regeneration amount or regenerative target current value (where feedback is used) (described below) is determined , corrected and output. For example, the regenerative duty ratio, which is determined based on the vehicle speed or the regenerative current value, is multiplied by 1.1. It should be noted that in the following description, the regenerative duty cycle or the regenerative current target value is generally referred to as the regenerative duty cycle.
Wo andererseits die Veränderung des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags klein ist, geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S15 weiter, in welchem eine Abwärtsgefälleunterscheidung durchgeführt wird. Die Unterscheidung, ob das motorunterstützte Fahrrad auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt oder nicht, kann beispielsweise abhängig davon durchgeführt werden, ob die Tretkraft im Wesentlichen ”0” ist und die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit höher als 10 km/h ist oder nicht. Wenn die Unterscheidung im Schritt S15 positiv ist, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S16 weiter, in welchem eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer, welche für ein Abwärtsgefälle gesetzt ist, ausgegeben wird. Die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer für ein Abwärtsgefälle ist so gesetzt, dass sie einen niedrigeren Wert besitzt, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zunimmt.On the other hand, where the variation of the brake operation amount is small, the processing proceeds to step S15, in which a downward-gradient discrimination is performed. For example, the discrimination as to whether or not the motor-assisted bicycle is traveling on a downhill slope may be made depending on whether the pedaling force is substantially "0" and the vehicle speed is higher than 10 km / h or not. If the discrimination in step S15 is affirmative, then the processing proceeds to step S16, in which a regenerative duty, which is set for a downward slope, is output. The regenerative duty for a downward slope is set to be a lower value as the vehicle speed increases.
Wenn andererseits die Unterscheidung im Schritt S15 negativ ist, d. h. wenn die Veränderung des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags niedriger als ein Referenzwert ist und erkannt wird, dass das motorunterstützte Fahrrad auch nicht auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S17 weiter, in welchem eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer für eine normale Bremsbetätigung, welche basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt wird, ausgegeben wird. Während der auf der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer basierenden Regeneration wirkt die Regenerativ-Bremsung. Zu bemerken ist, dass spezielle Beispiele der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer gemäß verschiedenen Bedingungen nachfolgend beschrieben werden.On the other hand, if the discrimination in step S15 is negative, i. H. if the change of the brake operation amount is lower than a reference value and it is detected that the motor-assisted bicycle is not traveling downhill, then the processing proceeds to step S17, in which a regenerative duty for a normal brake operation based on the vehicle speed is determined is issued. During regeneration based on regenerative duty cycle, regenerative braking acts. It should be noted that specific examples of the regenerative duty according to various conditions will be described below.
Im Schritt S18 wird unterschieden, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht. Solange der Bremsschalter 51 an bleibt, werden die Schritte S12 bis S17 ausgeführt, um die Regenerativ-Bremsung fortzusetzen. Wenn der Bremsschalter zu Aus wechselt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S19 weiter, in welchem die Regenerativ-Bremsung gestoppt wird.In step S18, it is discriminated whether the brake switch 51 is on or not. As long as the brake switch 51 remains on, the steps S12 to S17 are executed to continue the regenerative braking. When the brake switch turns off, the processing proceeds to step S19, in which the regenerative braking is stopped.
13 veranschaulicht ein Beispiel der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer entsprechend der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V. Auf 13 Bezug nehmend wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und dem Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags gesetzt. Während der Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr hier auf drei Stufen klein, mittel und groß eingestellt ist, kann er andererseits auf feinere Stufen eingestellt sein. 13 illustrates an example of the regenerative duty cycle corresponding to the vehicle speed V. Auf 13 Referring to, the regenerative duty is set based on the vehicle speed V and the amount of change ΔVbr of the brake operating amount. On the other hand, while the amount of change ΔVbr is set to three levels of small, medium and large, it may be set to finer levels.
Wie in 13 zu sehen, nimmt in einem niedrigen Geschwindigkeitsbereich, in welchem die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V niedriger als 10 km/h beträgt, die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zu, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zunimmt, aber in einem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich, in welchem die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V von 10 bis 20 km reicht, nimmt die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer ab, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit zunimmt. Ferner zeigt die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer in einem hohen Geschwindigkeitsbereich, in welchem die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V hoher als 20 km ist, geringe Veränderungen. Ferner ist in dem hohen Geschwindigkeitsbereich der Veränderungsbetrag der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer bezüglich des Veränderungsbetrags des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags kleiner als der in dem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich. Da die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer in dem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich und dem niedrigen Geschwindigkeitsbereich groß ist, kann eine Ladung der Batterie durch eine Regeneration effizient in einem Fahrzustand durchgeführt werden, in welchem ein Stoppen regelmäßig vorkommt wie beim Fahren in einer Stadt. Insbesondere da die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer höher gesetzt wird, wenn der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags größer wird, kann das Fahrzeug in einer kurzen Zeit gestoppt werden und außerdem kann der Ladebetrag durch die Regeneration erhöht werden.As in 13 In a low speed range in which the vehicle speed V is lower than 10 km / h, the regenerative duty increases as the vehicle speed increases but in a middle speed range in which the vehicle speed V ranges from 10 to 20 km , decreases the regenerative duty cycle as the vehicle speed increases. Further, the regenerative duty in a high speed range in which the vehicle speed V is higher than 20 km shows little change. Further, in the high speed range, the change amount of the regenerative duty ratio with respect to the change amount of the brake operation amount is smaller than that in the middle speed range. Since the regenerative duty ratio is large in the middle speed range and the low speed range, a charge of the battery can be efficiently performed by regeneration in a running state in which stopping occurs regularly like driving in a city. In particular, since the regenerative duty is set higher as the amount of change of the braking operation amount becomes larger, the vehicle can be stopped in a short time and, moreover, the amount of charge can be increased by the regeneration.
14 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer während des Fahrens auf einem Abwärtsgefälle zeigt, wo die Tretkraft im Wesentlichen ”0” ist. Wenn die Tretkraft im Wesentlichen 0 ist, nimmt die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer ab, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V in dem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich und dem hohen Geschwindigkeitsbereich zunimmt, in welchen die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V höher als 10 km/h ist, wie in 14 zu sehen. Die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer entspricht einem ungefähren Mittelwert zwischen Werten der in 13 gezeigten Kurven, wo der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags mittel und klein ist. 14 FIG. 12 is a view showing an example of the regenerative duty while driving on a downhill slope where the treading force is substantially "0". When the pedaling force is substantially 0, the regenerative duty ratio decreases as the vehicle speed V increases in the middle speed range and the high speed range in which the vehicle speed V is higher than 10 km / h, as in FIG 14 to see. The regenerative duty cycle corresponds to an approximate average between values of in 13 shown curves, where the change amount of the brake operation amount is medium and small.
