CN111148706A - Conveying device and conveying method - Google Patents
Conveying device and conveying method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111148706A CN111148706A CN201880039044.1A CN201880039044A CN111148706A CN 111148706 A CN111148706 A CN 111148706A CN 201880039044 A CN201880039044 A CN 201880039044A CN 111148706 A CN111148706 A CN 111148706A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- workpiece
- conveyance
- conveying
- detection
- guide
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B57/00—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices
- B65B57/10—Automatic control, checking, warning, or safety devices responsive to absence, presence, abnormal feed, or misplacement of articles or materials to be packaged
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G43/00—Control devices, e.g. for safety, warning or fault-correcting
- B65G43/08—Control devices operated by article or material being fed, conveyed or discharged
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G47/00—Article or material-handling devices associated with conveyors; Methods employing such devices
- B65G47/22—Devices influencing the relative position or the attitude of articles during transit by conveyors
- B65G47/24—Devices influencing the relative position or the attitude of articles during transit by conveyors orientating the articles
- B65G47/256—Devices influencing the relative position or the attitude of articles during transit by conveyors orientating the articles removing incorrectly orientated articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G47/00—Article or material-handling devices associated with conveyors; Methods employing such devices
- B65G47/74—Feeding, transfer, or discharging devices of particular kinds or types
- B65G47/88—Separating or stopping elements, e.g. fingers
- B65G47/8807—Separating or stopping elements, e.g. fingers with one stop
- B65G47/883—Fixed stop
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G2201/00—Indexing codes relating to handling devices, e.g. conveyors, characterised by the type of product or load being conveyed or handled
- B65G2201/02—Articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G2203/00—Indexing code relating to control or detection of the articles or the load carriers during conveying
- B65G2203/02—Control or detection
- B65G2203/0208—Control or detection relating to the transported articles
- B65G2203/0233—Position of the article
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G2203/00—Indexing code relating to control or detection of the articles or the load carriers during conveying
- B65G2203/04—Detection means
- B65G2203/042—Sensors
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Specific Conveyance Elements (AREA)
- Control Of Conveyors (AREA)
- Attitude Control For Articles On Conveyors (AREA)
Abstract
The invention provides a conveying device, a boxing device and a conveying method, which can convey a subsequently conveyed workpiece without interfering with the workpiece even when the posture and the position of the workpiece are changed. When the end-side sensor detects that the workpiece is not present at the detection position at the timing when the workpiece is conveyed to the detection position, the control unit determines that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal.
Description
Technical Field
The present invention relates to a conveying apparatus for conveying a workpiece by a conveying mechanism and a conveying method for conveying a workpiece by a conveying mechanism.
Background
Conventionally, there has been proposed a device for placing a rice ball in a box without relying on manual work by holding the rice ball and housing the held rice ball in the box. As such a device, for example, there is a device disclosed in patent document 1. In patent document 1, when the rice ball is conveyed to a predetermined position, the rice ball is held by the device, and the device moves the held rice ball into the box.
Patent document 1, Japanese patent application laid-open No. 2011-251702
However, before a workpiece such as a rice ball is conveyed to a held position, the workpiece may change its posture or position for some reason. When the posture and position are greatly changed, the apparatus may not hold the workpiece. Further, when the apparatus cannot hold the workpiece, there is a possibility that the workpiece cannot be disposed in the box.
If the workpiece with the changed posture is left at the position held by the holding portion of the apparatus as it is, the workpiece to be transported next becomes an obstacle, and there is a possibility that the workpiece to be transported next cannot be transported to the position held by the holding portion. Further, if the next workpiece cannot be conveyed to the position held by the holding portion, the apparatus cannot hold the next workpiece, and therefore there is a possibility that the subsequent workpiece cannot be disposed in the magazine.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above circumstances, an object of the present invention is to provide a conveying apparatus, a boxing apparatus, and a conveying method, which are capable of conveying a workpiece to be conveyed subsequently without interfering with the workpiece even when the posture or position of the workpiece is changed.
The conveying device of the present invention is characterized by comprising: a conveying mechanism for conveying a workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle; a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, the stopper being disposed such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or greater than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece; a 1 st detection unit that detects whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing unit; and a 1 st determination unit configured to determine that there is an abnormality in conveyance of the workpiece when the 1 st detection unit detects that the workpiece is not present at the detection position at a timing when the workpiece is conveyed to the detection position.
In the conveying device having the above-described configuration, when the workpiece is not conveyed to the detection position detected by the 1 st detection means in the normal position and posture, the detection of the workpiece can be performed, and therefore the workpiece that is not conveyed in the normal position and posture can be removed from the conveying path of the conveying means. Therefore, the workpiece that is not conveyed in the normal position or posture can be prevented from remaining on the conveying path and interfering with the next conveyed workpiece, and the continuous conveyance of the workpieces can be efficiently performed.
Further, the workpiece detecting device may include a passage detecting means for detecting passage of the workpiece at a trigger position on an upstream side of the conveying means in a conveying direction from the detection position, and the timing may be a time after passage of a time taken for the workpiece to be conveyed from the trigger position to the detection position from the detection of passage at the trigger position by the passage detecting means.
When the 1 st detecting means detects that there is no workpiece at the detection position at a timing when the time taken for the workpiece to be conveyed from the trigger position to the detection position has elapsed since the passage of the workpiece at the trigger position is detected by the passage detecting means, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpiece. Therefore, whether the conveyance of the workpiece is performed normally can be reliably detected.
Further, a conveying device according to the present invention includes: a conveying mechanism for conveying a workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle; a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and arranged such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or larger than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece; a 1 st detection unit that detects whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing unit; a 2 nd detection means for detecting whether or not the workpiece is retained at a retention position on an upstream side of the 1 st detection means; and a 2 nd determination unit configured to determine that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal when the 1 st detection unit detects that the workpiece is not present at the detection position and the 2 nd detection unit detects that the workpiece is retained at the retention position.
In the conveying apparatus having the above-described configuration, when the workpiece is retained at the retaining position detected by the 2 nd detection means, the retaining position can be detected, and therefore the workpiece retained in the conveying path of the conveying means can be removed from the conveying path. Therefore, the workpiece retained in the conveyance path can be prevented from remaining in the conveyance path as it is and interfering with the next conveyed workpiece, and the continuous conveyance of the workpieces can be efficiently performed.
Further, the retention position may be located upstream of the detection position and apart from the workpiece by at least a length of the workpiece along the conveying direction.
The retention position is located upstream of the detection position and at least apart from the workpiece by the length in the conveying direction, and therefore, when the workpiece is retained, the retention position can be reliably detected.
Further, the workpiece may have a triangular prism shape having 3 acute angle portions.
Since the workpiece has a triangular prism shape, the workpiece easily enters the region sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing portion, and the presence or absence of the workpiece at the detection position by the 1 st detection means can be reliably detected.
Further, the workpiece conveying device may further include a stopper moving mechanism that moves the stopper from a stop position at which the pressing portion stops conveying the workpiece to a conveying position at which the pressing portion does not stop conveying the workpiece.
Since the stopper is moved by the stopper moving mechanism from the stop position at which the conveyance of the workpiece is stopped to the conveyance position at which the conveyance of the workpiece is not stopped, when it is determined that there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpiece, it is possible to suppress the workpiece from being conveyed to the downstream side of the conveyance path and interfering with the workpiece conveyed next.
Further, when it is determined that there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpiece, the workpiece may be disposed in a retreat portion retreated from a conveyance path of the conveyance mechanism.
When it is determined that there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpiece, the workpiece is disposed in the retreat portion retreated from the conveyance path of the conveyance mechanism, and therefore, the workpiece can be prevented from remaining in the conveyance path as it is and interfering with the workpiece to be conveyed next.
Further, a conveying method according to the present invention is a conveying method for conveying a workpiece using a conveying device, the conveying device including: a conveying mechanism that conveys the workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle; a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; and a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and disposed such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or greater than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece, the conveyance method including: a 1 st detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing portion; and a 1 st determination step of determining that there is an abnormality in conveyance of the workpiece when it is detected in the 1 st detection step that the workpiece is not present at the detection position at a timing when the workpiece is conveyed to the detection position.
In the conveying method having the above configuration, when the position or posture of the workpiece is abnormal at the detection position, it is determined that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal in the first determination step 1, and therefore, in this case, the workpiece that has not been conveyed in the normal position or posture can be removed from the conveyance path of the conveying mechanism. Therefore, the workpiece that is not conveyed in the normal position or posture can be prevented from remaining on the conveying path and interfering with the next conveyed workpiece, and the continuous conveyance of the workpieces can be efficiently performed.
Further, a conveying method according to the present invention is a conveying method for conveying a workpiece using a conveying device, the conveying device including: a conveying mechanism that conveys the workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle; a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; and a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and disposed such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or greater than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece, the conveyance method including: a 1 st detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing portion; a 2 nd detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is retained at a retention position on an upstream side of the detection position; and a 2 nd determination step of determining that there is an abnormality in conveyance of the workpiece when it is detected in the 1 st detection step that the workpiece is not present at the detection position and it is detected in the 2 nd detection step that the workpiece is retained at the retention position.
In the conveying method having the above-described configuration, when the workpiece is retained at the retaining position, it is determined in the 2 nd determination step that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal, and therefore the workpiece retained in the conveyance path of the conveyance mechanism can be removed from the conveyance path. Therefore, the workpiece retained in the conveyance path can be prevented from remaining in the conveyance path as it is and interfering with the next conveyed workpiece, and the continuous conveyance of the workpieces can be efficiently performed.
According to the present invention, it is possible to detect an abnormality in the posture or position of the workpiece during conveyance. Therefore, the workpiece in which the abnormality has occurred can be removed from the conveyance path, and the next workpiece can be reliably conveyed. This enables continuous conveyance of workpieces to be performed reliably.
Drawings
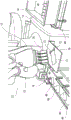
Fig. 1 is a plan view of a packaging apparatus according to embodiment 1 of the present invention.
Fig. 2 is a perspective view of a conveying device of the packaging device of fig. 1.
Fig. 3 is a front view of a main body of the packing device of fig. 1.
Fig. 4 (a) is a front view of the suction head configured as a hand of the packaging device main body portion of fig. 3, and (b) is a side view of the suction head.
Fig. 5 (a) is a front view of the gripper unit configured as a hand of the packaging device main body portion of fig. 3, and (b) is a side view of the gripper unit.
Fig. 6 is a block diagram showing the configuration of a control system of the boxing apparatus in fig. 1.
Fig. 7 is a perspective view of the boxing apparatus in a state where the suction head performs suction of the workpiece in the boxing apparatus of fig. 1.
Fig. 8 is a perspective view of the boxing apparatus in fig. 1, in which the front end portion of the suction head having the suction port attached thereto is rotated, and the workpiece is arranged on the table while changing its posture.
Fig. 9 is a perspective view of the boxing apparatus in a state where 4 workpieces are arranged on a table with their postures changed in the boxing apparatus of fig. 1.
Fig. 10 is a perspective view of the boxing apparatus in a state where 4 workpieces arranged on a table are collectively held by a holding unit and the holding unit is moved in a direction toward a box in the boxing apparatus in fig. 1.
Fig. 11 is a plan view showing a state where the workpiece is conveyed to the holding position in a normal position and posture in the conveying apparatus of fig. 2.
Fig. 12 is a side view showing a state in which the workpiece is conveyed to the holding position in a normal position and posture in the conveying apparatus of fig. 2.
Fig. 13 is a plan view showing a state in which the workpiece is conveyed to the holding position when there is an abnormality in the posture of the workpiece in the conveying apparatus of fig. 2.
Fig. 14 is a plan view showing a state in which the stopper is moved to retract the workpiece to the retracted position when there is an abnormality in the posture of the workpiece in the conveying apparatus of fig. 2.
Fig. 15 is an explanatory view for explaining a configuration for accommodating a workpiece in a region sandwiched between a stopper and a guide portion even if the posture of the workpiece is unstable at the time of conveyance in the conveying apparatus of fig. 2.
Fig. 16 is a flowchart showing a flow of packing the workpieces by the packing device of fig. 1.
Fig. 17 is a plan view of the conveying device in the boxing device according to embodiment 2 of the present invention, showing a state in which the workpiece stays in the conveying device.
Fig. 18 is a plan view of the conveying device in fig. 16 showing a state in which the stoppers are moved and the plurality of workpieces are retracted to the retracted positions when the plurality of workpieces are retained.
Fig. 19 is a flowchart showing a flow of boxing of the workpiece by the boxing apparatus according to embodiment 2.
Fig. 20 is a plan view showing an example of a distal end side sensor and a retention sensor according to another embodiment.
Detailed Description
Hereinafter, a packaging apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
Fig. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of a packaging apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in fig. 1, the boxing apparatus 10 carries the workpieces 40 and boxes the workpieces into boxes 41.
In the present embodiment, the workpiece 40 is a rice ball having a triangular prism shape. Further, the work 40 may be not a rice ball, and a food such as a sandwich having a triangular prism shape may be applied. Further, the workpiece 40 may not be a food, and the workpiece 40 may be another article having a triangular prism shape. The workpiece 40 may not have a triangular prism shape, and may have another shape as long as a portion (acute angle portion) having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle can be brought into contact with a portion formed at an acute angle by the guide portion and the stopper as described below.
The packaging device 10 includes: a boxing apparatus main body portion 11; a conveying device 50 that conveys the workpiece 40 to a holding position where the workpiece 40 is held by the boxing device main body portion 11; a work table 70 on which the workpiece 40 held by the box device main body 11 is temporarily placed; and a box 41 for accommodating the workpiece 40 and supported by the support table 80.
The conveying device 50 includes: a conveyor belt (conveying mechanism) 51, a guide 52, a stopper 53, a retreat portion 54, a tip end side sensor (1 st detecting mechanism) 55, and a retention sensor (2 nd detecting mechanism) 56.
The conveyor 51 conveys the workpiece 40 in one direction until the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51 a. When the workpiece 40 is conveyed by the conveyor 51 and reaches the holding position 51a, the boxing apparatus main body portion 11 holds the workpiece 40 and moves the workpiece 40 into the box 41.
The guide 52 extends along the conveying direction of the conveyor 51 so as to guide the conveyance of the workpiece 40 conveyed on the conveyor 51. The guide 52 is attached to the conveying path of the conveyor belt 51. The guide 52 is fixedly attached to the frame outside the conveyor 51 so that the guide 52 does not move even when the conveyor 51 is driven to move the workpiece 40. Therefore, the guide portion 52 maintains a stationary state.
The stopper 53 is configured to stop conveyance of the workpiece 40 by pressing the workpiece 40 conveyed on the conveyor 51. The stopper 53 has a pressing portion 53a which is a portion that abuts against the workpiece 40 and presses the workpiece 40. The stopper 53 is disposed such that the pressing portion 53a extends in a direction intersecting the conveying direction of the workpiece 40 by the driving of the conveyor belt 51. The conveyance of the workpiece 40 can be stopped by the workpiece 40 abutting against the pressing portion 53a extending in the direction intersecting the conveyance direction.
The stopper 53 is disposed to be inclined with respect to the conveying direction of the conveyor belt 51. Therefore, the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 is disposed obliquely to the guide surface 52a extending in the conveying direction of the conveyor belt 51. Therefore, the stopper 53 is disposed so that the angle formed between the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 becomes an acute angle. In particular, the angle formed between the guide surface 52a and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 is an acute angle having an angle equal to or larger than that of the acute angle portion of the workpiece 40 so that the workpiece 40 can enter the region sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a.
The stopper 53 has a rotating shaft 53b and a motor 53 c. The rotation shaft 53b is rotationally driven by the motor 53c, and the portion of the stopper 53 where the pressing portion 53a is formed is rotatable about the rotation shaft 53 b. In this way, the rotational driving of the portion of the stopper 53 where the pressing portion 53a is formed is controlled about the rotational shaft 53b by controlling the rotational driving of the rotational shaft 53 b.
When it is determined that the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is abnormal, the escape unit 54 guides the workpiece 40 to the inside and causes the workpiece 40 to escape from the conveyance path. The workpiece 40 determined to have an abnormal posture or position is temporarily stored in the retraction portion 54, and then the workpiece 40 is taken out from the retraction portion 54.
The work table 70 is provided as a space for temporarily disposing the workpiece 40. The work table 70 is substantially square in plan view, and is attached at a position close to the holding position 51a of the conveyor 51. A rectangular sheet 71 in a plan view is disposed at a predetermined position on the work table 70. The sheet 71 is formed so as to be able to hold the workpiece 40 on the upper surface. The workpiece 40 having reached the holding position 51a of the conveyor 51 is held by the boxing apparatus main body portion 11 and is disposed on the upper surface of the sheet 71 on the work table 70. Thereby, the workpiece 40 is held by the upper surface of the sheet 71 on the work table 70.
The case 41 is supported by a support table 80. The box 41 is configured to accommodate the workpiece 40 therein. The plurality of workpieces 40 arranged on the upper surface of the sheet 71 of the work table 70 are collectively gripped by the magazine main body 11, and the plurality of workpieces 40 are collectively accommodated in the box 41.
The end-side sensor 55 includes a light emitting portion 55a and a light receiving portion 55 b. The light emitting portion 55a and the light receiving portion 55b of the end-side sensor 55 detect whether or not the workpiece 40 is present at a predetermined position at a position close to the end of the conveyor belt 51. In the present embodiment, the end-side sensor 55 detects whether or not the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a where the workpiece 40 on the conveyor belt 51 is held by the boxing apparatus main body 11 in a normal position and posture. In the present embodiment, the light emitting portion 55a is provided on the side of the conveyor belt 51 on which the stopper 53 is provided, and the light receiving portion 55b is provided on the side opposite to the side on which the stopper 53 is provided. The positional relationship between the light emitting section 55a and the light receiving section 55b may be reversed. In the present embodiment, an LED is used as the light emitting portion 55 a. The light receiving unit 55b receives light from the light emitting unit 55a of the LED.
