#Git Collaboration
##Learning Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to...
- Collaborate on a git project
- Use feature branches appropriately
- Fix merge conflicts
- Use Github's features effectively
##Git tools for Collaboration
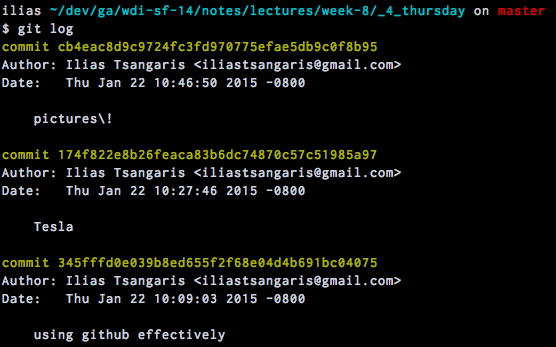
####git log
- Displays all the past commits
- Useful for viewing previous code changes and a list of individual contributions
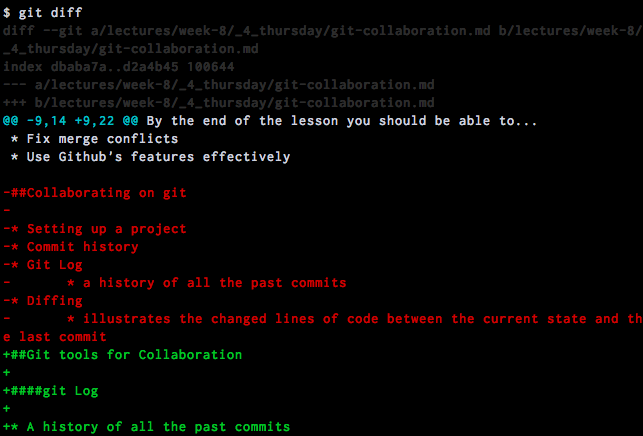
####git diff
- Illustrates the changed lines of code between the current state and the last commit
##Feature Branching
Think about Elon Musk designing a car at Tesla
- There exists a 2014 master Tesla
- Elon wants to build a 2015 concept Tesla
- In order to preserve the master, he decides that it's better to copy the master than directly modify it
- Once copied Elon can feel free to iterate without any destructive consequences as he will now always be able to revert back to the existing 2014 master
- Once Elon is satisfied he can merge the concept features into a new 2015 master Tesla
in other words...
- A branch represents an independent line of development
