CN103330545A - Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures - Google Patents
Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN103330545A CN103330545A CN2013101577721A CN201310157772A CN103330545A CN 103330545 A CN103330545 A CN 103330545A CN 2013101577721 A CN2013101577721 A CN 2013101577721A CN 201310157772 A CN201310157772 A CN 201310157772A CN 103330545 A CN103330545 A CN 103330545A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- sensor
- instrument
- tissue
- endoscope
- present
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/012—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor characterised by internal passages or accessories therefor
- A61B1/018—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor characterised by internal passages or accessories therefor for receiving instruments
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0059—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence
- A61B5/0082—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence adapted for particular medical purposes
- A61B5/0084—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence adapted for particular medical purposes for introduction into the body, e.g. by catheters
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/05—Detecting, measuring or recording for diagnosis by means of electric currents or magnetic fields; Measuring using microwaves or radio waves
- A61B5/053—Measuring electrical impedance or conductance of a portion of the body
- A61B5/0538—Measuring electrical impedance or conductance of a portion of the body invasively, e.g. using a catheter
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/41—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the immune or lymphatic systems
- A61B5/414—Evaluating particular organs or parts of the immune or lymphatic systems
- A61B5/415—Evaluating particular organs or parts of the immune or lymphatic systems the glands, e.g. tonsils, adenoids or thymus
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/41—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the immune or lymphatic systems
- A61B5/414—Evaluating particular organs or parts of the immune or lymphatic systems
- A61B5/418—Evaluating particular organs or parts of the immune or lymphatic systems lymph vessels, ducts or nodes
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/48—Other medical applications
- A61B5/4836—Diagnosis combined with treatment in closed-loop systems or methods
- A61B5/4839—Diagnosis combined with treatment in closed-loop systems or methods combined with drug delivery
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/01—Measuring temperature of body parts ; Diagnostic temperature sensing, e.g. for malignant or inflamed tissue
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B8/00—Diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves
- A61B8/13—Tomography
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
- Instruments For Viewing The Inside Of Hollow Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
An endoscopic system for in-vivo tissue characterization, using a nonirradiative electromagnetic sensor, is described. The endoscopic system is further configured to employ several follow-up procedures, for example, biopsy sampling, localized surgery, dispensing a medicament, and the like, so that on the whole, the endoscopic system provides for the early detection of cancerous and pre-cancerous tissue, in vivo, and for the application of immediate follow-up procedures to any such tissue.
Description
The application is for dividing an application, and the applying date of original application is on January 4th, 2006, and application number is 200680006513.7 (PCT/IL2006/000015), and denomination of invention is " endoscopic system of in-vivo procedures ".
Invention field and background
The present invention relates to characterize with radiationless electromagnetic transducer the endoscopic system of in-vivo tissue.
The influence of cancer is very big.Although expended a large amount of financial resources and manpower, the medical science target of early discovery malignant tumor still fails to realize.Though if known a lot of cancer early discovery is treatable, owing to lack reliable screening procedure, cause to find and to treat these cancers.
There is various ways in the endoscope that uses at present.For example, usually with the different colonic diseases of colonoscope diagnosis.For the operator, the far-end of representative colonoscope comprises light source, video chip and suction channel.But these elements all contact by ensconcing steel wire in the musical form pipeline and passage and colonoscope near-end.Far-end is inserted patient's rectum, can operate along colon length.Colonoscope enough can be inserted patient's colonic deeply, make far-end enter patient's caecum.Also can handle the colonoscope top and enter terminal ileum by ileocecal valve.
Colonoscope only provides the visual pattern of the colon regions that is directly adjacent to light source and video chip, has to the visual information of fraction colon regions at any given time.Usually determine the infringement of patient's colon by the whole colons of propelling property ground perusal, this process is brought misery for the patient.Yet the single colonoscopy is not enough to determine the source of RCH usually, and this source is generally sporadic, preferably locatees through observing whole colons after a while under many circumstances.
When making colonoscopy, the various adnexaes of colonoscope can carry out the minor operation operation, as biopsy.
The splanchnoscopy of small intestinal also comes out.For example, authorize the United States Patent (USP) 5 of Shan, 984,860, be entitled as " Pass-throughduodenalenteroscopicdevice (by duodenal intestinal mirror device); " its disclosure is attached to herein by reference, describes absorbable tether intestinal mirror camera, utilizes natural small intestinal contraction wave to impel it to pass through small intestinal with the speed that is same as any other object therein.Camera is included in the light source of its front end.Be enclosed within camera lens and light source outer be transparent inflatable bladders, be used for the small intestinal in expansion next-door neighbour camera the place ahead lightly, so that better the observation.When camera moved by small intestinal, path communication channel and light source cable launched in the camera back by aperture.After moving through small intestinal, optical cable separates automatically, and optical cable is withdrawed from from the harmonization of the stomach intestinal.Camera continues by large intestine, by patient's rectum.
Though above-mentioned endoscope can provide the instrument that enters and see the gastrointestinal tract part, can not provide the method that detects not obvious visible gastrointestinal disease.Specifically, they do not provide the method with invisible tumor-localizing and discriminating.Usually, with the naked eye be easy to locate big tumor.Yet, in the time can not with the naked eye finding tumor with sense of touch, for the success of subsequent procedures and the success of other form of therapy, must manage to be located in the tumor concealment phase.
Similarly, pulmonary carcinoma all is the major causes of death of cancer in the masculinity and femininity of Western society.Before diffusing to lymph node or other organ, if early discovery and treatment, survival rate was about 42% in 5 years.Yet, seldom early discovery.5 years survival rates in all pulmonary carcinoma stages amount to the factor that is about low 3 times of 14%-.
When symptom occurring, most of patients is just diagnosed, as carrying out bronchoscopy with the endoscope that is designed for lung especially.For example, the macroscopy bronchial wall, desirable small pieces tissue carries out biopsy.Perhaps, can carry out aspiration biopsy from lung taking-up cell by inserting a needle between the rib.Perhaps, undergo surgery resection organization for biopsy.The diagnosis of malignant tumor is carried out in laboratory usually, uses the feature of microscopy cell at the biopsy samples of excision.
Yet, the biopsy diagnosis that in laboratory, carries out and have following inherent defect based on the subsequent operation of laboratory biopsy:
I. biopsy is carried out when symptom occurs usually, and cancer is in late period;
Ii. biopsy may be taken from the tumor near zone, is not tumor itself, the false negative result that leads to errors;
Iii. the biopsy accurate location of carrying out is difficult to reproduce; With
Iv. the biopsy result can not produce immediately.
Therefore, be starved of carcinous and preceding equipment and the method for organizing of cancer of early discovery in vivo.
Summary of the invention
The present invention is used for the endoscopic system that in-vivo tissue characterizes (tissue characterization) by providing with radiationless electromagnetic transducer, successfully overcomes the shortcoming of existing known configurations.Also endoscopic system configuration is used for several subsequent operations, as biopsy sampling, local operation, dispense medicament etc., so that endoscopic system is organized before the carcinous and cancer of early discovery basically in vivo, any this type of is organized used subsequent operation immediately.
Therefore according to an aspect of the present invention, provide endoscope, it comprises:
Configuration is used for inserting the interior part of body in the body, comprising:
The radiationless electromagnetic transducer of characterizing tissues;
Communication channel (communication line) fixedly has or not the electromagnetic radiation sensor on it;
With
Outer body.
In addition, communication channel adopts the form of instrument bundle (instrument bundle).
And for the operator, the instrument bundle extends beyond endoscope's distal-most end, and can radiationless electromagnetic transducer be contacted with tissue characterize in external manipulation instrument bundle distal-most end.
In addition, part also comprises instrument channels in the body, and wherein the radiationless electromagnetic transducer with characterizing tissues inserts in the instrument channels.
And the radiationless electromagnetic transducer of characterizing tissues can take out from instrument channels, replaces with another kind of instrument.
In addition, endoscope also can comprise conduit, wherein radiationless electromagnetic transducer is inserted in the conduit, and conduit is inserted in the instrument channels.
And for the operator, the extensible endoscope's distal-most end that surpasses of conduit can be independent of endoscope's distal-most end control lead distal-most end.
In addition, the interior part of body also comprises the optical channel for optical instrument.
And the optical instrument of configuration is used for observing radiationless electromagnetic transducer.
In addition or, part also comprises second kind of instrument in the body.
And second kind of instrument is selected from optical pickocff, x-ray sensors, RF sensor, MW sensor, exothermal infrared record sensor or sonac, MR sensor, impedance transducer, temperature sensor, biosensor, chemical sensor, radioactive emission sensor and mechanical pick-up device.
In addition, second of configuration kind of instrument is used for the radiationless electromagnetic transducer of induction.
And part can move in body cavity in the body of design.
In addition, but in the body of design the part percutaneous insert to arrive body cavity.
And the endoscope of configuration can be along chamber wall characterizing tissues.
Perhaps, the endoscope of configuration organizes by penetrating outside the wall sign chamber, chamber.
In addition, body cavity is selected from oral cavity, nostril, esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, rectum, colon, bronchus, vagina, cervix uteri, urethra, bladder, uterus and blood vessel.
Perhaps, the inner lease making sleeve pipe of the body of design needle-valve inserts.
In addition, tissue characterization relates to the discovery malignant tumor.
In addition or, tissue characterization relates to the discovery precancerous condition.
Therefore according to a further aspect of the invention, provide the method for characterizing tissues, it comprises:
Radiationless electromagnetic transducer is inserted in the body; With
Characterize in-vivo tissue.
Therefore provide method in the body also on the one hand according to of the present invention, comprising:
Endoscope with instrument channels is provided;
The tissue characterization's sensor that is fixed on the communication channel is inserted in the instrument channels;
Characterizing tissues;
Take out the sensor that is used for tissue characterization;
Second kind of instrument inserted in the instrument channels, arrive by the position of characterizing tissues; With
Carry out second kind of operation with second kind of instrument.
Therefore provide method in the body also on the one hand according to of the present invention, comprising:
Endoscope with instrument channels is provided;
The tissue characterization's sensor that is fixed on the communication channel is inserted in the instrument channels;
Be fixed on sensor on the communication channel extend beyond instrument channels in one's power outside;
Characterizing tissues;
Seal wire is inserted by the position of characterizing tissues;
Take out tissue characterization's sensor;
Along seal wire second kind of instrument inserted instrument channels, make arrival by the position of characterizing tissues; With
Carry out second kind of operation with second kind of instrument.
Therefore provide the method for tissue characterization also on the one hand according to of the present invention, comprising:
Seal wire is inserted in the body;
Tissue characterization's sensor that will be fixed on the communication channel along seal wire inserts in the body; With
Characterize tissue with sensor.
Therefore provide endoscopic system also on the one hand according to of the present invention, it comprises:
Configuration is used for inserting the interior part of body in the body, comprising:
The radiationless electromagnetic transducer of characterizing tissues;
Communication channel fixedly has or not the electromagnetic radiation sensor on it; With
Outer body;
Control unit; With
Signal analyzer.
Unless otherwise defined, otherwise be used for implication identical with one skilled in the art's common sense of the present invention all of whole scientific and technical terminologies of this paper.Although similar or be equal to that those methods described herein and material can be used for implementing or test the present invention, suitable method and material are described hereinafter.Under the situation of conflict, with the edition with parallel text patent specification, comprise definition.In addition, material, method and embodiment only are used for illustrating, and are not to plan to limit it.
The accompanying drawing summary
This paper only by the mode of embodiment, is described with reference to the drawings the present invention.Now at length specifically with reference to the accompanying drawings, be stressed that details passes through the mode of embodiment and show, purpose only is used for illustrative the preferred embodiments of the invention is discussed, and furnishes us with the description of thinking to the most effective and easy understanding of principle of the present invention and concept aspect.In this, do not attempt showing than basic comprehension more detailed CONSTRUCTED SPECIFICATION of the present invention required for the present invention, those skilled in the art know that among the figure and describe how in practice several forms of the present invention to be specialized.
In the drawings:
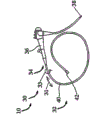
Figure 1A and 1B illustrate overall endoscope system according to embodiments of the present invention with figure;
Fig. 2 illustrates part in the body of endoscope according to embodiments of the present invention with figure;
Fig. 3 A-3C illustrates distal top and the synergism between distal top sensor and optical instrument in the body of endoscope according to embodiments of the present invention with figure;
Fig. 3 D-3H illustrates the different embodiments of the interior part of body of endoscope of the present invention with figure;
Fig. 4 A-4D further specifies endoscopic system according to embodiments of the present invention;
Fig. 5 A-5D general introduction is in vivo different move modes according to an embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 6 A-6D with figure explanation according to an embodiment of the present invention with the tissue characterization of at least a additional operations pairing;
Fig. 7 A and 7B are with the figure explanation tissue characterization that other embodiment and at least a additional operations match according to the present invention; With
Fig. 8 A-8C inserts sensor along seal wire according to an embodiment of the present invention with the figure explanation.
The description of preferred embodiment
The present invention relates to characterize with radiationless electromagnetic transducer the endoscopic system of in-vivo tissue.The endoscopic system of configuration also can carry out several subsequent operations, as biopsy sampling, local operation, dispense medicament etc., so that endoscopic system is organized before the carcinous and cancer of early discovery basically in vivo, any this type of is organized used subsequent operation immediately.
With reference to the accompanying drawings and the description followed can understand principle and the operation of equipment and method according to embodiments of the present invention better.
Before in detail explaining at least one embodiment of the present invention, be to be understood that application of the present invention is listed in being not limited to describe hereinafter or figure shown in the formation of assembly and the details of arrangement.The present invention can have other embodiment, perhaps can or carry out by variety of way enforcement.And, be to be understood that wording and term that the present invention uses are intended to describe, and should not be considered as limitation of the present invention.
With reference now to accompanying drawing,, Figure 1A and 1B illustrate overall endoscope system 10 according to embodiments of the present invention.
In addition, endoscopic system 10 comprises endoscope 30, and it has for the outer body 34 (preferably including manipulator 36) of handling endoscope 30 and is used for the adapter 38 that connector is controlled device 20 outward.
And endoscope 30 comprises part 32 in the body, it is designed for inserts in the body as insert in intracavity or the sleeve pipe needle-valve, but form musical form pipeline 40, and this pipeline has the top 42 that is in the distally for operator's (not shown).
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 2 illustrates part 32 in the body of endoscope 30 according to embodiments of the present invention with figure.
But the musical form pipeline 40 of part 32 comprises instrument channels 44 in the preferred body.In addition, the sensor 52 with configuration inserts in the instrument channels 44, preferably within conduit 48.Sensor 52 is fixed on the communication channel 50 of transmitting signal, is preferably formed instrument bundle 50.Instrument bundle 50 can comprise feed cable, the communication channel of transmitting signal, data cable and machinery control cable.
Perhaps, sensor 52 can be the radiationless electromagnetic transducer of characterizing tissues, and as described in the U.S. Patent application of owning together 60/665,842, it is open to be attached to herein by reference.U.S. Patent application 60/665,842 describe the sensor of characterizing tissues, comprise: the resonant element that forms conductive structure, configuration is used for recently being placed on by the edge of characterizing tissues, penetrate tissue not, have diameter equivalent D, it limits the area of section of resonant element on the plane that is basically parallel to the edge; With at least a lead of getting in touch with external system that provides, wherein Pei Zhi resonant element is at the free gas wave-length coverage internal resonance of about λ to about 10 λ, wherein λ at least about 10 times to diameter equivalent D, wherein receiving about λ to the signal of about 10 λ scopes, the sensor of configuration is the zone nearby, tissue is induced electromagnetic field, near zone is for beginning the hemisphere scope that diameter is essentially D from the edge, but can ignore away from area radiation, so that the tissue of near zone is effectively brought into play the function of resonant element part, sensor is produced different resonance responses, therefore characterize the tissue of near zone by the electromagnetic property to the resonance response of sensor.
Should understand according to embodiment of the present invention, can use other electromagnetic transducer.
Also comprise and be fixed on optical channel 46 for optical instrument 43 on the optical communication channel 45 but should understand usually musical form pipeline 40, be preferably formed optical fibers 45.Perhaps, can use the light guide bundles (optical hundle) 45 that comprises as feed cable, optical data cable and machinery control cable.
Preferably with optical instrument 43 from visually and with sensor 52 carrying out tissue characterization.Yet the present invention also can not need optical channel 46 and optical instrument 43 to operate.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 3 A-3C illustrates distal top 42 in the body of endoscope 30 according to embodiments of the present invention with figure, and the synergism between sensor 52 and the optical instrument 43.
Preferred conduit 48 has distal top 47, its extensible distal top 42 that surpasses endoscope.In addition, shown in Fig. 3 A-3C, can be independent of pipeline 40 by instrument bundle 50 control leads 48, but so that the ad-hoc location of sensor 52 contact tissues 60, as body cavity walls or another kind of tissue location, be used for characterizing suspicious unusual 62, shown in Fig. 3 A and 3B.Known can machinery (as passing through seal wire) or electric control lead 48.
In addition, but the healthy part (shown in Fig. 3 C) of sensor 52 contact tissues 60 to characterize reference tissue.
Perhaps, do not use conduit 48, instrument bundle 50 is the extensible top 42 that surpasses the endoscope distally still, can make sensor 52 contact tissues 60 in the distal-most end of external manipulation instrument bundle 50, is used for characterizing.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 3 D-3H illustrates the different embodiments of the interior part 32 of body of endoscope 30 of the present invention with figure.
Fig. 3 D describes another embodiment, does not wherein use conduit 48, and the sensor 52 that is fixed on the instrument bundle 50 is directly inserted in the instrument channels 44.
Fig. 3 E describes another embodiment, but wherein musical form pipeline 40 has single chamber, forms instrument channels 44.Do not use optical channel 46.
Fig. 3 F describes another embodiment, but wherein instrument bundle 50 is merged into an integral body (integrated) with musical form pipeline 40.
Fig. 3 G describes another embodiment, but wherein instrument bundle 50 forms musical form pipeline 40 with light guide bundles 45.
Fig. 3 H describes another embodiment, and wherein part 32 has two passages in the body, and sensor 52 is the mobile instrument channels 44 that is fixed on the instrument bundle 50 therein, and second kind of instrument 84 can insert second passage 88 on the instrument bundle 82 of being fixed on wherein.
Second kind of sensor 84 can be known optical pickocff, x line sensor, RF sensor, MW sensor, exothermal infrared record sensor, sonac, MR sensor, impedance transducer, temperature sensor, biosensor, chemical sensor, radioactive emission sensor, mechanical pick-up device and (or) any in the another kind of tissue characterization sensor.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 4 A-4D further specifies the interior part 32 of body of endoscope 30 according to embodiments of the present invention.
Shown in Fig. 4 A, endoscope 30 can be inserted body cavity 64, characterize the tissue 60 of the wall that forms body cavity 64.Can insert by health opening 66, as mouth, nose or Another Body opening or hole.
Shown in Fig. 4 B, when body cavity 64 is blood vessel, can insert endoscope 30 by skin 68 percutaneous, insert body cavity 64 then, characterize the tissue 60 of the wall that forms body cavity 64.
In addition, shown in Fig. 4 B, the tissue that is characterized can be positioned at tube chamber infall 65.
Shown in Fig. 4 C and 4D, as when the minimally invasive surgical, can insert endoscopies 30, characterizing tissues 60 through sleeve pipe needle-valve 35 by skin 68.
According to embodiment of the present invention, when minimally invasive surgical, the tissue 60 that characterizes with sensor 52 can be body cavity 64 wall and (or) wall or the open human body of infall, accessibility other body cavity of body cavity (as stomach or uterus).In addition, tissue characterization can comprise and penetrates body cavity and characterizing tissues piece.
According to an embodiment, can be substantially 64 import sensors 52, characterizing tissues 60 along the body cavity total length along body cavity.
Perhaps, can sensor 52 be imported characterizing tissues 60 along body cavity 64 along its predetermined portions.
In addition or, optical instrument 43 can be suspicious unusual 62 from visually finding, control pick-up 52 is in order to contact suspicious unusual 62 and to its sign.
In addition or, other imaging pattern such as x line, MRI, ultrasonic or another kind of Noninvasive mode detection are suspicious unusual 62, control pick-up 52 is so that contact and characterize it.
Perhaps, shown in Fig. 4 C and 4D, in the operation of minimally-invasive, available following dual mode uses sensor 52:
Ii. excising with surgical unit 70, characterize the wall of otch 72 at unusual 62 o'clock, guarantee that it is formed by health tissues, unusual 62 comprise within it.
Should understand endoscope 30 can be multichannel endoscope, so that several instrument such as optical instrument 43, sensor 52 and another kind of instrument such as surgical unit 70 can be operated together.Perhaps, as required, can only use one or two passage, pull out instrument and replace with Other Instruments.
On other imaging pattern such as x line, ultrasonic and MRI, preferred sensor 52 is observable, available another kind of imaging pattern guiding in order to it can be directed to the zone that optical instrument 43 can not arrive, perhaps is directed to it this zone under the situation of not using optical instrument 43.
The diameter of preferred conduit 48 is about 0.5-4mm, and the diameter of sensor 52 is about 0.3-3mm, and the diameter of instrument bundle is about 2mm, and part 32 is about 2-5mm in the body.Should understand same available other greater or lesser size.
Preferably measure by near the reflection of the electromagnetic fields sensor 52, as it is described to authorize the United States Patent (USP) of owning together 6,813,515 of Hashimshony, it is open to be attached to herein by reference.Perhaps, according to U.S. Patent application 60/665,842 described measurement of owning together, it openly is attached to herein by reference.Should understand according to embodiment of the present invention, also available other electromagnetic transducer.
The control unit 22 of the outer control station 20 of preferred body is analyzed reflection and is shown the result.Should understand available another known computer.The result can be used for characterizing tissues 60, as chamber wall 60 (as bronchial wall 60) and unusual 62.Should understand the tissue part that tissue 60 can right and wrong chamber wall part, shown in following texts and pictures 5C and the 5D.Available diagram, numeral or positive or negative answer show the result.Available literal expression result also.
The result can be relative, that is to say, unusual 62 dissimilar and reference tissues 60 or take from comparison between several reference tissues 60 of diverse location.Perhaps, the result can written historical materials be the basis, wherein according to previous test and (or) the data characterizing tissues found in the document.
Tissue characterization about unusual 62 can relate to discovery malignant tumor or precancerous condition.In addition or may relate to and find another kind of pathological changes, as internal hemorrhage.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 5 A-5D summarizes according to embodiment of the present invention, the different modes that endoscopic system moves in vivo.
Shown in Fig. 5 A, but the musical form pipeline 40 of endoscope 30 is mobile in body cavity 64, along chamber wall characterizing tissues 60.Inlet point is the hole of health, as the hole of oral cavity, nostril, rectum mouth, vaginal orifice, urethral orifice or another body of placing oneself.
Shown in Fig. 5 B, but the musical form pipeline 40 of endoscope 30 is mobile in body cavity 64 fully, but enters at inlet point 74 percutaneous.Preferred sensor 52 and sharp edge 76 associatings are convenient to enter.For example, tube chamber can be blood vessel, and inlet point can be femoral vein or jugular vein.Should understand equally can be with other percutaneous inlet point.
Shown in Fig. 5 C, inlet point is the hole of health, but in order to characterize the tissue 60 outside the tube chamber 64, makes sensor 52 penetrate tube chamber 64 at point 72.Preferred sensor 52 moves to the point close to as far as possible from the measuring point at intracavity, penetrates tube chamber then.Preferred sensor 52 and sharp edge 76 associatings are convenient to penetrate.
Shown in Fig. 5 D, sensor 52 enters tube chamber at inlet point 74 percutaneous, penetrates tube chamber 64 at point 72, characterizes the tissue 60 outside the tube chamber 64.λ
Point out the biopsy diagnosis that carries out at laboratory and have following inherent defect based on the subsequent operation of laboratory biopsy:
I. biopsy is carried out when symptom occurs usually, and cancer is in late period;
Ii. biopsy may be taken from the tumor near zone, is not tumor itself, the false negative result that leads to errors;
Iii. the biopsy accurate location of carrying out is difficult to reproduce; With
Iv. the biopsy result can not produce immediately.
In case the present invention aims to provide and finds in vivo to organize before the carcinous and cancer then carry out the application of subsequent operation immediately.Therefore, be provided at note abnormalities after, auxiliary instrumentation is inserted the method that is characterized the position.Available these instruments by other sensor add sign, biopsy sampling, carry out local operation, dispense medicament and (or) other operation.In conjunction with Fig. 6 A-6D and 7A-7B these methods are described hereinafter.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 6 A-6D is with the another kind of according to embodiments of the present invention tissue characterization of figure explanation method, preferably with at least a additional operations pairing.
In some cases, endoscope is subject to the diameter of its about 2-3mm in one's power, yet the sensor 52 that need be fixed on the instrument bundle 50 extends beyond it, and its diameter can be as small as about 0.3mm.
Therefore, as shown in Figure 6A, sensor 52 extends beyond the distal top 42 of instrument channels 44, unusual 62 of characterizing tissues 60.
Shown in Fig. 6 B, seal wire 80 is inserted the position that instrument channels 44 arrives sensor 52.
Shown in Fig. 6 C, characterize the back and take out sensor 52.
Shown in Fig. 6 D, the second kind of instrument 84 that is fixed on second kind of instrument bundle 82 inserted in the instrument channels 44, arrive the position of sensor 52, carry out a kind of at least additional operations at tissue 60.Available at least a additional operations by another kind of sensor add sign, biopsy sampling, carry out local operation, dispense medicament and (or) another kind of operation.
Should understand and then can take out second kind of instrument 84, still can insert another kind of instrument in its position.
Should understanding not, movable sensor 52 inserts second kind of instrument 84.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 7 A and 7B according to another embodiment of the invention, carry out second kind operation without seal wire with the figure explanation.
Shown in Fig. 7 A, carry out tissue characterization with sensor 52.
Shown in Fig. 7 B, then take out sensor 52, insert the second kind of instrument 84 that is fixed on second kind of instrument bundle 82, carry out second kind of operation with second kind of instrument 84 at the sign position.
Second kind of instrument 84 of Fig. 6 D and 7B can be biopsy instrument (as biopsy brush, pin or cutter), local surgical unit (as by as ultrasonic, RF, MW or the excision of another kind of part cutting method, part excision, perhaps by cryosurgery, laser surgery etc.), send out medicine instrument (as dispense medicament or implantable brachytherapy radiotherapy nuclear) or be used for other characterize and (or) instrument for the treatment of operation.
Should understand second kind of instrument 84 and can be second kind of sensor 84 by second kind of pattern characterizing tissues.Second kind of sensor 84 can be known any optical pickocff, x line sensor, RF sensor, MW sensor, exothermal infrared record sensor, sonac, MR sensor, impedance transducer, temperature sensor, biosensor, chemical sensor, radioactive emission sensor, mechanical pick-up device and (or) another kind of tissue characterization sensor.
Again with reference to the accompanying drawings, Fig. 8 A-8C inserts sensor along seal wire according to an embodiment of the present invention with the figure explanation.
Shown in Fig. 8 A, seal wire 80 is inserted in the body.
Shown in Fig. 8 B and 8C, the sensor 52 usefulness wire loops 86 that are fixed on the instrument bundle 50 are wrapped on the seal wire 80, insert in the body along seal wire 80.
According to embodiment of the present invention, the endoscope 30 of design can insert body cavity, as oral cavity, nostril, esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, rectum, colon, bronchus, vagina, cervix uteri, urethra, bladder, uterus and blood vessel or another kind of body cavity.In addition or, the endoscope of design can insert the sleeve pipe needle-valve.
Hope can be developed relevant device and method that multiple usefulness is fixed on the electromagnetic probe characterizing tissues in body cavity on the endoscopic apparatus the patient in life, and scope of the present invention is intended to comprise existing all this type of new techniques.
When being used for this paper, term " about " refers to ± 20%.
For clarity sake, should understand some feature of the present invention that is described in independent embodiment text also can make up in single embodiment and provide.On the contrary, for the sake of simplicity, the of the present invention various features that are described in single embodiment text also can provide separately or close with any suitable subgroup and provide.
Though be described in conjunction with a specific embodiment thereof the present invention, obviously those skilled in the art will know numerous variations, modification and change.Therefore, be intended to comprise the theme that drops on accessory claim and all these type of changes, modification and the change within the broad range.
All bulletins, patent and patent application that this description is mentioned all are attached in the description by reference at this paper, are attached to by reference herein if each concrete bulletin, patent or patent application are mentioned especially and specifically, and be then suitable equally.In addition, any reference any quotes or confirms should not to be considered as admitting that this type of is with reference to being the effective prior art of the present invention in the application's book.
Claims (1)
1. endoscope, it comprises:
Part in the body, its configuration is inserted in the body and is comprised:
The radiationless electromagnetic transducer of characterizing tissues, described sensor is applied to tissue with electric pulse, produce electric fringing field at tissue regions thus, thereby generation reflected impulse, the amount of radiation of penetrate tissue itself can be ignored, the electric pulse of described sensor detection of reflected, and will reflect the electrical feature of electric pulse and used electric pulse relatively, obtain examine and organize the dielectric property reading; And
Communication channel fixedly has or not the electromagnetic radiation sensor on it; With
Outer body.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US64108105P | 2005-01-04 | 2005-01-04 | |
| US60/641,081 | 2005-01-04 | ||
| US66584205P | 2005-03-29 | 2005-03-29 | |
| US60/665,842 | 2005-03-29 |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200680006513.7A Division CN101252878B (en) | 2005-01-04 | 2006-01-04 | Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN103330545A true CN103330545A (en) | 2013-10-02 |
Family
ID=36647864
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2013101577721A Pending CN103330545A (en) | 2005-01-04 | 2006-01-04 | Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures |
| CN200680006513.7A Expired - Fee Related CN101252878B (en) | 2005-01-04 | 2006-01-04 | Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200680006513.7A Expired - Fee Related CN101252878B (en) | 2005-01-04 | 2006-01-04 | Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1843696A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2008526347A (en) |
| CN (2) | CN103330545A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2594427A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2006072947A2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109475377A (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2019-03-15 | 奥林巴斯株式会社 | Medical instrument line and medical instrument |
Families Citing this family (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7505811B2 (en) | 2001-11-19 | 2009-03-17 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Method and apparatus for examining tissue for predefined target cells, particularly cancerous cells, and a probe useful in such method and apparatus |
| US20070255169A1 (en) * | 2001-11-19 | 2007-11-01 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Clean margin assessment tool |
| US8116845B2 (en) | 2005-08-04 | 2012-02-14 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Tissue-characterization probe with effective sensor-to-tissue contact |
| WO2005089065A2 (en) | 2004-03-23 | 2005-09-29 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Clean margin assessment tool |
| US7904145B2 (en) | 2004-03-23 | 2011-03-08 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Clean margin assessment tool |
| US9750425B2 (en) | 2004-03-23 | 2017-09-05 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Graphical user interfaces (GUI), methods and apparatus for data presentation |
| US8092384B2 (en) * | 2006-09-28 | 2012-01-10 | Tyco Healthcare Group Lp | System and method for continuous detection of an analyte in bloodstream |
| US8147423B2 (en) | 2007-03-01 | 2012-04-03 | Dune Medical Devices, Ltd. | Tissue-characterization system and method |
| US20090043184A1 (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2009-02-12 | Edwards Lifesciences Corporation | Catheter and probe for measuring analytes or other parameters |
| EP2228003A1 (en) * | 2009-03-13 | 2010-09-15 | Jürgen Blume | Multifunctional endoscopic device and methods employing said device |
| CN102100529B (en) * | 2010-12-10 | 2013-04-24 | 广州宝胆医疗器械科技有限公司 | Integrated infrared thermally scanning esophagoscope system |
| CN102100526B (en) * | 2010-12-10 | 2012-11-21 | 广州宝胆医疗器械科技有限公司 | Electronic esophagoscope system with infrared thermally scanning function |
| CN102100538B (en) * | 2010-12-10 | 2012-11-21 | 广州宝胆医疗器械科技有限公司 | Colonoscope system with infrared thermally scanning function |
| BR112013031872A2 (en) * | 2011-06-15 | 2016-12-13 | Koninkl Philips Nv | magnetic resonance spectroscopy set |
| EP3220809A4 (en) * | 2014-11-21 | 2018-07-11 | Elwha LLC | Systems to monitor body portions for injury after impact |
| CN104720752B (en) * | 2015-02-13 | 2017-09-15 | 亚太仿生学有限公司 | A kind of detector and system and device for thermal imaging inside cavity structure |
| CN105125238B (en) * | 2015-09-02 | 2018-03-02 | 上海爱声生物医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of transurethral bladder supersonic detection method, diagnostic equipment and transducer |
| CN108837283A (en) * | 2018-04-12 | 2018-11-20 | 上海市东方医院 | Stem bronchi cell precise positioning slow-released system |
| WO2020093239A1 (en) * | 2018-11-06 | 2020-05-14 | Shenzhen Xpectvision Technology Co., Ltd. | Apparatus for imaging the prostate |
| CN111543991A (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-18 | 华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院 | Gastrointestinal tract mucous epithelium electrical impedance measurement and evaluation device |
| CN113057570B (en) * | 2021-03-16 | 2023-06-02 | 上海微创微航机器人有限公司 | Bronchoscope, scope holding arm, controllable sheath, operation method and patient end device |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1106246A (en) * | 1993-11-01 | 1995-08-09 | 波拉技术有限公司 | Method and apparatus for tissue type recognition |
| US6055451A (en) * | 1997-12-12 | 2000-04-25 | Spectrx, Inc. | Apparatus and method for determining tissue characteristics |
| CN1341003A (en) * | 1999-01-26 | 2002-03-20 | 牛顿实验室公司 | Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy |
| US20030130575A1 (en) * | 1991-10-18 | 2003-07-10 | Ashvin Desai | Method and apparatus for tissue treatment with laser and electromagnetic radiation |
| US20030187366A1 (en) * | 2002-01-04 | 2003-10-02 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Method and system for examining tissue according to the dielectric properties thereof |
| WO2004032621A2 (en) * | 2002-08-01 | 2004-04-22 | The Johns Hopkins University | Techniques for identifying molecular structures and treating cell types lining a body lumen using fluorescence |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS53100691A (en) * | 1977-02-16 | 1978-09-02 | Kogyo Gijutsuin | Method of and device for inspecting living tissue surface by microwave |
| JP2615301B2 (en) * | 1991-04-02 | 1997-05-28 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | Electronic laparoscope |
| CA2142338C (en) * | 1992-08-14 | 1999-11-30 | John Stuart Bladen | Position location system |
| US5227730A (en) * | 1992-09-14 | 1993-07-13 | Kdc Technology Corp. | Microwave needle dielectric sensors |
| JP3276197B2 (en) * | 1993-04-19 | 2002-04-22 | 旭光学工業株式会社 | Endoscope |
| US6004263A (en) * | 1996-03-13 | 1999-12-21 | Hihon Kohden Corporation | Endoscope with detachable operation unit and insertion unit |
| JPH09243576A (en) * | 1996-03-13 | 1997-09-19 | Kagaku Gijutsu Shinko Jigyodan | Tomographic imaging method and apparatus by two-dimensional time region reflecting method |
| US6728565B2 (en) * | 2000-02-25 | 2004-04-27 | Scimed Life Systems, Inc. | Diagnostic catheter using a vacuum for tissue positioning |
| CA2416581A1 (en) * | 2000-07-25 | 2002-04-25 | Rita Medical Systems, Inc. | Apparatus for detecting and treating tumors using localized impedance measurement |
| US6871086B2 (en) * | 2001-02-15 | 2005-03-22 | Robin Medical Inc. | Endoscopic examining apparatus particularly useful in MRI, a probe useful in such apparatus, and a method of making such probe |
| ATE343347T1 (en) * | 2001-07-26 | 2006-11-15 | Medrad Inc | ELECTROMAGNETIC SENSORS FOR APPLICATIONS ON BIOLOGICAL TISSUE |
| JP4133013B2 (en) * | 2002-06-18 | 2008-08-13 | Hoya株式会社 | OCT observation probe |
-
2006
- 2006-01-04 CN CN2013101577721A patent/CN103330545A/en active Pending
- 2006-01-04 JP JP2007550012A patent/JP2008526347A/en active Pending
- 2006-01-04 WO PCT/IL2006/000015 patent/WO2006072947A2/en active Application Filing
- 2006-01-04 CN CN200680006513.7A patent/CN101252878B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2006-01-04 EP EP06700052A patent/EP1843696A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2006-01-04 CA CA002594427A patent/CA2594427A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030130575A1 (en) * | 1991-10-18 | 2003-07-10 | Ashvin Desai | Method and apparatus for tissue treatment with laser and electromagnetic radiation |
| CN1106246A (en) * | 1993-11-01 | 1995-08-09 | 波拉技术有限公司 | Method and apparatus for tissue type recognition |
| US6055451A (en) * | 1997-12-12 | 2000-04-25 | Spectrx, Inc. | Apparatus and method for determining tissue characteristics |
| CN1341003A (en) * | 1999-01-26 | 2002-03-20 | 牛顿实验室公司 | Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy |
| US20030187366A1 (en) * | 2002-01-04 | 2003-10-02 | Dune Medical Devices Ltd. | Method and system for examining tissue according to the dielectric properties thereof |
| WO2004032621A2 (en) * | 2002-08-01 | 2004-04-22 | The Johns Hopkins University | Techniques for identifying molecular structures and treating cell types lining a body lumen using fluorescence |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109475377A (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2019-03-15 | 奥林巴斯株式会社 | Medical instrument line and medical instrument |
| CN109475377B (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2021-04-20 | 奥林巴斯株式会社 | Medical instrument wire and medical instrument |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CA2594427A1 (en) | 2006-07-13 |
| WO2006072947A2 (en) | 2006-07-13 |
| JP2008526347A (en) | 2008-07-24 |
| EP1843696A2 (en) | 2007-10-17 |
| CN101252878A (en) | 2008-08-27 |
| EP1843696A4 (en) | 2010-01-06 |
| WO2006072947A8 (en) | 2006-09-28 |
| WO2006072947A3 (en) | 2007-09-07 |
| CN101252878B (en) | 2013-06-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101252878B (en) | Endoscopic system for in-vivo procedures | |
| US20080154090A1 (en) | Endoscopic System for In-Vivo Procedures | |
| ES2704827T3 (en) | Tissue characterization probe with effective sensor to tissue contact | |
| US8206315B2 (en) | Real-time pathology | |
| US6296608B1 (en) | Diagnosing and performing interventional procedures on tissue in vivo | |
| US8024027B2 (en) | Infrared endoscopic balloon probes | |
| CN101437455B (en) | Tissue-characterization probe with effective sensor-to-tissue contact | |
| Neuhaus et al. | Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of early neoplastic gastric lesions using a new double-channel endoscope (the” R-scope”) | |
| US6741884B1 (en) | Infrared endoscopic balloon probes | |
| US7904145B2 (en) | Clean margin assessment tool | |
| US20100280409A1 (en) | Real-time pathology | |
| JPH04500619A (en) | Medical detection method and device using fiber bundles for remote optical transmission | |
| CN109349982A (en) | Multi-modal Cholangiopancreatogrinhy system | |
| JP2002113018A (en) | System for detecting internal body position | |
| Roberts‐Thomson et al. | The future of endoscopy | |
| Hawes et al. | Endoscopic ultrasonography of the pancreas | |
| Balci et al. | Exploring breast with therapeutic ductoscopy | |
| Katanuma et al. | The difference in the capability of delineation between convex and radial arrayed echoendoscope for pancreas and biliary tract; case reports from the standpoint of both convex and radial arrayed echoendoscope | |
| JP2575395B2 (en) | Antenna device for NMR measurement | |
| CN209529081U (en) | Multi-modal Cholangiopancreatogrinhy system | |
| Leeds et al. | Investigating pancreaticobiliary disorders through the use of endoscopic ultrasound | |
| Bigio et al. | Elastic scattering spectroscopy for detection of prostate cancer: preliminary feasibility study | |
| JPS63270037A (en) | Endoscope | |
| Conway et al. | Linear endoscopic ultrasound | |
| Varadarajulu et al. | Novel endoscopic tools for the evaluation of pancreatic disease: Pancreatoscopy, intraductal ultrasound, and pancreatic cyst fluid analysis |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C05 | Deemed withdrawal (patent law before 1993) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Application publication date: 20131002 |