The retention sensor 56 includes a light emitting portion 56a and a light receiving portion 56b, similarly to the end-side sensor 55. The light emitting section 56a and the light receiving section 56b of the retention sensor 56 detect whether or not the workpiece 40 is present at the upstream side of the conveyor belt 51 from the end-side sensor 55. The retention sensor 56 detects whether or not the workpiece 40 has reached a position on the conveyor 51 upstream of the end-side sensor 55 in a normal position and posture. In the present embodiment, the light emitting section 56a is provided on the side of the conveyor belt 51 on which the stopper 53 is provided, and the light receiving section 56b is provided on the side opposite to the side on which the stopper 53 is provided. The positional relationship between the light emitting section 56a and the light receiving section 56b may be reversed. In the present embodiment, an LED is used as the light emitting unit 56 a. The light receiving section 56b receives light from the light emitting section 56a of the LED.
Next, the structure of the packaging apparatus main body 11 will be explained.
Fig. 3 is a front view of the packaging device main body 11 according to the present embodiment. As shown in fig. 3, the boxing apparatus main body portion 11 is constituted by a horizontal articulated double-arm robot including a pair of robot arms 13.
The boxing apparatus main body portion 11 includes a 1 st robot arm 13A and a 2 nd robot arm 13B. A 1 st holding portion 26 is provided at a distal end portion of the 1 st robot arm 13A. A 2 nd holding portion 27 is provided at a distal end portion of the 2 nd robot arm 13B. Hereinafter, the first robot arm 13A and the second robot arm 13B may be simply referred to as the robot arm 13 without distinction.
The boxing apparatus main body portion 11 includes a control portion 14 and a vacuum generating device 60.
The control unit 14 is provided inside the support base 12 of the packaging device main body 11, for example. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and may be provided inside the robot arm 13, for example. In addition, the present invention may be provided in other vacant spaces.
The vacuum generator 60 includes, for example, a vacuum pump, a CONVUM (registered trademark), and the like. The vacuum generator 60 is also provided inside the support table 12, for example, as in the control unit 14. However, the vacuum generating apparatus 60 is not limited to this, and may be installed in another place such as inside the robot arm 13. The vacuum generator 60 is connected to the suction head 18 described later via a pipe not shown. The piping is provided with, for example, an opening/closing valve, not shown, and the piping is opened and closed by the opening/closing valve. The operation of the vacuum generator and the opening and closing of the on-off valve are controlled by the control device. The vacuum generator 60 is configured to be able to generate a negative pressure in the suction port 22 of the suction head 18.
The 1 st robot arm 13A moves the 1 st holding portion 26 within a predetermined operation range. The 2 nd robot arm 13B moves the 2 nd holding portion 27 within a predetermined operation range. The robot arm 13 is, for example, a horizontal articulated robot arm, and includes an arm portion 15 and a toggle link portion 17. The 1 st robot arm 13A and the 2 nd robot arm 13B can operate independently of each other or in association with each other.
The 1 st holding portion 26 and the 2 nd holding portion 27 are configured to be able to hold a hand having a function.
The boxing apparatus main body portion 11 includes a support base 12 and a base shaft 16 extending upward in the vertical direction from the support base 12. The base shaft 16 is rotatably attached to the support base 12.
An arm portion 15 is attached to the base shaft 16 so as to extend in the horizontal direction. The arm portion 15 is rotatably attached around a base shaft 16.
The arm portion 15 includes a 1 st link 15a and a 2 nd link 15 b. The 1 st link 15a and the 2 nd link 15b are supported to be rotatable in the horizontal direction. The 1 st robot arm 13A and the 2 nd robot arm 13B are connected to the base shaft 16 via the arm 15.
The arm portion 15 positions a toggle link portion 17 attached to the tip end portions of the 1 st robot arm 13A and the 2 nd robot arm 13B at an arbitrary position within the operation range.
The base end portion of the 1 st link 15a is coupled to the base shaft 16 of the support base 12 via a rotary joint J1 and is rotatable about a rotation axis L1 passing through the axial center of the base shaft 16. The 2 nd link 15b is coupled to the distal end portion of the 1 st link 15a via a rotary joint J2 and is rotatable about a rotation axis L2 defined by the distal end portion of the 1 st link 15 a.
The toggle part 17 changes the mechanism connected to the tip thereof to an arbitrary posture. The elbow lever portion 17 includes a lift portion 17a and a rotation portion 17 b. The lifting unit 17a is coupled to the distal end portion of the 2 nd link 15b via a linear joint J3, and is capable of lifting and lowering relative to the 2 nd link 15 b. The turning unit 17b is coupled to the lower end of the lifting unit 17a via a turning joint J4 and is turnable around a rotation axis L3 defined by the lower end of the lifting unit 17 a.
In the present embodiment, the rotation axes L1 to L3 are parallel to each other and extend, for example, in the vertical direction. The extending direction of the rotation axes L1 to L3 and the lifting/lowering direction of the lifting/lowering unit 17a are parallel to each other.
The arm 13 is provided with a servomotor (not shown) for driving and an encoder (not shown) for detecting a rotation angle of the servomotor (not shown) so as to correspond to the joints J1 to J4. The rotation axis L1 of the 1 st robot arm 13A and the rotation axis L1 of the 2 nd robot arm 13B are on the same straight line, and the 1 st link 15a of the 1 st robot arm 13A and the 1 st link 15a of the 2 nd robot arm 13B are arranged so as to have a step difference between the upper and lower portions.
Next, a hand which can be gripped by the 1 st and 2 nd holding portions 26 and 27 will be described. In the present embodiment, the 1 st holding portion 26 holds the suction head 18 as a hand.
Fig. 4 (a) shows a front view of the suction head 18, and fig. 4 (b) shows a side view of the suction head 18. The suction head 18 is configured to hold the workpiece 40 in a 1 st posture with the 1 st surface portion 40a horizontal, and to be able to change the posture of the workpiece 40 from the 1 st posture to a 2 nd posture with the 2 nd surface portion 40b horizontal.
The adsorption head 18 has: a base portion 20 including a rotating portion 17b of the elbow lever portion 17; a rotary joint J5 having a rotation axis L4 extending in the horizontal direction; a tip portion 21 rotatably coupled to the base portion 20; and a suction port 22 provided at the tip end portion 21 and sucking the workpiece 40 (the 1 st surface portion 40 a).
The base portion 20 is coupled to the raising and lowering portion 17a of the toggle link portion 17 via a rotary joint J4, and is coupled to the distal end portion 21 via a rotary joint J5. The base 20 is bent in a substantially L-shape in side view (see fig. 4 (b)). The base 20 includes a drive unit 25 having a rotary joint J5 inside the L-shaped member.
The distal end portion 21 is coupled to the base portion 20 via a rotary joint J5. Further, a suction port 22 is attached to the distal end portion 21. The distal end portion 21 is bent substantially in an L shape in side view (see fig. 4 (b)). In the present embodiment, the suction port 22 is provided at the distal end portion 21 at 6 positions. The suction port 22 is connected to a vacuum generator 60 via a pipe (not shown). The piping is provided with, for example, an on-off valve (not shown). The suction port 22 can suck and release the workpiece 40 by opening and closing the pipe with the opening and closing valve.
The posture of the workpiece 40 can be changed from the 1 st posture to the 2 nd posture by holding the workpiece 40 by suction through the suction port 22 of the suction head 18 and rotating the distal end portion 21 by 90 degrees with respect to the base portion 20 by the rotary joint J5.
The 2 nd holding portion 27 serves as a hand holding clamp unit 19. Fig. 5 (a) shows a front view of the gripper unit 19, and fig. 5 (b) shows a side view of the gripper unit 19.
The gripping unit 19 is configured to hold 4 workpieces 40 supplied in the 2 nd posture in a superimposed manner at predetermined positions on the work table 70. The clamp unit 19 has: 4 pairs of holding members 32, and 4 driving members 33 capable of independently driving the 4 pairs of holding members 32, respectively.
The rotating portion 17b of the toggle link 17 extends in a horizontal direction perpendicular to the rotation axis L3 in front view. Each holding member 32 is connected to the rotating portion 17b of the elbow lever portion 17 via a driving member 33.
Each pair of holding members 32 is configured to hold the workpieces 40 stacked in the 2 nd posture with the 1 st surface portion 40a facing the 1 st direction at a predetermined position on the work table 70.