Nachfolgend wird eine Modifikation beim Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle beschrieben. Die 15 und 16 sind Flussdiagramme einer regenerativen Steuerung/Regelung gemäß der Modifikation. In der vorliegenden Modifikation wird beim Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle eine Regenerativ-Bremsung durchgeführt, ungeachtet davon, ob der Bremsschalter an ist oder nicht. Während bei dem oben beschriebenen Beispiel der Stellantrieb 7 zur Durchführung der Umschaltung zur Regeneration unter Strom gesetzt wird, wenn der Bremsschalter an ist, wird bei der vorliegenden Modifikation dann, wenn Bedingungen der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit und der Tretkraft, welche nachfolgend beschrieben werden, erfüllt sind, der Stellantrieb 7 mit Strom versorgt, um ein Umschalten zur Regeneration so durchzuführen, dass ein regeneratives Bremsen ungeachtet davon, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an oder aus ist, durchgeführt werden kann.Hereinafter, a modification when driving on a downhill slope will be described. The 15 and 16 FIG. 10 are flowcharts of a regenerative control according to the modification. In the present modification, when driving on a downward slope, a regenerative Braking, regardless of whether the brake switch is on or not. While in the example described above, the actuator 7 is energized to carry out the regeneration switching when the brake switch is on, in the present modification, when conditions of the vehicle speed and the treading force, which are described below, are satisfied, the actuator 7 energized to perform a regeneration switch so that a regenerative braking regardless of whether the brake switch 51 on or off, can be performed.
Auf 15 Bezug nehmend wird im Schritt S21 unterschieden, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht. Wenn der Bremsschalter 51 an ist, geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S22 weiter, in welchem die Tretkraft TRQA erfasst wird. Im Schritt S23 wird erkannt, ob das kraftunterstützte Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt oder nicht. Wenn das kraftunterstützte Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S24 weiter, in welchem eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer für den Fall, in welchem die Tretkraft im Wesentlichen 0 ist, ausgegeben wird. Folglich wirkt die Regenerativ-Bremsung. Ebenso wird im Schritt S25 erkannt, ob das motorunterstützte Fahrzeug auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt oder nicht. Solange das Fahren auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fortdauert, bleibt die Unterscheidung im Schritt S25 positiv und die Verarbeitung kehrt zum Schritt S24 zurück, um die Regenerativ-Bremsung fortzusetzen. Wenn die Erkennung der Fahrt auf einem Abwärtsgefälle negativ wird, geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S26 weiter, in welchem die Regenerativ-Bremsung gestoppt wird.On 15 Referring to step S21, it is discriminated whether the brake switch 51 is on or not. When the brake switch 51 is on, the processing proceeds to step S22 in which the treading force TRQA is detected. In step S23, it is recognized whether or not the power assisted vehicle is traveling on a downhill slope. When the power-assisted vehicle is traveling on a downhill slope, the processing proceeds to step S24, in which a regenerative duty ratio is output for the case where the treading force is substantially zero. Consequently, the regenerative braking acts. Also, it is recognized in step S25 whether or not the motor-assisted vehicle is traveling on a downhill slope. As long as the driving continues on a downward gradient, the discrimination in step S25 remains positive and the processing returns to step S24 to continue the regenerative braking. If the detection of the travel on a downward slope becomes negative, the processing proceeds to step S26, in which the regenerative braking is stopped.
Wenn erkannt wird, dass das motorunterstützte Fahrrad nicht auf einem Abwärtsgefälle fährt, d. h. wenn die Unterscheidung im Schritt S23 negativ ist oder die Unterscheidung im Schritt S25 negativ ist und die Regenerativ-Bremsung gestoppt ist, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S27 weiter. Die Schritte S27 bis Schritt S35 sind jeweils dieselben wie die Schritte S3 bis S11 der 11 und daher wird eine Beschreibung von ihnen ausgelassen.If it is detected that the motor-assisted bicycle is not traveling on a downward slope, that is, if the discrimination in step S23 is negative or the discrimination in step S25 is negative and the regenerative braking is stopped, then the processing proceeds to step S27. The steps S27 to S35 are the same as the steps S3 to S11 of FIG 11 and therefore a description of them will be omitted.
Wenn andererseits der Bremsschalter 51 nicht an ist, ist die Unterscheidung im Schritt S21 positiv und die Verarbeitung geht zum Schritt S36 weiter (16). Im Schritt S36 werden die Ausgabe Vbr des Bremsschalters 51, die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und die Tretkraft TRQA erfasst. Im Schritt S37 wird unterschieden, ob der Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags größer als ein Veränderungsbetragreferenzwert (beispielsweise 1,5 V) ist oder nicht. Wenn die Unterscheidung positiv ist, d. h. wenn der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags groß ist, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S38 weiter, in welchem die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer korrigiert und ausgegeben wird. Beispielsweise wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer, welche basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt wird, mit 1,1 multipliziert.If, on the other hand, the brake switch 51 is not on, the discrimination in step S21 is affirmative, and the processing proceeds to step S36 ( 16 ). In step S36, the output Vbr of the brake switch becomes 51 which detects vehicle speed V and treading force TRQA. In step S37, it is discriminated whether or not the amount of change ΔVbr of the brake operation amount is greater than a change amount reference value (for example, 1.5V). If the discrimination is positive, that is, if the amount of change of the braking operation amount is large, then the processing proceeds to step S38 in which the regenerative duty is corrected and output. For example, the regenerative duty ratio, which is determined based on the vehicle speed, is multiplied by 1.1.
Wenn der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags klein ist, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S39 weiter, in welchem eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer für eine herkömmliche Bremsbetätigung, welche basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt wird, ausgegeben wird. Eine Regenerativ-Bremsung wirkt durch die Regeneration gemäß der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer.If the change amount of the brake operation amount is small, then the processing proceeds to step S39 in which a regenerative duty for a conventional brake operation determined based on the vehicle speed is output. A regenerative braking acts through the regeneration according to the regenerative duty cycle.
Im Schritt S40 wird unterschieden, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht. Solange der Bremsschalter 51 an bleibt, werden die Schritte S36 bis S39 ausgeführt, um die Regenerativ-Bremsung fortzusetzen. Wenn der Bremsschalter zu aus wechselt, dann geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt S41 weiter, in welchem die Regenerativ-Bremsung gestoppt wird.In step S40, it is discriminated whether the brake switch 51 is on or not. As long as the brake switch 51 remains on, the steps S36 to S39 are executed to continue the regenerative braking. When the brake switch turns off, the processing proceeds to step S41 in which the regenerative braking is stopped.
1 ist ein Blockdiagramm, welches Funktionen von wesentlichen Teilen der Steuer/Regeleinrichtung 100 zeigt. Es ist zu bemerken, dass die Funktionen von einem Mikrocomputer, welcher eine CPU umfasst, durchgeführt werden können. Auf 1 Bezug nehmend werden Ausgabedaten (eine Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V) eines Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeitssensors 40 in ein Antriebseinschaltdauerkennfeld (Hilfskraftkennfeld) 41 und ein Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld (Regenerativladekennfeld) 52 bei einer vorbestimmten Unterbrechungszeiteinstellung eingegeben. Ausgabedaten (eine Tretkraft TRQA) des Potenziometers 82, welches als Tretkraftsensor dient, wird in das Hilfskraftkennfeld 41 eingegeben, einen Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitt 43, einen zweiten Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitt 50 und einen Höchstwertunterscheidungsabschnitt 46. 1 Fig. 10 is a block diagram showing functions of essential parts of the control device 100 shows. It should be noted that the functions can be performed by a microcomputer including a CPU. On 1 Referring to, output data (a vehicle speed V) of a vehicle speed sensor becomes 40 in a drive duty cycle map (auxiliary power map) 41 and a regenerative duty cycle map (regenerative charge map) 52 entered at a predetermined interrupt timing. Output data (a pedaling force TRQA) of the potentiometer 82 , which serves as a pedaling force sensor, is in the auxiliary power map 41 entered, a tread force discriminating section 43 , a second tread force discriminating section 50 and a maximum value discriminating section 46 ,
Das Hilfskraftkennfeld 41 ist so gesetzt, dass Hilfskraftdaten ausgegeben werden, bei welchen ein optimales Unterstützungsverhältnis erhalten wird, basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und der Tretkraft TRQA. Beispielsweise ist das Hilfskraftkennfeld so gesetzt, dass selbst dann, wenn die Tretkraft TRQA gleich ist, während die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V zunimmt, die Hilfskraft abnimmt, d. h. das Hilfs- bzw. Unterstützungsverhältnis abnimmt.The auxiliary power map 41 is set to output auxiliary force data in which an optimal assist ratio is obtained based on the vehicle speed V and the treading force TRQA. For example, the assist force map is set so that even when the treading force TRQA is equal as the vehicle speed V increases, the assist power decreases, ie, the assist ratio decreases.
Unterdessen wird eine Ausgabe des Bremsschalters 51, d. h. ein Bremssignal, welches den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag repräsentiert, in einen Betätigungsbetragveränderungsbetragerfassungsabschnitt 53 eingegeben. Der Betätigungsbetragveränderungsbetragerfassungsabschnitt 53 berechnet eine Differenz zwischen Ausgaben des Bremsschalters 51 im Augenblick und im vorangehenden Zyklus, um den Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags zu erfassen. Der Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr wird in das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 eingegeben.Meanwhile, an output of the brake switch 51 that is, a brake signal representing the brake operation amount, in an operation amount change amount detection section 53 entered. The operation amount change amount detection section 53 calculates a difference between outputs of the brake switch 51 at the moment and in the preceding cycle to detect the amount of change ΔVbr of the brake operation amount. The change amount ΔVbr becomes the regenerative on-period map 52 entered.
Das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 ist so gesetzt, dass es eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer (Regenerativsteuer/regelsignal) ausgibt, mit welchem eine optimale Regenerationsausgabe basierend auf der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und dem Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr erhalten wird, wenn der Bremschelter 51 angeschaltet ist. Ein spezielles Beispiel des Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfelds 52 ist in 13 gezeigt. Es ist zu bemerken, dass das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 zusätzlich ein Kennfeld umfassen kann, welches gesetzt ist, indem Korrekturwerte (Werte, welche durch Multiplizieren eines Koeffizienten oder von Koeffizienten erhalten werden) in Betracht gezogen werden, wo der Veränderungsbetrag ΔVbr größer als der Veränderungsbetragreferenzwert ist.The regenerative duty cycle map 52 is set to output a regenerative duty (regenerative control signal) with which an optimal regeneration output is obtained based on the vehicle speed V and the change amount ΔVbr when the brake chuck 51 is turned on. A specific example of the regenerative duty cycle map 52 is in 13 shown. It should be noted that the regenerative duty cycle map 52 may additionally include a map set by taking into account correction values (values obtained by multiplying a coefficient or coefficients) where the change amount ΔVbr is larger than the change amount reference value.
Ferner werden die von dem Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeitssensor 40 erfasste Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V und die von dem Tretkraftsensor 82 erfasste Tretkraft TRQA in eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauertabelle (Regenerativladetabelle) 54 eingegeben. Die Regenerativladetabelle 54 wird verwendet, wenn die Tretkraft TRQA im Wesentlichen gleich 0 ist und die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V höher als der mittlere Geschwindigkeitsbereich ist. Ein spezielles Beispiel der Regenerativladetabelle 54 ist in 14 gezeigt. Es ist zu bemerken, dass die Regenerativladetabelle 54 nur bei einer Bremsbetätigung verwendet werden kann oder anderenfalls ungeachtet einer Bremsbetätigung verwendet werden kann.Further, those of the vehicle speed sensor 40 detected vehicle speed V and that of the pedaling force sensor 82 recorded pedaling force TRQA in a regenerative power-on table (regenerative charging table) 54 entered. The regenerative loading table 54 is used when the treading force TRQA is substantially equal to 0 and the vehicle speed V is higher than the middle speed range. A specific example of the regenerative loading table 54 is in 14 shown. It should be noted that the regenerative loading table 54 can only be used in a brake application or otherwise can be used regardless of a brake application.
