Mars' irradiated surface is a godforsaken place.
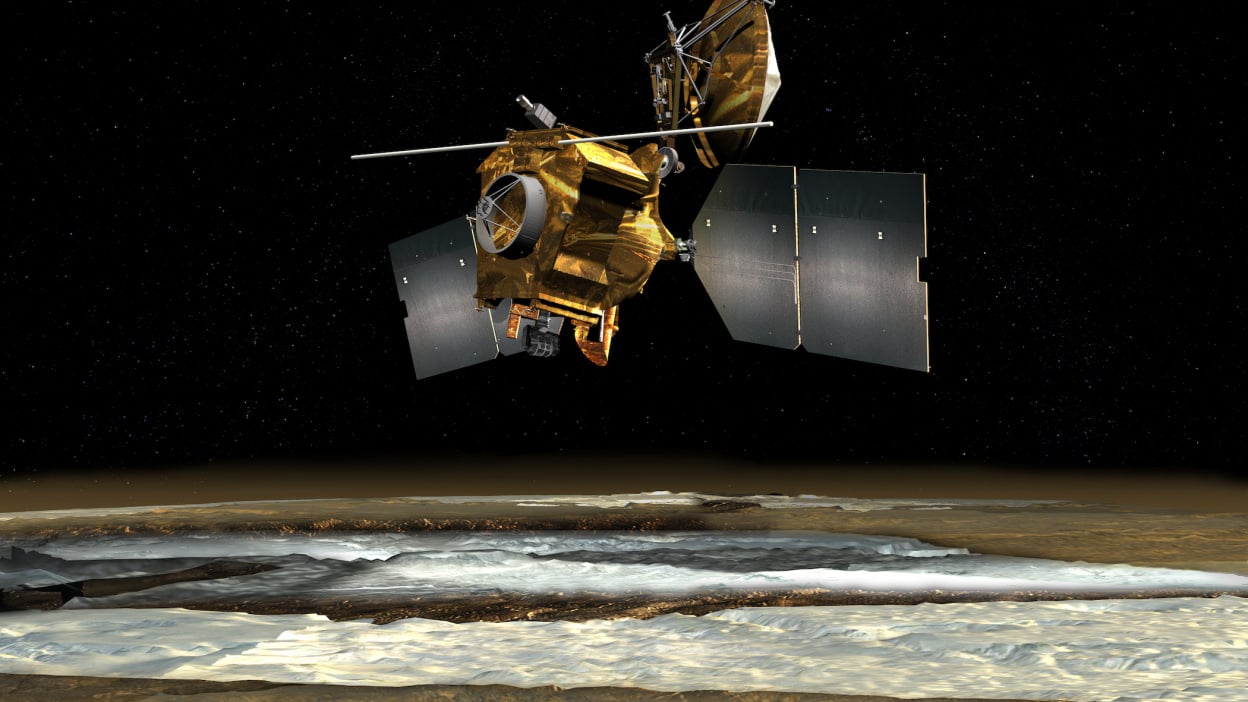
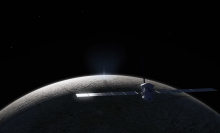
And yet there may be shallow pools of water near the Martian surface, a place 1,000 times drier than the driest desert on Earth. NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter — a satellite that's been orbiting Mars for nearly two decades — spotted white material lining dry gullies on Mars. The space agency, which recently released the image below, suspects it's dusty water ice that could heat up and form pools, similar to processes on our planet.
"Scientists believe dust particles within this ice act similarly to dust that falls onto glaciers on Earth, warming up in sunlight and causing subsurface pockets of meltwater to form," NASA explained.
"These pockets of water on our planet are often teeming with simple life, including algae, fungi, and cyanobacteria," the agency added. "Scientists believe similar shallow pools of water could exist on Mars, and may also be excellent places to search for life on the Red Planet today."
Black Friday deals you can shop right now
-
Apple AirPods Pro 2 ANC Earbuds With USB-C Charging Case — $153.99 (List Price $249.00)
-
Apple iPad 10.9" 64GB Wi-Fi Retina Tablet (2022 Release) — $249.99 (List Price $349.00)
-
Meta Quest 3S 128GB VR Headset + $75 Digital Credit — $299 With Code "QUEST75"
-
Blink Outdoor 4 1080p Security Camera (3-Pack) — $99.99 (List Price $259.99)
-
Bose QuietComfort Wireless Noise Cancelling Headphones — $199.00 (List Price $349.00)
-
Apple Watch Series 10 (GPS, 42mm, Black, S/M, Sports Band) — $329.00 (List Price $399.00)
-
Samsung Odyssey G93SC 49" Dual QHD OLED Curved Monitor — $949.99 (List Price $1599.99)
Such glacial dust on Earthly glaciers creates phenomena called "cryoconite holes," which can cover glaciers by the hundreds or more. One is depicted in the second image below.
Although the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter wields a giant camera that can "see features as small as a kitchen table" from its orbit 155 to 196 miles above the surface in space, it can't detect any potential shallow pools. But the image clearly shows the white patches on the Mars gullies in an area called Terra Sirenum. (The blue seen at the gullies' bottom is coarse sand, a color not visible with the human eye but viewed here in infrared light wavelengths.)


There are many gullies on Mars today, but they're not created by any flowing water. Rather, planetary scientists suspect that carbon dioxide frost seasonally transitions from a solid to a gas (a process called sublimation), and provides "lubrication" for Martian soil and rocks to move downhill. Blocks of ice might even sled down the sides of Martian craters or other terrain.
Mars, which has lost most of its insulating atmosphere, can't support much liquid water on its surface anymore — but there could be bounties of water deep underground.
Planetary scientists recently used unprecedented data collected by the space agency's InSight lander, which recorded geologic activity on Mars for four years, to reveal that water may exist many miles down in the Martian crust. The research, which invites further investigation, may explain where bounties of the Red Planet's water went as the world dried up, and suggests that Mars may host hospitable environs for life.
"We identified the Martian equivalent of deep groundwater on Earth," Michael Manga, a planetary scientist at UC Berkeley who coauthored the new research, told Mashable.
For now, NASA's car-sized rovers explore the past remains of Martian lakes and rivers for past habitability and potential evidence of Martian life — if it ever existed, that is.
Topics NASA