In the present embodiment, each pair of holding members 32 is configured to sandwich the 2 nd surface portion 40b of the workpiece 40 from both sides thereof. Each holding member 32 has a shape corresponding to the inclination of the 2 nd surface portion 40b of the workpiece 40, and has an abutment surface 32a that abuts against the workpiece 40. The holding member 32 has, for example, a rectangular flat plate shape.
As the material of the holding member 32, for example, a resin plate or a metal plate is used. In the present embodiment, since the workpiece 40 uses a triangular lump of rice, the respective pairs of holding members 32 are arranged such that the distance therebetween becomes narrower toward the upper end portion, and a mountain shape (inverted V shape) that expands downward is formed.
The driving member 33 is configured to be able to move the pair of holding members 32. The driving member 33 includes an actuator (not shown) and the like, and in the present embodiment, can linearly move each of the pair of holding members 32. This enables the distance between the pair of holding members 32 to be changed. When the workpiece 40 is clamped by the clamping unit 19, the pair of holding members 32 narrows the interval therebetween by the driving member 33, and the workpiece 40 is clamped and held between the pair of holding members 32.
In the present embodiment, the pair of holding members 32 are controlled so as to maintain the angle formed by each other at an angle (approximately 60 degrees) matching the inclination of the 2 nd surface portion 40b of the workpiece 40, and so as to expand and contract the interval therebetween in the arrow direction of fig. 5 (b). In the present embodiment, the workpiece 40 is held by the frictional force generated when the abutment surface 32a of the holding member 32 comes into contact with the 2 nd surface portion 40b of the workpiece 40. Further, a suction port may be provided in the contact surface 32a, and the workpiece 40 may be held by a suction force from the suction port.
Next, the control unit 14 that controls the operation of the packaging apparatus main body 11 will be described. Fig. 6 is a block diagram schematically showing a configuration example of a control system of the packaging apparatus main body portion 11.
As shown in fig. 6, the control unit 14 includes a calculation unit 14a, a storage unit 14b, and a servo control unit 14 c.
The control unit 14 is a robot controller provided with a computer such as a microcontroller, for example. The control unit 14 may be constituted by a single control unit 14 that performs centralized control, or may be constituted by a plurality of control units 14 that perform distributed control in cooperation with each other.
The storage unit 14b stores information such as a basic program and various kinds of fixed data as a robot controller. The computing unit 14a reads out and executes software such as a basic program stored in the storage unit 14b, thereby controlling various operations of the packaging apparatus main body 11. That is, the computing unit 14a generates a control command for the packaging apparatus main body 11 and outputs the control command to the servo control unit 14 c.
The servo controller 14c is configured to control driving of the servo motors corresponding to the joints J1 to J4 of the 1 st robot arm 13A and the 2 nd robot arm 13B of the boxing apparatus main body portion 11, based on the control command generated by the arithmetic unit 14 a.
Next, an operation when the boxing apparatus 10 performs boxing of the workpiece 40 will be described.
Fig. 7 is a perspective view of the packaging apparatus 10 in a state where the suction head 18 sucks the workpiece 40 through the suction port 22. In the present embodiment, the workpiece 40 is conveyed by the conveyor 51 in the 1 st posture in which the 1 st surface portion 40a is horizontal. The workpiece 40 is conveyed while being guided by a guide 52 provided on the conveyor 51 so as to extend in the conveying direction. When the workpiece 40 is conveyed and the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the workpiece 40 abuts against the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53. When the workpiece 40 abuts against the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53, the workpiece 40 is sucked through the suction port 22 of the suction head 18.
At this time, the suction head 18 (the elevating portion 17a of the toggle link portion 17) is lowered, and the suction port 22 is brought into contact with the 1 st surface portion 40a of the workpiece 40 on the conveyor belt 51. The workpiece 40 in the 1 st posture is sucked and held by the suction head 18.
The workpiece 40 sucked and held by the suction head 18 is temporarily placed on the table 70. Fig. 8 is a perspective view of the packaging apparatus 10 in a state where one workpiece 40 is disposed on the work table 70.
The workpiece 40 sucked and held by the suction head 18 is disposed on a sheet 71 provided on the work table 70. A pair of support members 50b for supporting the workpiece 40 when the workpiece 40 is disposed are disposed on the sheet 71. Therefore, the workpiece 40 disposed on the sheet 71 is stably supported.
When the workpiece 40 is placed on the sheet 71, the controller 14 controls the operation of the arm 13A to rotate the distal end portion 21 of the suction head 18 by 90 degrees about the rotation axis L4 with respect to the base 20 via the rotary joint J5. Thereby, the suction port 22 is rotated by 90 degrees from the reference position. The posture of the workpiece 40 sucked and held in the 1 st posture is changed from the 1 st posture to the 2 nd posture by the rotation of the tip end portion 21 of the suction head 18. When the posture of the workpiece 40 is changed to the 2 nd posture, the workpiece 40 is disposed on the sheet 71.
At this time, the controller 14 controls the operation of the arm 13A to supply the workpiece 40 held in the 2 nd posture by the suction head 18 to the position of the sheet 71 on the work table 70. The sheet 71 is capable of supporting 4 workpieces 40 simultaneously. Therefore, by repeating the operation of arranging the workpiece 40 on the sheet 71 4 times, 4 workpieces 40 can be arranged.
By repeating the above operations, 4 workpieces 40 are sequentially supplied onto the sheet 71 of the work table 70.
Fig. 9 is a perspective view of the boxing apparatus 10 in a state where 4 workpieces 40 are arranged on the sheet 71.
When 4 workpieces 40 are arranged on the sheet 71, the control unit 14 controls the operation of the arm 13B to superimpose and hold the workpieces 40 supplied in the 2 nd posture at the position on the sheet 71 of the work table 70 by the gripping unit 19. In fig. 9, 4 workpieces 40 are collectively held by the holding unit 19.
Next, the held 4 workpieces 40 are accommodated in the box 41 by the movement of the gripping unit 19. Fig. 10 is a perspective view showing the packaging apparatus 10 in a state where the clamping unit 19 holds 4 workpieces 40 collectively and moves them to the inside of the box 41.
At this time, the controller 14 controls the movement of the gripping unit 19 by controlling the operation of the arm 13B. Since the 4 workpieces 40 arranged on the sheet 71 can be collectively arranged inside the box 41, the workpieces 40 can be efficiently packed.
As described above, the boxing apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment can perform boxing of the workpiece 40, and can efficiently perform the work of loading the workpiece 40 into the box 41.
(detection of workpiece 40 by end-side sensor 55)
Next, the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveying device 50, which conveys the workpiece 40 to the holding position 51a where the workpiece 40 is held by the boxing device main body 11, will be described.
The workpiece 40 is conveyed by the conveyor belt 51, and thereby the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a at which the workpiece 40 can be sucked by the suction head 18 of the boxing apparatus main body portion 11.
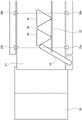
Fig. 11 is a plan view showing the periphery of the holding position 51a of the conveying device 50 in a state where the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. Fig. 12 is a side view showing the periphery of the holding position 51a of the conveying device 50 in a state where the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. Fig. 13 is a plan view showing the periphery of the holding position 51a of the conveying device 50 when there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40.
At the timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the light emitting portion 55a of the end side sensor 55 emits light. When the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture when the light emitting section 55a emits light, the light from the light emitting section 55a is blocked by the workpiece 40 and does not reach the light receiving section 55 b. When the light from the light emitting unit 55a is not received by the light receiving unit 55b, it is determined that the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture.
When the light emitting section 55a emits light, if there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40, the light reaches the light receiving section 55b without being blocked by the workpiece 40. When the light from the light emitting unit 55a is received by the light receiving unit 55b, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40.
In this way, when the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 and the absence of the workpiece 40 at the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 is detected, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40. In other words, when the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 and the absence of the workpiece 40 at the detection position is detected by the end-side sensor 55, it is determined that the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is abnormal. In the present embodiment, the control unit 14 functions as a determination means (1 st determination means) for determining whether or not the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is abnormal.
Here, the timing at which the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the detection position by the end side sensor 55 is a time after a time taken for the workpiece 40 to be conveyed from the detection position by the retention sensor 56 to the detection position by the end side sensor 55 has elapsed from the detection of the passage of the workpiece 40 at the detection position (trigger position) by the retention sensor 56. Since the retention sensor 56 is attached upstream of the end-side sensor 55, it is possible to detect that the workpiece 40 passes upstream of the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 in the conveying direction. Therefore, in the present embodiment, the passage detection means detects passage of the workpiece 40 at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55.
As described above, in the present embodiment, the retention sensor 56 also functions as a passage detection means for detecting passage of the workpiece 40 at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55. Therefore, a sensor for detecting whether or not a plurality of workpieces 40 are retained at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55, and a sensor for detecting passage of a workpiece 40 at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 are configured as the same sensor. However, different sensors may be used between a sensor for detecting whether or not a plurality of workpieces 40 are retained at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 and a sensor for detecting passage of a workpiece 40 at a position upstream in the conveying direction from the detection position by the end-side sensor 55.