Die Hilfskraftdaten und das Regenerativsteuer/regelsignal werden einem Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 eingegeben, welcher den Motor M gemäß der Hilfskraftdaten oder des Regenerativsteuer/regelsignals steuert/regelt. Es ist zu bemerken, dass der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeitssensor 40 beispielsweise aus Mitteln ausgebildet sein kann, welche magnetisch regelmäßige Vorsprungs- und Vertiefungsabschnitte erfasst, welche an einem äußeren Rand der Tragplatte 102 in der Motorunterstützungseinheit 1 vorgesehen sind und gibt die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V basierend auf der Anzahl an erfassten Vorsprungs- oder Vertiefungsabschnitten oder den Intervallen zwischen solchen erfassten Vorsprungs- oder Vertiefungsabschnitten aus.The assist power data and the regenerative control signal become a drive / regeneration driver 42 which controls the motor M according to the assist power data or the regenerative control signal. It should be noted that the vehicle speed sensor 40 may be formed, for example, from means which magnetically regular projection and recessed portions detected, which at an outer edge of the support plate 102 in the engine support unit 1 are provided and outputs the vehicle speed V based on the number of detected protrusion or depression portions or the intervals between such detected protrusion or depression portions.
Der Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitt 43 erkennt, ob die Tretkraft TRQA gegenwärtig größer oder kleiner als Tretkraftreferenzwerte (beispielsweise der obere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQUP und der untere Tretkraftgrenzwert TRQBT, welche oben erwähnt sind) ist und stellt den Zählerwert CNTBT eines Niedriges-Niveau-Zählers 44 als einen Unterstützungsabschaltbestimmungszähler gemäß einem Ergebnis der Unterscheidung. Ein Vergleichsabschnitt 45 vergleicht den Zählerwert CNTBT des Zählers 44 mit den Unterstützungsabschaltreferenzwerten und gibt eine Unterstützungsabschaltinstruktion ACI an den Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 aus, wenn der Zählerwert CNTBT den Unterstützungsabschaltbestimmungsreferenzwert TTED erreicht. Hier bilden der Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitt 43, der Zähler 44 und der Vergleichsabschnitt 45 ein Regenerationsniveauerfassungsmittel.The tread force discriminating section 43 detects whether the treading force TRQA is currently greater or less than treadle reference values (for example, the upper treadmill threshold TRQUP and the lower treadle threshold TRQBT mentioned above) and sets the counter value CNTBT of a low level counter 44 as a support cutoff determination counter according to a result of the discrimination. A comparison section 45 compares the counter value CNTBT of the counter 44 with the support disable reference values, and outputs a backup shutdown instruction ACI to the drive / regeneration driver 42 when the counter value CNTBT reaches the support cutoff determination reference value TTED. Here is the tread force discriminating section 43 , the counter 44 and the comparison section 45 a regeneration level detection means.
Der Höchstwertunterscheidungsabschnitt 46 empfängt eine Zufuhr der Tretkraft TRQA von dem Tretkraftsensor 82 und erfasst periodisch einen Höchstwert der variierenden Tretkraft TRQA. Der Höchstwert wird in einen Tretkraftniveauunterscheidungsabschnitt 47 eingegeben und der Tretkraftniveauunterscheidungsabschnitt 47 aktualisiert den Zählerwert CNTASL eines Unterstützungsstartzählers 48, wenn er erkennt, dass der Höchstwert das vorbestimmte Tretkraftniveau TRQASL übersteigt. Der Unterstützungsstartzähler 48 gibt eine Unterstützungserlaubnisinstruktion AI aus, wenn der Zählerwert CNTASL gleich einem vorbestimmten Wert wird. Die Unterstützungserlaubnisinstruktion AI wird dem Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 durch ein Gate G eingegeben.The maximum value discriminating section 46 receives a supply of treading force TRQA from the treading force sensor 82 and periodically detects a maximum value of the varying pedaling force TRQA. The maximum value becomes a treadle level discriminating section 47 and the treadle level discriminating section 47 updates the counter value CNTASL of a support start counter 48 when it detects that the maximum value exceeds the predetermined treadle level TRQASL. The backup start counter 48 outputs a support permission instruction AI when the counter value CNTASL becomes equal to a predetermined value. The assistance permission instruction AI becomes the drive / regeneration driver 42 entered through a gate G.
Der zweite Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitt 50 gibt ein Erfassungssignal aus, wenn die gegenwärtige Tretkraft TRQA ein Tretkraftniveau TRQASL übersteigt. Das Gate G wird geöffnet, wenn ein Erfassungssignal des zweiten Tretkraftunterscheidungsabschnitts 50 diesem zugeführt wird und die Unterstützungserlaubnisinstruktion AI wird dem Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 eingegeben. Hier bilden der Höchstwertunterscheidungsabschnitt 46, der Tretkraftniveauunterscheidungsabschnitt 47 und der Unterstützungsstartzähler 48 Tretkraftveränderungsniveauerfassungsmittel.The second tread force discriminating section 50 outputs a detection signal when the current treading force TRQA exceeds a treading level TRQASL. The gate G is opened when a detection signal of the second tread force discriminating section 50 is supplied to this and the assistance permission instruction AI is the drive / regeneration driver 42 entered. Here is the maximum value discriminating section 46 , the treadle level discrimination section 47 and the backup start counter 48 Tretkraftveränderungsniveauerfassungsmittel.
Der Antrieb/Regenerationstreiber 42 versorgt den Motor M mit Strom gemäß der Unterstützungserlaubnisinstruktion AI, um eine Antriebskraft zu erzeugen, welche den Hilfskraftdaten entspricht, um die Antriebskraft des Fahrzeugs zu unterstützen. Ferner steuert/regelt der Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 den Motor M zur Regeneration, sodass der Motor M einen Regenerationsbetrag entsprechend dem Regenerationssteuer/regelsignal gemäß der Regenerationsinstruktion ACI erzeugt. Insbesondere wird die Einschaltdauer oder der Durchlasswinkel eines FETs, welcher die Treiberschaltung für den Motor M bildet, gemäß den Hilfskraftdaten oder dem Regenerationssteuer/regelsignal bestimmt, um die Höhe der Hilfskraft oder der Regeneration zu steuern/zu regeln. Zu bemerken ist, dass der Tretkraftniveauunterscheidungsabschnitt 47 ein Reset-Signal ausgibt, um den Zählerwert des Unterstützungsstartzählers 48 auf seinen Anfangswert zurückzusetzen, wenn der Höchstwert das Tretkraftniveau TRQASL nicht übersteigt.The drive / regeneration driver 42 supplies power to the motor M according to the assistance permission instruction AI to generate a driving force corresponding to the assisting force data to assist the driving force of the vehicle. Further, the drive / regeneration driver controls 42 the engine M for regeneration so that the engine M generates a regeneration amount corresponding to the regeneration control signal according to the regeneration instruction ACI. Specifically, the duty ratio or the passage angle of an FET constituting the drive circuit for the motor M is determined according to the assist force data or the regeneration control signal to control the amount of assist power or regeneration. It should be noted that the treadle level discriminating section 47 outputs a reset signal to the counter value of the assistance start counter 48 to reset to its initial value if the maximum value does not exceed the treadle level TRQASL.
In der oben beschriebenen Ausführungsform wird vorausgesetzt, dass ein bürstenloser Motor als der Motor M verwendet wird. Jedoch kann die vorliegende Erfindung nicht nur bei einem Fahrzeug, welches einen bürstenlosen Motor verwendet, sondern auch bei einem Motor, welcher eine Bürste besitzt, angewendet werden. 17 ist ein Blockdiagramm einer Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung, welche einen Motor mit einer Bürste verwendet. Auf 17 Bezug nehmend umfasst die Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung eine Antriebssteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 und eine Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56. Eine aus einer Batterie 4 erhaltene Steuer/Regelenergieversorgung ist mit der Antriebsteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 und der Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56 durch ein Relais 57 verbunden. Ferner ist die Batterie 4 mit der Antriebsteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 und der Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56 verbunden, um Strom einem Bürstenmotor 60 zuzuführen und um die Batterie mit Regenerativstrom zu laden. Die Antriebsteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 und die Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56 sind mit dem Bürstenmotor 60 durch Relais 58 und 59 verbunden. Ferner werden die Relais 57, 58 und 59 durch ein An/Aus-Signal des Bremsschalters 51 gesteuert/geregelt.In the embodiment described above, it is assumed that a brushless motor is used as the motor M. However, the present invention can be applied not only to a vehicle using a brushless motor but also to a motor having a brush. 17 FIG. 10 is a block diagram of a regenerative control apparatus using a motor with a brush. FIG. On 17 Referring to the regenerative control apparatus, a drive controller 55 and a regeneration controller 56 , One from a battery 4 The control power supply received is with the drive control device 55 and the regeneration controller 56 through a relay 57 connected. Further, the battery 4 with the drive control / regulating device 55 and the regeneration controller 56 connected to power a brush motor 60 to feed and to charge the battery with regenerative current. The drive control device 55 and the regeneration controller 56 are with the brush motor 60 through relays 58 and 59 connected. Furthermore, the relays 57 . 58 and 59 by an on / off signal of the brake switch 51 controlled / regulated.
Wenn der Bremsschalter 51 an ist, d. h. wenn eine Bremsbetätigung durchgeführt wird, werden die Relais 57, 58 und 59 zur Seite der Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56 umgeschaltet. Wenn andererseits der Bremsschalter 51 aus ist, d. h. wenn keine Bremsbetätigung durchgeführt wird, werden die Relais 57, 58 und 59 zur Seite der Antriebsteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 umgeschaltet.When the brake switch 51 is on, that is, when a brake operation is performed, the relays 57 . 58 and 59 to the side of the regeneration tax 56 switched. If, on the other hand, the brake switch 51 is off, that is, if no brake operation is performed, the relays 57 . 58 and 59 to the side of the drive control / regulating device 55 switched.
Die Antriebsteuer/regeleinrichtung 55 umfasst eine Steuer/Regel-FET 551 und dem Motor 60 zuzuführender Strom wird durch eine Durchlasssteuerung/regelung der FET 551 gesteuert/geregelt. Unterdessen umfasst die Regenerationssteuer/regeleinrichtung 56 ein Steuer/Regel-FET 561 und eine auf einen gewünschten Wert erhöhte Regenerativspannung kann durch Steuern/Regeln der Zerhackereinschaltdauer des FET 561 erhalten werden.The drive control device 55 includes a control FET 551 and the engine 60 current to be supplied is through a pass control of the FET 551 controlled / regulated. Meanwhile, the regeneration controller includes 56 a control FET 561 and a regenerative voltage increased to a desired value can be achieved by controlling the chopper ON duration of the FET 561 to be obtained.
In der vorliegenden Ausführungsform wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer basierend auf dem Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt. Jedoch kann die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer im Übrigen basierend auf dem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt werden. In diesem Fall wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer so gesteuert/geregelt, dass sie zunimmt, wenn der Bremsbetätigungsbetrag zunimmt. 18 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel der Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer veranschaulicht, welche dem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit entspricht. Wie aus 18 zu sehen ist, wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer so gesteuert/geregelt, dass sie in Antwort auf den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag zunimmt und insbesondere wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer vergleichsweise groß, wenn die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V in dem niederen Geschwindigkeitsbereich und dem mittleren Geschwindigkeitsbereich ist (3 bis 14 km/h oder in der Nähe).In the present embodiment, the regenerative duty ratio is determined based on the amount of change of the brake operation amount and the vehicle speed. Incidentally, the regenerative duty can be otherwise determined based on the brake operation amount and the vehicle speed. In this case, the regenerative duty is controlled so as to increase as the amount of the brake operation increases. 18 FIG. 14 is a view illustrating an example of the regenerative duty corresponding to the brake operation amount and the vehicle speed. FIG. How out 18 3, the regenerative duty ratio is controlled to increase in response to the brake operation amount, and in particular, the regenerative duty ratio becomes comparatively large when the vehicle speed V is in the low speed range and the middle speed range (3 to 14 km / h or nearby).
Die oben beschriebene Ausführungsform kann so modifiziert werden, dass die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer in Antwort auf einen Ladezustand der Batterie 4 bestimmt wird. Es ist offensichtlich, dass der Ladezustand der Batterie 4, d. h. die Restkapazität der Batterie 4, nicht immer fest ist. Die Batterie 4 kann eine geringe Restkapazität besitzen oder kann in einem fast vollständig geladenen Zustand sein. Beispielsweise wird in einem Zustand, in welchem die Batterie 4 fast vollständig geladen ist, eine Ladung durch Regeneration nicht benötigt, aber wenn die Restkapazität gering ist, wird vorzugsweise ein Laden der Batterie 4 durch Regeneration positiv durchgeführt. Dann ist es eine mögliche Idee, die Batterie 4 in Antwort auf die Restkapazität der Batterie 4 zu laden, wenn die Restkapazität kleiner als ein vorbestimmter Wert ist. Beispielsweise wird in der amtlichen Veröffentlichung der japanischen Patentoffenlegungsschrift Nr. JP H11-227 668 A eine Regenerativ-Steuer/Regelvorrichtung offenbart, in welcher ein regeneratives Bremsen durchgeführt wird, wenn die Batteriespannung unter einem vorbestimmten Wert liegt.The embodiment described above may be modified such that the regenerative duty cycle in response to a state of charge of the battery 4 is determined. It is obvious that the state of charge of the battery 4 ie the remaining capacity of the battery 4 not always firm. The battery 4 may have a low residual capacity or may be in an almost fully charged state. For example, in a state in which the battery 4 is almost completely charged, a charge through regeneration is not needed, but if the residual capacity is low, it is preferable to charge the battery 4 performed positively by regeneration. Then it's a possible idea, the battery 4 in response to the remaining capacity of the battery 4 to charge when the remaining capacity is smaller than a predetermined value. For example, in the official publication of Japanese Laid-Open Patent Publication No. Hei. JP H11-227 668 A discloses a regenerative control apparatus in which regenerative braking is performed when the battery voltage is below a predetermined value.
Jedoch wird gemäß der in der amtlichen Veröffentlichung offenbarten Steuer/Regelvorrichtung, wenn der Batteriespannungswert abfällt, bis er unter den vorbestimmten Wert kommt, ein regeneratives Bremsen plötzlich ausgeführt. Daher besteht die Möglichkeit, dass die Laufruhe verschlechtert werden kann. Daher ist es erwünscht, dass der Regenerationsbetrag moderat verändert werden kann.However, according to the control device disclosed in the official publication, when the battery voltage value drops until it comes below the predetermined value, regenerative braking is suddenly performed. Therefore, there is a possibility that the smoothness may be deteriorated. Therefore, it is desirable that the regeneration amount can be moderately changed.
Bei der unten beschriebenen Ausführungsform wird in Antwort auf die Restkapazität der Batterie 4 der Regenerationsbetrag verringert, wenn die Restkapazität hoch ist, aber der Regenerationsbetrag wird erhöht, wenn die Restkapazität niedrig ist und ferner wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer unter Berücksichtigung der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit bestimmt. Durch diese Gegenmaßnahme kann eine plötzliche Veränderung des Regenerationsbetrags durch die Restkapazität einer Batterie verhindert werden und außerdem wird ein geeigneter Regenerativ-Bremsbetrag gemäß der Fahrsituation des Fahrzeugs erhalten. Folglich kann ein reibungsloser Fahrzustand leicht erreicht werden. Zu bemerken ist, dass die Restkapazität der Batterie 4 insbesondere aus einer Spannung (Batteriespannung) zwischen Ausgabeanschlüssen der Batterie 4 erkannt wird.In the embodiment described below, in response to the remaining capacity of the battery 4 the regeneration amount decreases when the remaining capacity is high, but the regeneration amount is increased when the remaining capacity is low, and further, the regenerative duty is determined in consideration of the vehicle speed. By this countermeasure, a sudden change of the regeneration amount can be prevented by the remaining capacity of a battery and, in addition, a suitable regenerative braking amount according to the driving situation of the vehicle is obtained. Consequently, a smooth running state can be easily achieved. It should be noted that the remaining capacity of the battery 4 in particular from one Voltage (battery voltage) between output terminals of the battery 4 is recognized.
19 ist ein Blockdiagramm eines wesentlichen Teils einer Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung, welche eine Funktion zur Bestimmung einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer in Antwort auf eine Batteriespannung umfasst und gleiche Referenzzeichen zu jenen der 1 bezeichnen gleiche Elemente. Auf 19 Bezug nehmend ist ein Batteriespannungserfassungsabschnitt 61 vorgesehen und eine Batteriespannung VB einer Batterie 4 wird von dem Batteriespannungserfassungsabschnitt 61 erfasst. Die erfasste Batteriespannung VB wird in ein Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 eingegeben. Das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 umfasst ein Kennfeld (als ein Hauptkennfeld bezeichnet). Beispielsweise kann das in 13 gezeigte Kennfeld als das Hauptkennfeld verwendet werden, in welchem die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer als eine Funktion des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags Vbr oder des Bremsbetätigungsbetragveränderungsbetrags ΔVbr und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V ausgegeben wird. Ferner umfasst das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 ein Hilfskennfeld, welches einen Korrekturkoeffizienten zur Korrektur der mit dem Hauptkennfeld bestimmten Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer ausgibt. Dem Hilfskennfeld wird die Batteriespannung VB zugeführt und ein Korrekturkoeffizient wird als eine Funktion der Batteriespannung VB und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V ausgegeben. Die mit dem Hauptkennfeld erhaltene Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer wird mit dem Korrekturkoeffizienten multipliziert. 19 FIG. 12 is a block diagram of an essential part of a regenerative control device which includes a function for determining a regenerative duty in response to a battery voltage, and like reference numerals to those of FIG 1 denote the same elements. On 19 Reference is made to a battery voltage detection section 61 provided and a battery voltage VB of a battery 4 is from the battery voltage detection section 61 detected. The detected battery voltage VB becomes a regenerative ON duration map 52 entered. The regenerative duty cycle map 52 includes a map (referred to as a main map). For example, this can be done in 13 shown map may be used as the main map, in which the regenerative duty cycle as a function of the brake operation amount Vbr or the brake operation amount change amount ΔVbr and the vehicle speed V is output. Furthermore, the regenerative duty cycle map includes 52 an auxiliary map which outputs a correction coefficient for correcting the regenerative duty determined with the main map. The auxiliary map is supplied with the battery voltage VB, and a correction coefficient is output as a function of the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V. The regenerative duty cycle obtained with the main map is multiplied by the correction coefficient.
20 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel des Hilfskennfelds zeigt. In 20 ist die Batteriespannung auf die X-Achse gesetzt und die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit auf die Y-Achse und der Korrekturkoeffizient auf die Z-Achse. Wie in 20 gezeigt, ist das Kennfeld so gesetzt, dass der Korrekturkoeffizient in Antwort auf die Batteriespannung VB abnimmt, um die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zu verringern, wenn die Batteriespannung VB zunimmt, d. h. wenn der völlig geladene Zustand fast erreicht wird. In der vorliegenden Ausführungsform wird eine Batterie mit einer Nennspannung von 24 Volt verwendet. 20 Fig. 13 is a view showing an example of the auxiliary map. In 20 For example, the battery voltage is set to the X axis and the vehicle speed to the Y axis and the correction coefficient to the Z axis. As in 20 2, the map is set so that the correction coefficient decreases in response to the battery voltage VB to decrease the regenerative duty ratio as the battery voltage VB increases, that is, when the fully charged state is almost reached. In the present embodiment, a battery having a rated voltage of 24 volts is used.
21 ist ein Flussdiagramm einer Steuerung/Regelung, welche die Batteriespannung VB und die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V berücksichtigt und die Schritte S12 bis S19 der 12 ersetzt. Insbesondere, wenn die Unterscheidung im Schritt S1 der 11 positiv ist, wird die Verarbeitung der 21 ausgeführt. Im Schritt S21 werden die Bremsschalterausgabe Vbr, die Batteriespannung VB und die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V erfasst. Im Schritt S22 wird das Hauptkennfeld verwendet, um eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer basierend auf der Differenz ΔVbr zwischen der Ausgangsspannung Vbr, welche durch die vorangehende arithmetische Operation erhalten wird, und der gegenwärtigen Ausgangsspannung Vbr oder der Ausgangsspannung Vbr und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V zu berechnen. 21 FIG. 14 is a flowchart of a control taking into account the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V, and steps S12 to S19 of FIG 12 replaced. In particular, if the distinction in step S1 of 11 is positive, the processing of the 21 executed. In step S21, the brake switch output Vbr, the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V are detected. In step S22, the main map is used to calculate a regenerative duty based on the difference ΔVbr between the output voltage Vbr obtained by the foregoing arithmetic operation and the present output voltage Vbr or the output voltage Vbr and the vehicle speed V.
Im Schritt S23 wird das Hilfskennfeld verwendet, um den Korrekturkoeffizienten basierend auf der Batteriespannung VB und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V zu berechnen. Im Schritt S24 wird die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer mit dem Korrekturkoeffizienten multipliziert, um die Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zu korrigieren. Im Schritt S25 wird die korrigierte Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer an den Antriebs/Regenerationstreiber 42 ausgegeben. Als ein Ergebnis wird ein regeneratives Bremsen unter Verwendung dieser Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer durchgeführt. Im Schritt S26 wird unterschieden, ob der Bremsschalter 51 an ist oder nicht. Solange der Bremsschalter 51 an bleibt, werden die Schritte S21 bis S25 ausgeführt, um die Regenerativ-Bremsung fortzusetzen. Wenn der Bremsschalter zu aus wechselt, geht die Verarbeitung zum Schritt 27 weiter, in welchem die Regenerativ-Bremsung gestoppt wird.In step S23, the auxiliary map is used to calculate the correction coefficient based on the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V. In step S24, the regenerative duty is multiplied by the correction coefficient to correct the regenerative duty. In step S25, the corrected regenerative duty is applied to the drive / regeneration driver 42 output. As a result, regenerative braking is performed by using this regenerative duty. In step S26, it is discriminated whether the brake switch 51 is on or not. As long as the brake switch 51 remains on, the steps S21 to S25 are executed to continue the regenerative braking. When the brake switch turns off, the processing goes to step 27 continue, in which the regenerative braking is stopped.
Zu bemerken ist, dass die Batteriespannung VB nicht als ein Parameter zur Berechnung eines Korrekturkoeffizienten für eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer verwendet werden kann, sondern direkt als ein Parameter zur Bestimmung einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer verwendet werden kann. Insbesondere ist das Kennfeld so ausgebildet, dass eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer als eine Funktion der Batteriespannung VB und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V ausgegeben wird. Wo das Kennfeld in dieser Weise ausgebildet ist, kann eine Regenerativ-Bremsung gemäß einer Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer durchgeführt werden, welche direkt mit der Batteriespannung VB und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V verbunden ist. 22 ist eine Ansicht, welche ein Beispiel des Kennfelds zeigt, welches derart ausgebildet ist, dass eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer als eine Funktion der Batteriespannung VB und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V ausgegeben wird.It should be noted that the battery voltage VB can not be used as a parameter for calculating a regenerative duty ratio correction coefficient, but can be directly used as a parameter for determining a regenerative duty ratio. In particular, the map is configured to output a regenerative duty as a function of the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V. Where the map is formed in this way, regenerative braking may be performed according to a regenerative duty, which is directly connected to the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V. 22 FIG. 12 is a view showing an example of the map that is configured to output a regenerative duty as a function of the battery voltage VB and the vehicle speed V. As shown in FIG.
Es ist im Übrigen möglich, umgekehrt zu dem oben Beschriebenen, einen Korrekturkoeffizienten zu berechnen, welcher eine Funktion der Bremsausgangsspannung Vbr oder des Ausgangsspannungsveränderungsbetrags ΔVbr und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit V ist und den Korrekturkoeffizienten zu verwenden, um eine Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer zu korrigieren, welche mit dem Kennfeld der 22 erhalten wird.Incidentally, conversely to the above, it is possible to calculate a correction coefficient which is a function of the brake output voltage Vbr or the output voltage change amount ΔVbr and the vehicle speed V and to use the correction coefficient to correct a regenerative duty corresponding to the map of the 22 is obtained.
Bei den oben beschriebenen Ausführungsformen wird eine Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung beschrieben, welche auf einen Antriebsmotor gerichtet ist, der in ein motorunterstütztes Fahrrad eingebaut ist. Jedoch ist die vorliegende Erfindung nicht darauf begrenzt, sondern kann bei einem motorbetriebenen Fahrzeug verwendet werden, welches mit elektrischer Energie läuft, ohne Anwendung von Tretkraft, um den Regenerationsbetrag in Antwort auf einen Veränderungsbetrag eines Betätigungsbetrags einer Bremse oder einer Batteriespannung zu steuern/regeln. Zusammenfassend ist es nur notwendig, dass das motorbetriebene Fahrzeug so ausgebildet ist, dass ein Umschalten zur Regeneration in Antwort auf eine Betätigung einer Bremse durchgeführt wird und der Regenerationsbetrag dann in Antwort auf die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit und den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag oder den Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags oder in Antwort auf die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit und die Batteriespannung bestimmt wird.In the above-described embodiments, a regenerative control apparatus directed to a drive motor installed in a motor-assisted bicycle will be described. However, the present invention is not limited thereto, but may be applied to a motor vehicle running on electric power without using pedaling force to control the regeneration amount in response to a change amount of an operation amount of a brake or a battery voltage. In summary, it is only necessary that the engine-operated vehicle is configured to perform a regeneration switching in response to an operation of a brake, and the regeneration amount is then responsive to the vehicle speed and the brake operation amount or the change amount of the brake operation amount or in response to the brake operation amount Vehicle speed and the battery voltage is determined.
Wie es aus der vorangehenden Beschreibung ersichtlich ist, verändert sich gemäß der in den Ansprüchen 1 bis 8 angegebenen Erfindung die Effizienz der Regenerativ-Bremsung in Antwort auf den Bremsbetätigungsbetrag. Insbesondere wird gemäß der in den Ansprüchen 2 bis 6 angegebenen Erfindung der Regenerationsbetrag so gesteuert/geregelt, dass ein größerer Regenerationsbetrag auf der Niedergeschwindigkeitsseite in Antwort auf die Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit erhalten wird. Folglich wird in einem Fahrzustand, in welchem eine Bremsbetätigung regelmäßig durchgeführt wird und eine rasche Bremsbetätigung wahrscheinlich beim Fahren in einer Stadt oder dgl. vorkommt, eine starke Regenerativ-Bremsung verwendet und die Batterie kann konstant mit durch die Regeneration erhaltenem Strom geladen werden. Ferner kann gemäß der im Anspruch 7 angegebenen Erfindung auf einem Abwärtsgefälle eine komfortable Fahrt und Ladung der Batterie durchgeführt werden durch eine Regenerativ-Bremsung ohne Durchführung einer Bremsbetätigung.As apparent from the foregoing description, according to the invention set forth in claims 1 to 8, the efficiency of the regenerative braking changes in response to the brake operation amount. More specifically, according to the invention set forth in claims 2 to 6, the regeneration amount is controlled so that a larger regeneration amount is obtained on the low-speed side in response to the vehicle speed. Consequently, in a driving state in which a brake operation is regularly performed and a quick brake operation is likely to occur when driving in a city or the like, a strong regenerative braking is used and the battery can be constantly charged with current obtained by the regeneration. Further, according to the invention defined in claim 7 on a downhill gradient, a comfortable ride and charge the battery can be performed by a regenerative braking without performing a brake application.
Ferner wird gemäß der in den Ansprüchen 3 und 8 angegebenen Erfindung in Antwort auf die Restkapazität der Batterie, welche durch die Regenerativ-Bremsung geladen wird, wenn die Batterierestkapazität hoch ist, ein kleiner Regenerationsbetrag erhalten. Folglich wird, wenn die Batterie in einem Zustand ist, welcher einem vollgeladenen Zustand nahe liegt, eine geringe regenerative Ladung durchgeführt, aber wenn die Batterierestkapazität gering ist, wird eine regenerative Ladung mit einem hohen Regenerationsbetrag durchgeführt. Folglich kann eine effiziente regenerative Ladung erreicht werden und ein Überladen kann verhindert werden, um die Lebensdauer der Batterie zu verlängern. Ferner kann ebenso ein Energieverlust durch verschwenderisches Laden verhindert werden.Further, according to the invention recited in claims 3 and 8, in response to the remaining capacity of the battery charged by the regenerative braking when the remaining battery capacity is high, a small regeneration amount is obtained. Consequently, when the battery is in a state close to a fully charged state, a small regenerative charge is performed, but when the remaining battery capacity is small, a regenerative charge having a high regeneration amount is performed. As a result, an efficient regenerative charge can be achieved and overcharging can be prevented to prolong the life of the battery. Further, energy loss due to wasteful charging can also be prevented.
Ferner wird abweichend von der Konfiguration jene regenerative Ladung durchgeführt, wenn die Batterierestkapazität kleiner als ein vorbestimmter Betrag ist, und ein der verbleibenden Kapazität entsprechender Regenerationsbetrag erhalten. Daher zeigt die Regenerativ-Bremskraft eine moderate Veränderung und ein gutes Fahrgefühl kann erhalten werden.Further, unlike the configuration, that regenerative charge is performed when the remaining battery capacity is smaller than a predetermined amount, and a regeneration amount corresponding to the remaining capacity is obtained. Therefore, the regenerative braking force shows a moderate change and a good driving feeling can be obtained.
Ziel: Effektiv eine Regenerationsfunktion während des Fahrens auszunutzen, das regelmäßige Start- und Stoppvorgänge, wie z. B. beim Fahren in einer Stadt, umfasst, um eine effiziente Energierückgewinnung zu erreichen.Objective: Effectively use a regeneration function while driving, the regular start and stop operations, such. When driving in a city, in order to achieve efficient energy recovery.
Mittel zur Lösung: Die Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung ist für ein motorbetriebenes Fahrzeug mit einer Bremse, welche auf die Bremsen des Fahrzeugs eine Kraft ausübt, welche einem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag entspricht. Ein Bremsschalter 51 gibt ein Bremssignal aus, welches dem Bremsbetätigungsbetrag entspricht. Die Regenerativsteuer/regelvorrichtung umfasst Umschaltmittel zum Umschalten eines Motors zu der Regenerationsseite in Antwort auf eine Bremsbetätigung, welche aus dem Bremssignal erkannt wird. Ein Betätigungsbetragveränderungsbetragerfassungsabschnitt 53 gibt einen Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags aus und ein Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 bestimmt einen Regenerationsbetrag (Regenerativ-Einschaltdauer) in Antwort auf den Veränderungsbetrag. Das Regenerativ-Einschaltdauerkennfeld 52 kann so ausgebildet sein, dass es einen Regenerationsbetrag als eine Funktion des Veränderungsbetrags des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags und der Fahrzeuggeschwindigkeit ausgibt. Insbesondere wird der Regenerationsbetrag so bestimmt, dass er zunimmt, wenn der Veränderungsbetrag des Bremsbetätigungsbetrags zunimmt.Means for Resolving: The regenerative control device is for a motor vehicle having a brake which applies to the brakes of the vehicle a force corresponding to a brake operation amount. A brake switch 51 outputs a brake signal corresponding to the brake operation amount. The regenerative control device includes switching means for switching a motor to the regeneration side in response to a brake operation detected from the brake signal. An operation amount change amount detection section 53 outputs a change amount of the brake operation amount and a regenerative duty map 52 determines a regeneration amount (regenerative duty) in response to the amount of change. The regenerative duty cycle map 52 may be configured to output a regeneration amount as a function of the amount of change of the brake operation amount and the vehicle speed. Specifically, the regeneration amount is determined to increase as the amount of change of the brake operation amount increases.