- New features should be developed in a branch of the repository
- Once the feature is complete & working it can be merged into the main repository
- Commands
git branch <branch_name>— creates a new branchgit checkout <branch_name>— jumps into a specified branchgit merge <branch_name> master— merges a branch into master
##Merge Conflicts
- Occurs when there are disagreeing changes between your code and a previous commit
- This needs to be resolved before you can commit your code
Example conflict:
the number of planets are
<<<<<<< HEAD
nine
=======
eight
>>>>>>> branch-a
##Using Github Effectively
####Blaming
- Points out who change which lines in a file, showing the commit message
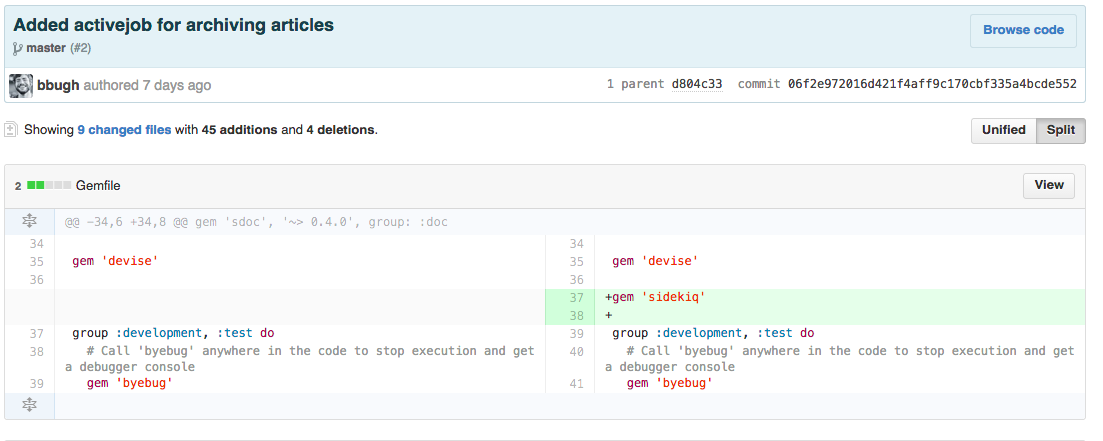
####Diffing (again)
- Displays the changed lines of code in a set of files or file
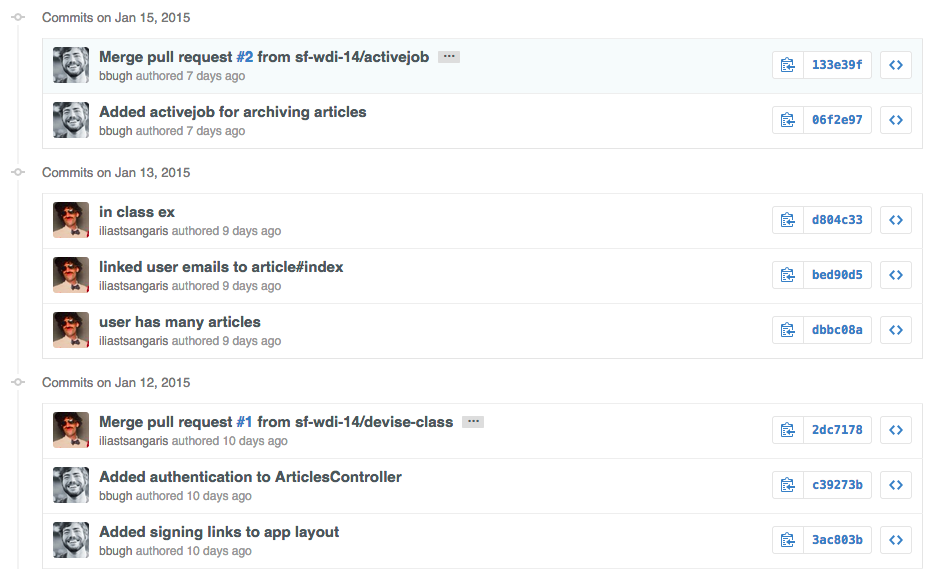
####History
- Shows readable history of all git commits and merges
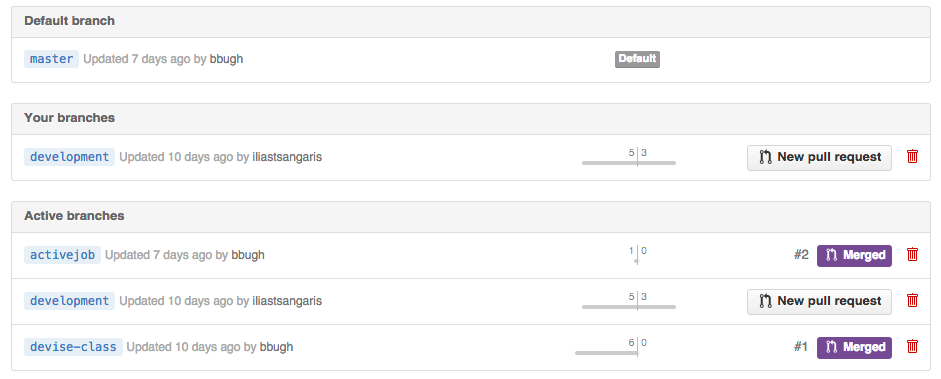
####Branches
- Enables one to view all the branches in a repository
- Again, branching is ideal for collaborating between individuals on team
####Forking
- Creates a remote clone that you now own which you can make changes to
- This is particularly useful for open source projects
- Forking is great for collaborating between separate teams
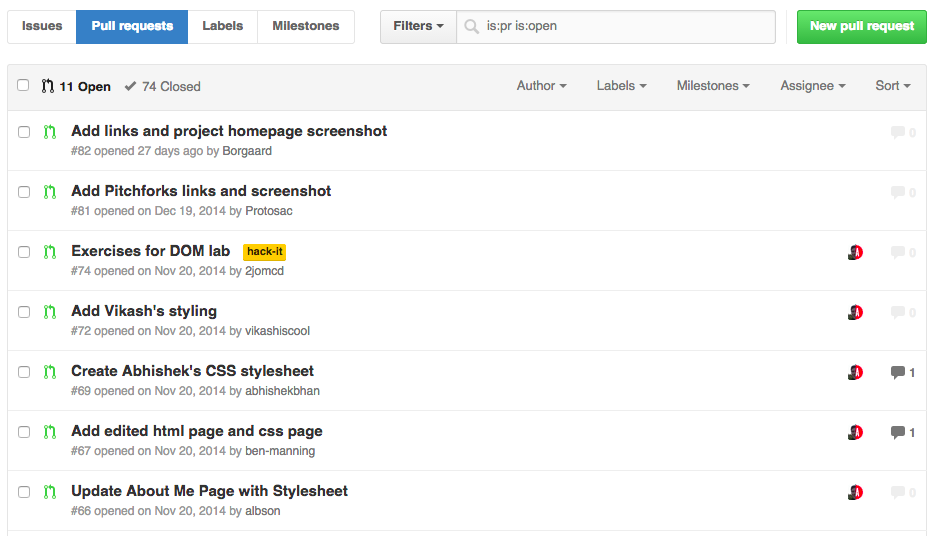
####Pull Requests
- Used to request that a forked repository is merged or "pulled" into its associated upstream repository
- This allows the upstream repository owner the discretion of which forks can be merged
- Enables one to safely and freely submit code to any public repository
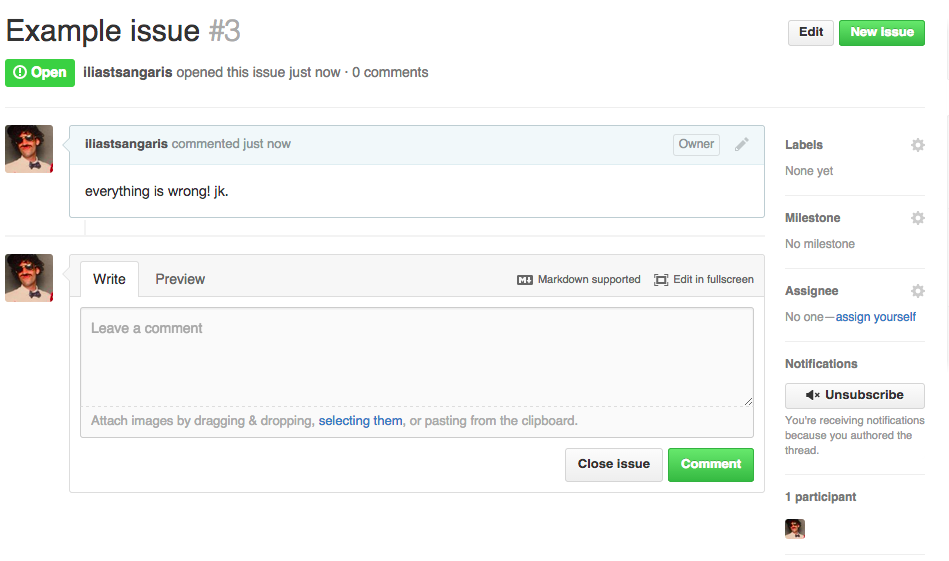
####Issues
- Anyone can submit an issue for a public repo that the owner will be made aware of
- Issues are open by anyone if they have identified a problem in the code
- Issues are closed by the project owner once the problem is solved
####Comments
- At the bottom of a specific commit, issue, or pull request you may leave a comment and @mention a user
####Wiki
- Typically used for more advanced documentation for your library; aka an expanded readme
- Also keep in mind, you can use it for whatever suits your needs best
##Additional Resources