When it is detected that the workpiece 40 passes through the detection position (trigger position) by the retention sensor 56, the signal is transmitted to the control unit 14. The control unit 14 determines whether or not the workpiece 40 is present at the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 when the time taken for the workpiece 40 to travel from the detection position by the retention sensor 56 to the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 has elapsed since the detection of the passage of the workpiece 40 at the detection position by the retention sensor 56.
Fig. 12 is a side view of the periphery of the holding position 51a of the conveying device 50 viewed from the light emitting portion 55a side of the distal end side sensor 55. As shown in fig. 12, the light emitting portion 55a of the distal end side sensor 55 is attached so that the optical axis L of the light emitted from the light emitting portion 55a passes below the guide portion 52. The optical axis L emitted by the light emitting portion 55a of the distal-side sensor 55 passes through the gap formed between the guide portion 52 and the conveyor belt 51 and enters toward the light receiving portion 55 b. Therefore, when the workpiece 40 is present at the detection position by the end-side sensor 55, the light emitted from the light-emitting portion 55a and passing through the gap formed between the guide portion 52 and the conveyor belt 51 is blocked by the workpiece 40 and does not reach the light-receiving portion 55 b. When the workpiece 40 is not present at the detection position by the end-side sensor 55, the light emitted from the light emitting portion 55a passes through the gap formed between the guide portion 52 and the conveyor belt 51, and is received by the light receiving portion 55 b.
When it is determined that there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40, the conveyor belt 51 is driven and the stopper 53 is moved. The rotation shaft 53b is rotated by driving the motor 53c, and the portion of the stopper 53 where the pressing portion 53a is formed is moved in a direction to retreat from the conveyance path of the workpiece 40.
Fig. 13 shows a region R1 sandwiched by the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53. The trajectory of the light emitted by the light emitting portion 55a of the distal end side sensor 55 passes through the region R1 sandwiched between the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53. That is, the detection position by the distal end side sensor 55 is located inside the region R1 sandwiched by the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53. The distal end side sensor 55 detects whether or not the workpiece 40 is present at a detection position inside the region R1 sandwiched between the guide surface 52a and the pressing portion 53a. In the present embodiment, the detection position by the distal end side sensor 55 is a position on the downstream side in the conveying direction by the conveyor belt 51 in the inside of the region R1 sandwiched by the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 and the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53. The presence or absence of an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40 is detected at a position on the downstream side in the conveying direction of the conveyor belt 51 of the region R1 sandwiched between the guide surface 52a and the pressing portion 53a.
Here, the region R1 sandwiched between the guide surface 52a and the pressing portion 53a is an isosceles triangle in which the length of the portion where the pressing portion 53a and the region R1 overlap and the length of the portion where the guide surface 52a and the region R1 overlap are equal to each other. That is, the length of the portion where the region R1 and the guide surface 52a overlap is equal to the length of the pressing portion 53a that protrudes inward in the conveyance path from the guide surface 52a.
Fig. 14 is a plan view of the conveying device 50 in a state where the portion of the stopper 53 where the pressing portion 53a is formed is moved in the retracting direction.
The stopper 53 moves from a position where it is extended in a direction blocking the conveying path by the conveyor belt 51 as shown in fig. 13 to a position where it is extended along the conveying path by the conveyor belt 51 as shown in fig. 14. That is, the stopper 53 moves from a stop position at which the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveyor 51 is stopped to a conveyance position at which the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveyor 51 is not stopped. At this time, the motor 53c functions as a stopper moving mechanism that moves the stopper 53 from the stop position to the conveyance position. Since the conveyor 51 is driven and the stopper 53 is moved, the workpiece 40 is further conveyed to the downstream side of the stopper 53, and the workpiece 40 is thrown into and disposed inside the retreat portion 54 as shown in fig. 14. The workpiece 40 disposed inside the escape portion 54 is, for example, taken out by a person and removed from the conveying device 50.
(Structure of stopper 53)
As shown in fig. 15, when the stopper 53 is disposed so as to stop the conveyance of the workpiece 40, it is disposed obliquely with respect to the direction orthogonal to the conveyance direction of the conveyor 51. The stopper 53 is disposed so that the tip end of the stopper 53 is inclined toward the upstream side from the direction orthogonal to the conveying direction of the conveyor belt 51.
Since the stopper 53 is disposed obliquely, the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53, which stops the conveyance of the workpiece 40, is inclined with respect to the conveyance direction of the conveyor belt 51. Therefore, the angle formed between the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 for guiding conveyance and the pressing portion 53a is smaller than 90 degrees and is an acute angle.
Since the angle formed between the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 and the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 is formed at an acute angle, a portion (acute angle portion) of the workpiece 40 having a triangular shape in plan view, which has two faces intersecting at an acute angle and is formed at an acute angle, is sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a. The part of the workpiece 40 formed at an acute angle is sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a and held by the holding position 51a, and therefore the workpiece 40 reaching the holding position 51a is reliably held by the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a.
As shown in fig. 15, the workpiece 40 may be inclined in a posture such that a portion in front in the conveying direction is separated from the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 (40c), or inclined in a posture such that a portion in rear in the conveying direction is separated from the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 (40 d). Such a small change in the posture of the workpiece 40 can be corrected by sandwiching the workpiece 40 between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a.
When the workpiece 40 enters the region R1 sandwiched by the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a, the entrance of the region R1 sandwiched by the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a is relatively wide, and therefore the workpiece 40 easily enters the region R1. Since the stopper 53 is disposed obliquely with respect to the conveying direction by the conveyor belt 51, the region R1 is formed to become narrower toward the downstream in the conveying direction. Therefore, the workpiece 40 moves downstream in the region R1, the position and posture of the workpiece 40 are corrected by the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a, and the workpiece 40 moves to the holding position 51a in a correct posture and position. Therefore, the workpiece 40 is highly likely to be disposed in the correct position and posture when it reaches the holding position 51 a.
In this way, even if the position and orientation of the workpiece 40 before entering the region R1 change, the position and orientation can be corrected within the region R1. Therefore, even if the position or posture of the workpiece 40 slightly deviates before the workpiece 40 enters the region R1, the deviation can be corrected inside the region R1. Therefore, when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the workpiece can be arranged in a correct position and posture.
Since the change in the posture of the workpiece 40 can be corrected, when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the workpiece 40 is more reliably placed at the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. Since the workpiece 40 is disposed in the normal position and posture when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the suction can be reliably performed when the suction head 18 of the box device main body 11 sucks the workpiece 40. Therefore, the workpiece 40 can be more reliably arranged on the sheet 71 of the work table 70.
If the pressing portion of the stopper is disposed to extend in a direction orthogonal to the conveying direction by the conveyor belt, the posture of the workpiece cannot be corrected when the workpiece reaches the holding position, and the workpiece is held while maintaining the posture of the workpiece, thereby performing binning of the workpiece. In this case, if the posture of the workpiece is deviated, the workpiece may not be held correctly. Therefore, when holding the workpiece, the workpiece may be held in a misaligned state, and the workpiece may not be accurately packaged.
In the present embodiment, the angle formed between the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 and the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52 is formed at an acute angle, and therefore the workpiece 40 is sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a and is stably held. Therefore, the holding of the workpiece 40 can be reliably performed when boxing is performed by the boxing apparatus main body portion 11, and boxing can be performed more accurately.
(procedure for packing)
Fig. 16 is a flowchart showing the case where the boxing apparatus 10 performs the boxing operation of the workpiece 40.
When the workpiece 40 is conveyed by the conveyor belt 51 and reaches the holding position 51a, (S1) the end-side sensor 55 determines whether the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. The determination as to whether or not the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a in the normal position or posture is made by whether or not the workpiece 40 is detected by the end-side sensor 55 at the timing when the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a (S2). At this time, the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 at the detection position inside the region R1 sandwiched between the guide surface 52a and the pressing portion 53a is detected (the 1 st detection step).
When the light emitting portion 55a of the end-side sensor 55 emits light and the light receiving portion 55b does not receive light at the timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, it is determined that the workpiece 40 is at the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. If it is determined that the workpiece 40 is at the holding position 51a in the normal position and posture, it is determined that the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a posture that can be accurately held by the suction head 18 (S3).
If it is determined that the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a posture in which it can be held accurately by the suction head 18, the suction head 18 holds the workpiece 40 by sucking it, and the workpiece 40 is disposed on the sheet 71 of the work table 70 (S4). In the present embodiment, the conveyance by the conveyor belt 51 is stopped while the suction head 18 is approaching the workpiece 40 and the suction head 18 is attempting to hold the workpiece 40 while sucking. In a state where the conveyor belt 51 is stopped, the suction head 18 sucks and holds the workpiece 40.
When the arrangement of the workpieces 40 on the sheet 71 of the work table 70 is repeated and the number of the workpieces 40 that can be arranged on the sheet 71 is increased, the workpieces 40 on the sheet 71 are collectively gripped by the gripping unit 19. In the present embodiment, 4 workpieces 40 are collectively held by the gripping unit 19. When the workpieces 40 on the sheet 71 are collectively held by the gripping unit 19, the gripping unit 19 moves to the box 41, and the workpieces 40 held by the gripping unit 19 are arranged inside the box 41 (S5). This enables the workpiece 40 to be efficiently disposed inside the box 41.
On the other hand, in S2, when the workpiece 40 cannot be detected by the end-side sensor 55 at the timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40 (S6). In other words, when the workpiece 40 is detected to be not present at the detection position by the end side sensor 55 at the timing when the workpiece 40 is conveyed to the detection position by the end side sensor 55, it is determined that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal (the 1 st determination step). When the light emitting portion 55a of the end side sensor 55 emits light at a timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a and the light receiving portion 55b receives the light from the light emitting portion 55a, it is determined that the article is not shielded from light at the predetermined position of the holding position 51 a. Therefore, the workpiece 40 is not present at the detection position inside the holding position 51a, and it is determined that the workpiece 40 is not held at the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. Therefore, it is determined that the posture or position of the workpiece 40 is abnormal.
If it is determined that there is an abnormality in the posture or position of the workpiece 40, there is a possibility that the suction holding by the suction head 18 cannot be performed correctly, and therefore, the workpiece 40 is moved to the evacuation unit 54 and the workpiece 40 is evacuated from the conveying path (S7).
When the workpiece 40 is retracted to the retraction portion 54, the conveyor 51 is driven to convey the workpiece 40, and the stopper 53 is moved to the downstream side in the conveying direction of the conveyor 51. Thereby, the workpiece 40 moves to the downstream side in the conveying direction of the conveyor 51 from the holding position 51 a. When the workpiece 40 reaches the end of the conveyor 51 on the downstream side, the workpiece is thrown into the escape portion 54. Thereby, the workpiece 40 is disposed inside the escape portion 54.
When the workpiece 40 is disposed inside the escape portion 54, the workpiece 40 is manually excluded from the escape portion 54 (S8). Thereby, the workpiece 40 is excluded from the conveying device 50.
As described above, according to the method of conveying the workpiece 40 of the present embodiment, when the posture or position of the workpiece 40 is abnormal when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, it is possible to detect this. When it is detected that there is an abnormality in the posture or position of the workpiece 40, the workpiece 40 can be retracted to the retraction portion 54, and the workpiece 40 can be excluded from the conveyance path.
When there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40, the workpiece 40 having the abnormality is excluded from the conveyance path, and therefore the workpiece 40 having the abnormality does not become an obstacle to the suction and holding of the workpiece 40 to be subsequently conveyed to the holding position 51 a. Therefore, the boxing operation of the workpieces 40 continuously conveyed can be performed more smoothly.
In the above embodiment, the workpiece 40 retracted to the retraction portion 54 is excluded by the hand of the person, but the present invention is not limited to this. The workpiece 40 retracted to the retraction portion 54 may be automatically removed from the conveying device 50. The workpiece 40 retracted to the retraction portion 54 may be returned to the conveyor 51, conveyed again, held by the packaging apparatus main body portion 11, and placed inside the box 41.
(embodiment 2)
Next, a packaging apparatus according to embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. Note that the same components as those in embodiment 1 are not described, and only different components will be described.
In embodiment 1, the end-side sensor 55 detects whether or not the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a normal position or posture. In embodiment 2, the end side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 are used to detect whether or not the plurality of workpieces 40 are retained around the holding position 51 a.
Fig. 17 is a plan view showing the periphery of the holding position 51a of the conveying apparatus 50 in a state where the plurality of workpieces 40 are arranged around the holding position 51a and the workpieces 40 are retained.
The workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a by being conveyed by the conveyor 51. At this time, if the next workpiece 40 continues to be conveyed in a state where the position or posture of the first workpiece 40 is abnormal, the workpiece 40 having the abnormal position or posture may hinder the holding of the subsequently conveyed workpiece 40, and the plurality of workpieces 40 may be left. Therefore, it is also possible to detect whether or not a plurality of workpieces 40 remain around the holding position 51 a. When the plurality of works 40 are accumulated, the accumulated works 40 may be removed from the conveying path.
When detecting whether or not a plurality of works 40 are left, first, the light emitting portion 55a of the end side sensor 55 emits light at a timing when the works 40 reach the holding position 51 a. When the light emitting section 55a emits light, if there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40, the light reaches the light receiving section 55b without being blocked by the workpiece 40. When the light from the light emitting section 55a is received by the light receiving section 55b, there is a high possibility that the position or posture of the workpiece 40 is abnormal. In embodiment 2, it is not yet determined at this stage that an abnormality has been detected in the conveyance of the workpiece 40. In this state, since the workpiece 40 is not detected at the position of the end side sensor 55, the conveyor 51 is continuously driven to continue the conveyance of the workpiece 40. Therefore, the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is then continued also toward the holding position 51 a.
Fig. 17 shows a state in which, when there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the first workpiece 40, two workpieces 40 are continuously conveyed toward the holding position 51a, and a total of 3 workpieces 40 are conveyed to the periphery of the holding position 51 a. Therefore, 3 pieces of the work 40 stay at the periphery of the holding position 51 a.
When 3 works 40 are retained, the retained works 40 are detected by the retention sensor 56. The retention sensor 56 detects the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 at a position upstream of the end side sensor 55. The detection position (retention position) by the retention sensor 56 is located at a position shifted toward the upstream side by at least the length of the workpiece 40 in the conveyance direction, compared with the detection position by the distal end side sensor 55. The detection position by the stay sensor 56 is located on the upstream side of the longitudinal size of the workpiece 40 than the detection position by the end side sensor 55, and thus it is possible to detect when a plurality of workpieces 40 have stayed. Whether or not the plurality of workpieces 40 are left can be detected based on the result of the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 detected by the end side sensor 55 and the result of the presence or absence of the left of the workpiece 40 detected by the left sensor 56.
The light emitted from the light emitting section 56a of the stagnation sensor 56 is blocked by the stagnant work 40 and is not received by the light receiving section 56 b. In this state, the presence of the workpiece 40 at the detection position of the retention sensor 56 is detected, and the retention sensor 56 detects that a plurality of workpieces 40 are retained.
As described above, when it is detected that the workpiece 40 is not present at the detection position by the end side sensor 55 and that the workpiece 40 is retained at the detection position (retention position) by the retention sensor 56, it is determined that the retention is caused by the plurality of workpieces 40. Therefore, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the conveyance of the workpiece 40. At this time, the control unit 14 functions as a determination means (2 nd determination means) for determining whether or not the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is abnormal.
As shown in fig. 18, when the retention of the plurality of workpieces 40 is detected, the conveyor 51 is driven and the stopper 53 is moved. When the motor 53c is driven to rotate the rotating shaft 53b, the portion of the stopper 53 where the pressing portion 53a is formed is moved in a direction to retreat from the conveyance path of the workpiece 40.
Fig. 18 is a plan view of the conveying apparatus 50 in a state where the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 is moved in the retracting direction while the plurality of workpieces 40 are retained.
When the occurrence of the stagnation of the plurality of workpieces 40 is detected, the stopper 53 moves from the position extended and disposed in the direction blocking the conveying path by the conveyor 51 as shown in fig. 17 to the position extended and disposed along the conveying path by the conveyor 51 as shown in fig. 18. That is, the stopper 53 moves from a stop position at which the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveyor 51 is stopped to a conveyance position at which the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveyor 51 is not stopped. At this time, the motor 53c functions as a stopper moving mechanism that moves the stopper 53 from the stop position to the conveyance position.
Since the conveyor 51 is driven and the stopper 53 is moved, the plurality of workpieces 40 are conveyed further downstream of the stopper 53, and as shown in fig. 18, the plurality of workpieces 40 are thrown into and arranged inside the retreat portion 54. The workpiece 40 disposed inside the escape portion 54 is taken out by a person, for example, and removed from the conveying device 50.
(procedure for packing)
Fig. 19 is a flowchart showing the case where the boxing device 10 performs the boxing operation of the workpiece 40.
When the workpiece 40 is conveyed by the conveyor belt 51 and reaches the holding position 51a, (S21) the end-side sensor 55 determines whether the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. The determination as to whether or not the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a in the normal position or posture is performed by determining whether or not the workpiece 40 can be detected by the end-side sensor 55 at the timing when the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a (S22) (the 1 st detection step).
When the light emitting portion 55a of the end-side sensor 55 emits light and is not received by the light receiving portion 55b at the timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, it is determined that the workpiece 40 is at the holding position 51a in the normal position and posture, and it is determined that the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in the posture that can be accurately held by the suction head 18 (S23).
If it is determined that the workpiece 40 is disposed at the holding position 51a in a posture in which it can be held accurately by the suction head 18, the suction head 18 holds the workpiece 40 by suction and disposes it on the sheet 71 of the work table 70 (S24). In the present embodiment, the conveyance by the conveyor belt 51 is stopped while the suction head 18 is approaching the workpiece 40 and the suction head 18 is attempting to hold the workpiece 40 while sucking. The suction head 18 sucks and holds the workpiece 40 while the conveyor belt 51 is stopped.
The arrangement of 4 workpieces 40 on the sheet 71 of the work table 70 is repeated, and when 4 workpieces 40 are arranged on the sheet 71, the 4 workpieces 40 on the sheet 71 are collectively gripped by the gripping unit 19. When the 4 works 40 on the sheet 71 are collectively held by the gripping unit 19, the gripping unit 19 moves to the box 41, and the 4 works 40 held by the gripping unit 19 are arranged inside the box 41 (S25).
In S22, even when the workpiece 40 cannot be detected by the end-side sensor 55 at the timing at which the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, it is not determined that conveyance is abnormal in embodiment 2. If the workpiece 40 cannot be detected by the end-side sensor 55, the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 is detected by the retention sensor 56 (S26). In other words, whether or not the workpiece 40 is retained at a position (retention position) on the upstream side of the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 is detected by the retention sensor 56 (2 nd detection step).
When the light emitted from the light emitting section 56a of the retention sensor 56 is not received by the light receiving section 56b, the workpiece 40 blocks the light between the light emitting section 56a and the light receiving section 56b, and it is determined that the workpiece 40 is present at a position between the light emitting section 56a and the light receiving section 56 b. That is, the workpiece 40 is detected by the retention sensor 56. When the workpiece 40 is detected by the retention sensor 56, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the position or posture of the workpiece 40, and the plurality of workpieces are arranged around the holding position 51a, and the plurality of workpieces 40 are retained (S27). In other words, when it is detected that there is no workpiece 40 at the detection position by the end side sensor 55 and that there is a workpiece 40 remaining at the detection position (remaining position) by the remaining sensor 56, it is determined that the remaining is caused by the plurality of workpieces 40. Therefore, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the conveyance of the workpiece 40. Thus, it is determined whether or not an abnormality occurs in the conveyance of the workpiece 40 (determination step 2).
If it is determined by the retention sensor 56 that a plurality of workpieces 40 are retained, it is determined that conveyance of the workpieces 40 is abnormal, and there is a possibility that suction holding by the suction head 18 cannot be performed accurately. Therefore, the plurality of workpieces 40 are moved to the retracting portion 54, and the plurality of workpieces 40 are retracted from the conveying path (S28).
When the plurality of workpieces 40 are moved to the retreat portion 54, the conveyor 51 is driven to convey the workpieces 40, and the stopper 53 is moved to the downstream side in the conveying direction of the conveyor 51. Thereby, the plurality of accumulated workpieces 40 move to the downstream side in the conveying direction of the conveyor 51 from the holding position 51 a. When the plurality of workpieces 40 reach the end portion on the downstream side of the conveyor 51, the plurality of workpieces 40 are thrown into the interior of the retreat portion 54. Thereby, the plurality of workpieces 40 are arranged inside the escape portion 54.
In the present embodiment, when 3 workpieces 40 are arranged around the holding position 51a, the retention sensor 56 detects the workpieces 40, and the retention of the workpieces 40 is detected. Therefore, when 3 workpieces 40 are retained around the holding position 51a, the 3 workpieces 40 move to the downstream side of the holding position 51a in the conveying direction of the conveyor 51, and the 3 workpieces 40 are disposed inside the retreat portion 54.
When the plurality of workpieces 40 are disposed inside the evacuation section 54, the plurality of workpieces 40 are manually excluded from the evacuation section 54 (S29). Thereby, the plurality of workpieces 40 are excluded from the conveying device 50.
In S26, when the workpiece 40 is not detected by the retention sensor 56, the workpiece 40 is not detected by the end side sensor 55, and the workpiece 40 is not detected by the retention sensor 56, so that the conveyance of the workpiece 40 by the conveyor belt 51 is continued. The flow returns to S22.
When the next workpiece 40 reaches the periphery of the holding position 51a, the end-side sensor 55 determines again in S22 whether or not the workpiece 40 has reached the holding position 51a in a normal position and posture. At the timing when the workpiece 40 reaches the holding position 51a, the workpiece 40 is detected by the end side sensor 55 (S22).
Next, it is determined whether or not the conveyance of the workpiece 40 is abnormal according to the above flow.
In this way, in order to determine whether or not there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpieces 40, it is determined not only based on the detection result of the presence or absence of a workpiece at the detection position by the end-side sensor 55 but also based on whether or not the stagnation sensor 56 detects the occurrence of stagnation due to the plurality of workpieces 40. Therefore, in embodiment 2, it is determined that the occurrence of an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpieces 40 is caused when the plurality of workpieces 40 are retained.
When the workpiece 40 is conveyed, the workpiece 40 may be intermittently conveyed in the conveyance path due to, for example, being determined to be defective in the spot inspection of the workpiece 40 on the upstream side and being removed from the conveyance path. In such a case, when the workpiece 40 is retracted to the retraction portion 54 when the workpiece 40 is not detected at the timing of conveying the coming workpiece 40, the number of times of the retraction process of the workpiece 40 to the retraction portion 54 increases, and accordingly, the conveying time of the workpiece 40 increases. Further, although the workpiece is normally conveyed, the retracting step to the retracting portion 54 is performed, and time may be unnecessarily consumed.
In the present embodiment, when a plurality of workpieces 40 are left, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the conveyance of the workpieces 40. Therefore, the workpiece 40 is conveyed by the intermittent conveyance, and when the workpiece 40 is not detected at the timing when the workpiece 40 is conveyed, the next workpiece 40 is conveyed to the holding position 51a without performing the retracting step to the retracting portion 54. Therefore, the number of unnecessary evacuation steps can be reduced, and the workpiece 40 can be conveyed more efficiently. Since the conveyance of the workpiece 40 can be performed more efficiently, the time taken to convey the workpiece 40 can be reduced. Therefore, the cost for conveying the workpiece 40 can be reduced.
As described above, according to the conveying method of the present embodiment, when the plurality of workpieces 40 stay at the positions around the holding position 51a, it is possible to detect this. When the stagnation of the plurality of workpieces 40 is detected, the plurality of workpieces 40 are retracted to the retraction unit 54, and the plurality of workpieces 40 can be excluded from the conveyance path. This enables the conveyance and boxing of the workpieces 40 conveyed later, and the conveyance and boxing of the workpieces 40 can be performed continuously.
(other embodiments)
In the above-described embodiment, the end-side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 are configured as optical sensors including a light-emitting portion and a light-receiving portion, and using LEDs as the light-emitting portion. However, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment. Other optical configurations may be used for the light emitting section and the light receiving section. For example, the light emitting unit may emit a laser beam. Any light emitting unit and light receiving unit may be used as long as the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 can be detected between the light emitting unit and the light receiving unit.
The tip-side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 may be mechanical sensors. Fig. 20 shows a plan view for an example using a mechanical sensor as the tip-side sensor 55.
As shown in fig. 20, a sensor member 57 is disposed in a region sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 and the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52. The sensor member 57 is configured such that an abutting portion 57a abutting against the workpiece 40 is rotatable about a rotation shaft 57 b. Further, the sensor member 57 includes: and a detection section 57c which comes into contact with the contact section 57a and detects that the workpiece 40 comes into contact with the contact section 57 a. The detection portion 57c is configured such that the contact portion 57a comes into contact with the contact portion 57a when the contact portion 57a rotates about the rotation shaft 57b, and can detect that the contact portion 57a comes into contact.
When the workpiece 40 is conveyed and reaches the region sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a of the stopper 53 and the guide surface 52a of the guide portion 52, the workpiece 40 abuts against the abutting portion 57a, and the abutting portion 57a abuts against the detection portion 57c, and this can be detected by the detection portion 57 c. Thus, when the workpiece 40 reaches the region sandwiched between the pressing portion 53a and the guide surface 52a, this can be detected by the sensor member 57.
In this way, the tip-side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 may be configured by mechanical sensors.
The tip-side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 may be mechanical sensors of different types from the sensor member 57 described above. Any other type of sensor may be used as long as the presence or absence of the workpiece 40 can be detected at each detection position. In addition, the tip-side sensor 55 and the retention sensor 56 may be different types of sensors.
Description of the reference numerals
A control portion; a handling device; a conveyor belt; a guide portion; a guide surface; 53... a stop; a pressing portion; a tip-side sensor; 56..
Claims (9)
1. A conveying device is characterized by comprising:
a conveying mechanism for conveying a workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle;
a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction;
a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and disposed such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle that is equal to or greater than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece;
a 1 st detection unit that detects whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside a region sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing unit; and
and a 1 st determination unit configured to determine that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal when the 1 st detection unit detects that the workpiece is not present at the detection position at a timing when the workpiece is conveyed to the detection position.
2. Handling device according to claim 1,
a passage detection means capable of detecting passage of the workpiece at a trigger position on an upstream side of the conveyance means in a conveyance direction from the detection position,
the timing is a time after a time taken for the workpiece to be conveyed from the trigger position to the detection position has elapsed since the passage of the workpiece at the trigger position is detected by the passage detection means.
3. A conveying device is characterized by comprising:
a conveying mechanism for conveying a workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle;
a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction;
a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and disposed such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle that is equal to or greater than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece;
a 1 st detection unit that detects whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside a region sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing unit;
a 2 nd detection means for detecting whether or not the workpiece is retained at a retention position on an upstream side of the 1 st detection means; and
and a 2 nd determination unit configured to determine that the conveyance of the workpiece is abnormal when the 1 st detection unit detects that the workpiece is not present at the detection position and the 2 nd detection unit detects that the workpiece is retained at the retention position.
4. Handling device according to claim 3,
the retention position is located upstream of the detection position and is separated from at least the workpiece by the length of the workpiece in the conveying direction.
5. The carrying device according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
the workpiece has a triangular prism shape having 3 of the acute-angled portions.
6. The carrying device according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
the stopper moving mechanism moves the stopper from a stop position at which the pressing portion stops the conveyance of the workpiece to a conveyance position at which the pressing portion does not stop the conveyance of the workpiece.
7. The carrying device according to any one of claims 1 to 6,
when it is determined that there is an abnormality in the conveyance of the workpiece, the workpiece is disposed in a retreat portion retreated from a conveyance path of the conveyance mechanism.
8. A conveying method for conveying a workpiece by using a conveying device, the conveying device comprising:
a conveying mechanism that conveys the workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle;
a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; and
a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and arranged such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or larger than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece,
the conveying method is characterized by comprising the following steps:
a 1 st detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing portion; and
a 1 st determination step of determining that there is an abnormality in conveyance of the workpiece when it is detected in the 1 st detection step that there is no workpiece at the detection position at a timing when the workpiece is conveyed to the detection position.
9. A conveying method for conveying a workpiece by using a conveying device, the conveying device comprising:
a conveying mechanism that conveys the workpiece having an acute angle portion having two surfaces intersecting at an acute angle;
a guide portion configured to guide conveyance of the workpiece conveyed by the conveyance mechanism, and configured to guide a guide surface of the workpiece to extend in a conveyance direction; and
a stopper having a pressing portion that stops conveyance of the workpiece by pressing the workpiece, and arranged such that an angle formed between the guide surface and the pressing portion is an acute angle having an angle equal to or larger than an angle of the acute angle portion of the workpiece,
the conveying method is characterized by comprising the following steps:
a 1 st detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is present at a detection position inside an area sandwiched between the guide surface and the pressing portion;
a 2 nd detection step of detecting whether or not the workpiece is retained at a retention position on an upstream side of the detection position; and
and a 2 nd determination step of determining that there is an abnormality in conveyance of the workpiece when it is detected in the 1 st detection step that the workpiece is not present at the detection position and it is detected in the 2 nd detection step that the workpiece is retained at the retention position.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017115171A JP6472485B2 (en) | 2017-06-12 | 2017-06-12 | Conveying apparatus and conveying method |
| JP2017-115171 | 2017-06-12 | ||
| PCT/JP2018/021894 WO2018230441A1 (en) | 2017-06-12 | 2018-06-07 | Conveyance device and conveyance method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111148706A true CN111148706A (en) | 2020-05-12 |
| CN111148706B CN111148706B (en) | 2021-08-10 |
Family
ID=64658661
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201880039044.1A Expired - Fee Related CN111148706B (en) | 2017-06-12 | 2018-06-07 | Conveying device and conveying method |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6472485B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20200043363A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN111148706B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI673208B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018230441A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113942812A (en) * | 2021-10-15 | 2022-01-18 | 海宁市海金照明有限公司 | LED cell-shell automatic feeding equipment |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113682766B (en) * | 2021-08-25 | 2023-05-30 | 深圳市佳康捷科技有限公司 | Robot code scanning conveying line detection method, system, device and storage medium |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0769429A (en) * | 1993-09-03 | 1995-03-14 | Mitsubishi Materials Corp | Abnormality detecting device for can transporting state |
| JPH11208864A (en) * | 1998-01-20 | 1999-08-03 | Canon Inc | Operation controller, method, and record medium |
| CN1065831C (en) * | 1995-12-25 | 2001-05-16 | Ykk株式会社 | Directional transport apparatus for parts |
| JP2008290042A (en) * | 2007-05-28 | 2008-12-04 | Anritsu Sanki System Co Ltd | Sorting apparatus |
| JP2011051763A (en) * | 2009-09-03 | 2011-03-17 | Fuji Seal International Inc | Article carrying device |
| JP2012131628A (en) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-07-12 | Showa Aluminum Kan Kk | Device for detecting abnormality of can body transport condition |
| CN105016004A (en) * | 2014-04-25 | 2015-11-04 | 新东工业株式会社 | Workpiece conveying device and workpiece conveying method |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5779843B2 (en) | 2010-05-31 | 2015-09-16 | 株式会社寺岡精工 | Boxing equipment |
-
2017
- 2017-06-12 JP JP2017115171A patent/JP6472485B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2018
- 2018-06-07 WO PCT/JP2018/021894 patent/WO2018230441A1/en active Application Filing
- 2018-06-07 KR KR1020207000459A patent/KR20200043363A/en active IP Right Grant
- 2018-06-07 CN CN201880039044.1A patent/CN111148706B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2018-06-12 TW TW107120202A patent/TWI673208B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0769429A (en) * | 1993-09-03 | 1995-03-14 | Mitsubishi Materials Corp | Abnormality detecting device for can transporting state |
| CN1065831C (en) * | 1995-12-25 | 2001-05-16 | Ykk株式会社 | Directional transport apparatus for parts |
| JPH11208864A (en) * | 1998-01-20 | 1999-08-03 | Canon Inc | Operation controller, method, and record medium |
| JP2008290042A (en) * | 2007-05-28 | 2008-12-04 | Anritsu Sanki System Co Ltd | Sorting apparatus |
| JP2011051763A (en) * | 2009-09-03 | 2011-03-17 | Fuji Seal International Inc | Article carrying device |
| JP2012131628A (en) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-07-12 | Showa Aluminum Kan Kk | Device for detecting abnormality of can body transport condition |
| CN105016004A (en) * | 2014-04-25 | 2015-11-04 | 新东工业株式会社 | Workpiece conveying device and workpiece conveying method |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113942812A (en) * | 2021-10-15 | 2022-01-18 | 海宁市海金照明有限公司 | LED cell-shell automatic feeding equipment |
| CN113942812B (en) * | 2021-10-15 | 2023-09-19 | 海宁市海金照明有限公司 | Automatic LED bulb feeding equipment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20200043363A (en) | 2020-04-27 |
| TW201919952A (en) | 2019-06-01 |
| WO2018230441A1 (en) | 2018-12-20 |
| JP2019001560A (en) | 2019-01-10 |
| TWI673208B (en) | 2019-10-01 |
| JP6472485B2 (en) | 2019-02-20 |
| CN111148706B (en) | 2021-08-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5949799B2 (en) | Parallel link robot, parallel link robot hand and parallel link robot system | |
| TWI691389B (en) | Food holding device | |
| US20190351563A1 (en) | Holding device for food | |
| KR102162311B1 (en) | robot | |
| TW201336762A (en) | Transmission apparatus and transmission method of glass substrate | |
| US20170106534A1 (en) | Transporter and transport method | |
| CN111148706B (en) | Conveying device and conveying method | |
| KR20170108154A (en) | Substrate carrying robot and substrate carrying method | |
| JP2018104004A (en) | Packaging system and its operating method | |
| TWI738829B (en) | Glass plate manufacturing method and glass plate manufacturing device | |
| JP6411852B2 (en) | Conveying device, conveying system, and conveying method | |
| US11590653B2 (en) | Method for orienting two workpieces to form a joining connection and manipulator | |
| JP2015196235A (en) | Work-piece conveyance system | |
| WO2023042649A1 (en) | Electronic component processing device | |
| WO2020040284A1 (en) | Food supply device and method for operating food supply device | |
| JP2005231712A (en) | Boxing apparatus | |
| US12115684B2 (en) | Holding device, robot, and robot system | |
| JP7443141B2 (en) | Industrial robots and industrial robot control methods | |
| JP6506375B2 (en) | Work transfer system | |
| JP2006281269A (en) | Workpiece-conveying device | |
| JP2022166656A (en) | Bag take-out method and bag take-out device | |
| TWI672261B (en) | Capping device and capping method | |
| JP6700884B2 (en) | Work transfer device | |
| JP2023053455A (en) | Industrial robot and control method for industrial robot | |
| CN118769213A (en) | Robot |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20210810 |
|
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |