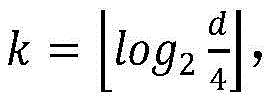CN113143284A - Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction - Google Patents
Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113143284A CN113143284A CN202110395294.2A CN202110395294A CN113143284A CN 113143284 A CN113143284 A CN 113143284A CN 202110395294 A CN202110395294 A CN 202110395294A CN 113143284 A CN113143284 A CN 113143284A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- prediction
- coding
- coefficient
- wavelet
- mode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7232—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes involving compression of the physiological signal, e.g. to extend the signal recording period
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A61B5/7253—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms
- A61B5/726—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms using Wavelet transforms
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
An electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction, comprising the following steps: first step, signal decomposition: performing first-level lifting wavelet transformation on a sampling signal of the electrocardiogram information to obtain high-frequency coefficients and low-frequency coefficients with the same quantity, removing the high-frequency coefficients and reserving the low-frequency coefficients; step two, scaling and smoothing: carrying out division scaling and smoothing operation on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficient; and thirdly, prediction: predicting the coefficient by adopting a method of combining linear prediction and template prediction to obtain a prediction error; step four, encoding: applying a secondary golomb-rice coding mode to the prediction error for coding; fifthly, packaging: the encoded values are packed together with the information needed for prediction to form the final compressed data stream. The invention realizes higher compression effect under lower distortion rate, and is suitable for wearable electrocardiogram monitoring equipment.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the field of biomedical information processing, in particular to an electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction
Background
With the development of science and technology and the improvement of human life quality, people pay more and more attention to their health conditions, and the global medical expenses also increase year by year. Meanwhile, the aging is getting more and more people need to take care of in real time, and the demand for medical resources is increasing. This set of social problems has greatly facilitated the rapid development of remote wearable health monitoring devices. Wearable remote medical equipment is through real-time supervision for patient in case produce the sick trend, just can take corresponding measure to deal with at the state of an illness development initial stage, has greatly reduced the probability that the state of an illness further worsens, and simultaneously, patient also can accomplish each item medical action just not enough to go home, need not regularly to come and go the hospital and do medical examination, has saved a large amount of time and economic cost. In recent years, with the rapid development of the internet of things and wireless communication, wearable remote medical equipment with the advantages of low cost, high efficiency and the like is applied, the labor cost is greatly reduced, and the method has important significance for the development of modern medical treatment.
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is an important physiological signal of a human body, records various physiological activities of the heart of the human body by taking time as a unit, can reflect the rhythm of the heart and physiological information of electric conduction of the heart, can objectively reflect the physiological conditions of various parts of the heart, and is widely applied to diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. The wearable electrocardio equipment can monitor electrocardiosignals of a human body for a long time, is used for diagnosing and preventing possible cardiovascular diseases, and has obvious advantages compared with clinical examination and diagnosis. In order to deal with sudden heart diseases, electrocardiosignals need to be collected uninterruptedly for a long time, so that great pressure is caused on the transmission and storage of the electrocardiosignals, and in wearable electrocardio monitoring equipment, the power consumption occupied by wireless transmission exceeds 70%, so that the compression of the electrocardiosignals becomes particularly important.
Disclosure of Invention
In order to overcome the defects of the prior art, the invention provides an electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction, which compresses electrocardiosignals based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction, realizes higher compression ratio, simultaneously reserves most effective information, ensures that the distortion degree of the electrocardiosignals after the compressed signals are reconstructed is smaller, and can finish the diagnosis of various heart diseases.
The invention can be realized by the following technical scheme:
an electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction, comprising the following steps:
first step, signal decomposition: performing first-level lifting wavelet transformation on a sampling signal of the electrocardiogram information to obtain high-frequency coefficients and low-frequency coefficients with the same quantity, removing the high-frequency coefficients and reserving the low-frequency coefficients;
step two, scaling and smoothing: carrying out division scaling and smoothing operation on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficient;
and thirdly, prediction: predicting the coefficient by adopting a method of combining linear prediction and template prediction to obtain a prediction error;
step four, encoding: applying a secondary golomb-rice coding mode to the prediction error for coding;
fifthly, packaging: the encoded values are packed together with the information needed for prediction to form the final compressed data stream.
Further, in the first step, 5/3 lifting wavelet transform is adopted in the wavelet transform, and low-frequency coefficients are retained, and the expression is as follows:
in the formula, X2 n +1 and X2 n are odd-even two sequences obtained by splitting input signal X n, d n is high-frequency wavelet coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, s n is low-frequency scale coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, when calculating high-frequency coefficient d n, it is necessary to obtain value X2 n +1 of odd sequence and values X2 n and X2 n +2 of two even sequences before and after odd sequence at the same time for calculation, when calculating low-frequency coefficient s n, it is necessary to obtain value X2 n of even sequence and values of two high-frequency coefficients d n and d n-1 before and after even sequence.
Further, in the second step, the division scaling and smoothing operations on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficient are as follows: to pairZooming the low-frequency signal to obtain electrocardiosignals with different signal qualities, smoothing wavelet coefficients, and continuously processing three wavelet coefficients x1、x2、x3If x is satisfied1=x3,|x2-x11 then x2=x1I.e. the middle point is considered as a spur, the value is modified to be equal to the previous and subsequent values.
In the third step, the dual-mode prediction adopts a mode of combining linear prediction and template prediction, 0-order linear prediction is adopted for a non-QRS region of the electrocardiosignal, and template prediction and 2-order linear prediction are adopted for a QRS region.
In the fourth step, the second-level golomb-rice coding mode is used for coding, and the size of the parameter k is closely related to the coding efficiency, namely k isOrThe code length of time coding is minimum, m is a value to be coded, the value of the parameter k is predicted before the golomb-rice coding is carried out, so that higher coding efficiency is obtained, and the formula of prediction is represented as: where d is a temporary variable and the initial value is 64.
And in the fourth step, coding the prediction error by applying a two-stage golomb-rice coding mode, in order to improve the golomb-rice coding algorithm to ensure that the compression performance is better, adding a prefix code '1110', for codes with quotient values more than or equal to 3 and less than 8, adding a bit '1' before unary coding of the quotient values, after continuous data 0 appears, coding the segment by using the prefix code and matching with self-defined run coding, and when a QRS interval or continuous data 0 appears, using the prefix code and looking up the table again.
The template prediction is: and for the coefficient of each QRS interval, predicting by using the value in the existing QRS template, selecting the closest one from different templates for prediction, simultaneously comparing with the value obtained by applying 3-order linear prediction, and selecting the result with the minimum error as the final prediction result.
Further, in the fifth step, the prediction error is encoded by applying a two-level golomb-rice encoding method, and is packed with information required for prediction to form a final compressed data stream, which includes encoding and data packing, the prediction error is encoded by using a two-level golomb-rice encoding obtained by improving based on a golomb-rice encoding algorithm, and a signal encoding value and information required for decoding are packed together.
Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following advantages:
(1) the invention provides an electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction, which realizes higher electrocardiosignal compression ratio under lower distortion degree and simultaneously supports various compression grades to adapt to different application scenes.
(2) 5/3 lifting wavelet transform is applied to process signals, the data correlation lifting compression rate is reduced, meanwhile, 5/3 lifting wavelet transform only needs simple addition operation, and compared with the traditional wavelet which needs a large number of multiplication operations, the method has lower operation complexity
(3) The wavelet coefficient is divided into a QRS area and a non-QRS area, for the non-QRS area, a linear prediction method is adopted for prediction, and for the QRS area, a method combining linear prediction and template prediction is adopted for prediction, so that the correlation among data is further reduced to realize higher compression ratio.
(4) A novel coding mode, namely secondary golomb-rice coding, is designed, different characteristic regions are separately coded, and then a better compression effect is obtained compared with other coding modes.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a flow chart of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is an experimental effect diagram based on the MIT-BIH database, where (a) is an original electrocardiographic sampling signal, (b) is a high-frequency coefficient obtained after lifting wavelet transform, (c) is a low-frequency coefficient obtained after lifting wavelet transform, (d) is a value obtained after scaling the low-frequency coefficient, (e) is a value obtained by further performing smoothing operation on the scaled coefficient, and (f) is a prediction error value obtained by performing dual-mode prediction on the smoothed coefficient.
Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a data packaging form.
Detailed Description
In order to make the technical solution of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described more fully with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples. The practice of the present invention includes the following examples but is not limited thereto. All other embodiments, which can be derived by a person skilled in the art from the embodiments given herein without making any creative effort, shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
Referring to fig. 1 to 3, a specific flow of a method for compressing cardiac information based on wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction is shown in fig. 1, and the method includes the following steps:
firstly, decomposing an electrocardiosignal sampling value by using 5/3 lifting wavelets, specifically, dividing an electrocardiosignal sampling sequence X [ n ] into two odd-even sequences X [2n +1] and X [2n ], wherein n is a positive integer greater than or equal to 1, converting the two sequences into a low-frequency coefficient and a high-frequency coefficient through a formula, and expressing the conversion formula as follows:
in the formula, X2 n +1 and X2 n are odd-even two sequences obtained by splitting input signal X n, d n is high-frequency wavelet coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, s n is low-frequency scale coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, when calculating high-frequency coefficient d n, it is necessary to obtain value X2 n +1 of odd sequence and values X2 n and X2 n +2 of two even sequences before and after odd sequence at the same time for calculation, when calculating low-frequency coefficient s n, it is necessary to obtain value X2 n of even sequence and values of two high-frequency coefficients d n and d n-1 before and after even sequence.
Secondly, the low-frequency coefficient obtained by decomposition is scaled, namely the coefficient is divided, different divisors are selected to be 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 according to different application scenes, so that the realization of an actual circuit is facilitated, the scaled value is further smoothed to increase the final compression ratio, and three continuous wavelet coefficients x are subjected to smoothing operation to increase the final compression ratio1、x2、x3If x is satisfied1=x3And | x2-x1If 1, then x2=x1. Namely, the intermediate point is regarded as a burr, and the value is modified to be equal to the front and rear values, so that the coefficient change after wavelet transformation is smoother, and the subsequent prediction is facilitated.
Thirdly, predicting the smoothed wavelet coefficient, wherein the process is as follows:
and (3) predicting the non-QRS interval by adopting a 0-order linear prediction method, namely predicting the value of each wavelet coefficient by using the previous coefficient, and reserving a prediction error value, namely a difference value obtained by subtracting the previous coefficient from the current coefficient.
Detecting the position of QRS interval by using R peak detection algorithm, when the electrocardiosignal sample enters the QRS area, starting to predict the low-frequency coefficient by using a method combining template prediction and 2-order linear prediction, and setting the number of templates as NtFor the electrocardiosignal with the sampling frequency f, the number of the corresponding low-frequency wavelet coefficients in the QRS interval is WqrsF/20, so the length of the die plate is WqrsI.e. the number of coefficients that can be predicted per template, the initial value is 0.
Specifically, the prediction needs to be at N firsttSelecting a predictor which minimizes the sum of absolute values of prediction errors of all coefficients in a QRS interval from the template predictors and the 1 second-order linear predictor, wherein the formula of the second-order linear prediction is expressed as follows:
wherein x [ n-1]]、x[n-2]、x[n-3]Respectively the three past coefficient values, and finding all W in the QRS intervalqrsThe predicted values of the coefficients are subtracted from the original values to obtain WqrsAnd the prediction error values are summed to obtain a prediction error sum. Then using all NtPredicting the current QRS interval value by the value stored by the template predictor and respectively solving NtA sum of prediction errors, adding NtSum of prediction errors and sum of errors of second-order linear predictor total NtAnd comparing the +1 values, selecting the predictor with the minimum prediction error sum, and predicting the coefficient value of the current QRS interval. And when each round of QRS interval prediction is completed, updating the template which is updated earliest by using all coefficient values of the current QRS interval.
Fourthly, coding the prediction error, firstly mapping the integer prediction error into a non-negative integer m, then carrying out secondary golomb-rice coding on the mapping value, and predicting the value of the parameter k before carrying out the golomb-rice coding, thereby obtaining higher coding efficiency, wherein the formula of prediction is expressed asAndthe initial value of d is 64, and the coding scheme is as follows:
1. for data with non-0 value or continuous 0 value and less than 8, the coding form of each data is conventional golomb-rice coding, and the range is obtained according to different quotient values and the corresponding number of bits '1' is added before unary coding.
2. For fragments with a number of consecutive "0" greater than or equal to 8, we encode the whole fragment in the form of "1110" + the golomb-rice code value for the number of data of the fragment.
The fifth step is toThe encoded values are encapsulated, and the encapsulated data includes all information required for decoding, and the specific form is shown in fig. 3, wherein the value of t is log2(Nt+1). Firstly, the binary coding of the first three wavelet coefficients is encapsulated, and the subsequent prediction can be carried out according to the first three values during decoding. And then packaging each electrocardio cycle according to the sequence of the error codes of the non-QRS interval, the QRS indicating codes, the QRS template indexes and the error codes of the QRS interval, thereby realizing real-time coding and decoding. There is a coding of multiple consecutive 0 value segments indicated by prefix code "1110" at each non-QRS interval and QRS interval simultaneously.
While the invention has been described with reference to the preferred embodiments, it is to be understood that the invention is not limited thereto and that the invention is not limited to the disclosed embodiments.
Claims (8)
1. An electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction is characterized by comprising the following steps:
first step, signal decomposition: performing first-level lifting wavelet transformation on a sampling signal of the electrocardiogram information to obtain high-frequency coefficients and low-frequency coefficients with the same quantity, removing the high-frequency coefficients and reserving the low-frequency coefficients;
step two, scaling and smoothing: carrying out division scaling and smoothing operation on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficient;
and thirdly, prediction: predicting the coefficient by adopting a method of combining linear prediction and template prediction to obtain a prediction error;
step four, encoding: applying a secondary golomb-rice coding mode to the prediction error for coding;
fifthly, packaging: the encoded values are packed together with the information needed for prediction to form the final compressed data stream.
2. The wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction based electrocardiosignal compression method as claimed in claim 1, wherein in the first step, 5/3 lifting wavelet transform is adopted in the wavelet transform, low-frequency coefficients are retained, and the expression is as follows:
wherein, X2 n +1 and X2 n are odd-even two sequences obtained by splitting input signal X n, d n is high frequency wavelet coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, s n is low frequency scale coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, when calculating high frequency coefficient d n, it needs to obtain the value X2 n +1 of odd sequence and the values X2 n and X2 n +2 of two even sequences before and after the odd sequence at the same time for calculation, when calculating low frequency coefficient s n, it needs to obtain the value X2 n of even sequence and the values of two high frequency coefficients d n and d n-1 before and after the even sequence.
3. The wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction based electrocardiographic signal compression method according to claim 1 or 2, wherein in the second step, the division scaling and smoothing operations on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficients are as follows: zooming the low-frequency signal to obtain electrocardiosignals with different signal qualities, smoothing wavelet coefficients, and continuously processing three wavelet coefficients x1、x2、x3If x is satisfied1=x3,|x2-x11 then x2=x1I.e. the middle point is considered as a spur, the value is modified to be equal to the previous and subsequent values.
4. The wavelet transform and bi-mode prediction based electrocardiosignal compression method as claimed in claim 1 or 2, wherein in the third step, the bi-mode prediction adopts a mode of combining linear prediction and template prediction, 0-order linear prediction is adopted for the non-QRS region of the electrocardiosignal, and template prediction and 2-order linear prediction are adopted for the QRS region.
5. The wavelet transform and bi-mode prediction based electrocardiosignal compression method as claimed in claim 1 or 2, wherein in the fourth step, the second-level golomb-rice coding mode is adopted for coding, and the size of the parameter k is closely related to the coding efficiency, namely k isOrThe code length of time coding is minimum, m is a value to be coded, the value of the parameter k is predicted before the golomb-rice coding is carried out, so that higher coding efficiency is obtained, and the formula of prediction is represented as: where d is a temporary variable and the initial value is set to 64.
6. The wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction-based electrocardiosignal compression method according to claim 5, wherein in the fourth step, the prediction error is encoded by applying a two-level golomb-rice coding method, so as to improve the golomb-rice coding algorithm and make the compression performance better, a prefix code "1110" is added, for the codes with quotient more than or equal to 3 and less than 8, a bit "1" needs to be added before unary coding of quotient, when continuous data 0 appears, the prefix code is used and then matched with custom run-length coding to encode the segment, and when a QRS interval or continuous data 0 appears, the prefix code and look-up table again need to be used.
7. The wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction based electrocardiograph signal compression method according to claim 4, wherein the template prediction is: and for the coefficient of each QRS interval, predicting by using the value in the existing QRS template, selecting the closest one from different templates for prediction, simultaneously comparing with the value obtained by applying 3-order linear prediction, and selecting the result with the minimum error as the final prediction result.
8. The wavelet transform and dual-mode prediction-based electrocardiosignal compression method according to claim 4, wherein in the fifth step, the prediction error is encoded by applying a two-level golomb-rice coding method, and is packed with the information required for prediction to form a final compressed data stream, which comprises encoding and data packing, the prediction error is encoded by using a two-level golomb-rice coding obtained by improving based on the golomb-rice coding algorithm, and the signal encoding value and the information required for decoding are packed together.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2A CN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2A CN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113143284A true CN113143284A (en) | 2021-07-23 |
| CN113143284B CN113143284B (en) | 2022-10-21 |
Family
ID=76890297
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2A Active CN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113143284B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024216514A1 (en) * | 2023-04-18 | 2024-10-24 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data compression method, data decompression method, and related apparatus |
Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1874162A (en) * | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-06 | 奥林巴斯映像株式会社 | Data encoding apparatus and data encoding method |
| CN1893659A (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2007-01-10 | 高通股份有限公司 | DCT compression using Golomb-Rice coding |
| CN101268936A (en) * | 2008-02-27 | 2008-09-24 | 天津大学 | Electrocardio-compression method and decrypting method of wireless cardiogram monitor |
| CN101404772A (en) * | 2008-11-19 | 2009-04-08 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | VLSI image compression encoder based on wavelet transformation |
| CN101572814A (en) * | 2008-04-29 | 2009-11-04 | 合肥坤安电子科技有限公司 | Secondary run length encoding method |
| CN102323977A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市吉天通信科技有限公司 | Electrocardio data storage method based on electrocardio characteristic points |
| CN102368385A (en) * | 2011-09-07 | 2012-03-07 | 中科开元信息技术(北京)有限公司 | Backward block adaptive Golomb-Rice coding and decoding method and apparatus thereof |
| CN103908243A (en) * | 2014-04-01 | 2014-07-09 | 南京普澳医疗设备有限公司 | Lifting wavelet and median filter combined algorithm |
| CN104000579A (en) * | 2014-06-11 | 2014-08-27 | 复旦大学 | Multifunctional electrocardiosignal processing SoC chip for remote medical monitoring |
| CN104159108A (en) * | 2014-08-11 | 2014-11-19 | 浙江大学 | Real-time lossless electrocardiosignal compression method and device based on adaptive prediction and variable length coding improvement |
| TW201622644A (en) * | 2014-12-16 | 2016-07-01 | 凌陽科技股份有限公司 | Method of compressing electrocardiography signal and electrocardiography signal sensing apparatus thereof |
| TWI662948B (en) * | 2018-08-10 | 2019-06-21 | 國立中央大學 | Ecg signals lossless compression system and its method |
| US10547843B1 (en) * | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-28 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Prefix coding method for high-throughput entropy coder in display interface compression |
| CN112134567A (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2020-12-25 | 北京航空航天大学 | Self-adaptive real-time compression method and system for absorption spectrum data |
-
2021
- 2021-04-13 CN CN202110395294.2A patent/CN113143284B/en active Active
Patent Citations (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1893659A (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2007-01-10 | 高通股份有限公司 | DCT compression using Golomb-Rice coding |
| CN1874162A (en) * | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-06 | 奥林巴斯映像株式会社 | Data encoding apparatus and data encoding method |
| US20060273937A1 (en) * | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-07 | Takashi Ishikawa | Data encoding apparatus, data encoding method, and recording medium recorded with program |
| CN101268936A (en) * | 2008-02-27 | 2008-09-24 | 天津大学 | Electrocardio-compression method and decrypting method of wireless cardiogram monitor |
| CN101572814A (en) * | 2008-04-29 | 2009-11-04 | 合肥坤安电子科技有限公司 | Secondary run length encoding method |
| CN101404772A (en) * | 2008-11-19 | 2009-04-08 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | VLSI image compression encoder based on wavelet transformation |
| CN102323977A (en) * | 2011-06-29 | 2012-01-18 | 无锡市吉天通信科技有限公司 | Electrocardio data storage method based on electrocardio characteristic points |
| CN102368385A (en) * | 2011-09-07 | 2012-03-07 | 中科开元信息技术(北京)有限公司 | Backward block adaptive Golomb-Rice coding and decoding method and apparatus thereof |
| CN103908243A (en) * | 2014-04-01 | 2014-07-09 | 南京普澳医疗设备有限公司 | Lifting wavelet and median filter combined algorithm |
| CN104000579A (en) * | 2014-06-11 | 2014-08-27 | 复旦大学 | Multifunctional electrocardiosignal processing SoC chip for remote medical monitoring |
| CN104159108A (en) * | 2014-08-11 | 2014-11-19 | 浙江大学 | Real-time lossless electrocardiosignal compression method and device based on adaptive prediction and variable length coding improvement |
| TW201622644A (en) * | 2014-12-16 | 2016-07-01 | 凌陽科技股份有限公司 | Method of compressing electrocardiography signal and electrocardiography signal sensing apparatus thereof |
| US10547843B1 (en) * | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-28 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Prefix coding method for high-throughput entropy coder in display interface compression |
| TWI662948B (en) * | 2018-08-10 | 2019-06-21 | 國立中央大學 | Ecg signals lossless compression system and its method |
| US20200046298A1 (en) * | 2018-08-10 | 2020-02-13 | National Central University | Ecg signal lossless compression system and method for same |
| CN112134567A (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2020-12-25 | 北京航空航天大学 | Self-adaptive real-time compression method and system for absorption spectrum data |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| JIANHUA CHEN: "A Wavelet-Based EGG Compression Algorithm Using Golomb Codes", 《INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMMUNICATIONS, CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS》 * |
| KRZYSZTOF DUDA: "Lossless ECG Compression with Lifting Wavelet Transform", 《IEEE INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE》 * |
| 徐焕章: "编码精度自调节的心电压缩ASIC", 《传感器与微系统》 * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024216514A1 (en) * | 2023-04-18 | 2024-10-24 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data compression method, data decompression method, and related apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113143284B (en) | 2022-10-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI494081B (en) | Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system | |
| Zigel et al. | ECG signal compression using analysis by synthesis coding | |
| Padhy et al. | Multilead ECG data compression using SVD in multiresolution domain | |
| Pandey et al. | Quality controlled ECG data compression based on 2D discrete cosine coefficient filtering and iterative JPEG2000 encoding | |
| Jha et al. | Electrocardiogram data compression techniques for cardiac healthcare systems: A methodological review | |
| Tiwari et al. | Lossless electrocardiogram signal compression: A review of existing methods | |
| Manikandan et al. | Wavelet threshold based TDL and TDR algorithms for real-time ECG signal compression | |
| Ahmeda et al. | A new hybrid algorithm for ECG signal compression based on the wavelet transformation of the linearly predicted error | |
| El B’charri et al. | The ECG signal compression using an efficient algorithm based on the DWT | |
| Kumar et al. | Electrocardiogram signal compression based on 2D-transforms: a research overview | |
| CN113143284B (en) | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction | |
| Rzepka | Low-complexity lossless multichannel ECG compression based on selective linear prediction | |
| Alam et al. | Zonal complexity based measure for lossy compression of photoplethysmogram using delta encoding | |
| Tsai et al. | VLSI implementation of multi-channel ECG lossless compression system | |
| Tsai et al. | Efficient lossless compression scheme for multi-channel ECG signal | |
| Ben-Romdhane et al. | Event-driven ECG sensor in healthcare devices for data transfer optimization | |
| Kim et al. | A low cost quadratic level ECG compression algorithm and its hardware optimization for body sensor network system | |
| Gupta et al. | An ECG compression technique for telecardiology application | |
| Zigel et al. | A diagnostic meaningful distortion measure for ECG compression | |
| Moses et al. | A novel lossless ECG compression technique for transmission in GSM networks | |
| Abdali-Mohammadi | 12 lead electrocardiography signals compression by a new genetic programming based mathematical modeling algorithm | |
| Lai et al. | An efficient method of ECG signal compression by using a DCT-IV spectrum | |
| El Hanine et al. | Lossless Compression Technique For ECG Signals Using A-law Companding Algorithm | |
| Baliarsingh et al. | ECG Compression using Decomposed Transform for E-Healthcare | |
| Baliarsingh et al. | An optimal transform based technique for ECG signal compression |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |