An OS is a collection of s/w programs. It mainly controls the allocation and usage of h/w resources such as memory, CPU time, hard disk space etc.
All application programs use the OS to gain access to these hardware resources as and when they are needed.
The OS is the 1st program to be loaded into the computer when it boots & it remains in memory at all times thereafter.
Single user OS – this OS supports 1 user at a time. The user can perform one task as well as multiple tasks on the OS.
- ** For ex, MS – DOS, MS – Windows**
Multi - user OS – in this OS, multiple users can execute single task or multiple tasks at any given point of time.
- For ex, UNIX, LINUX, Windows Server OS
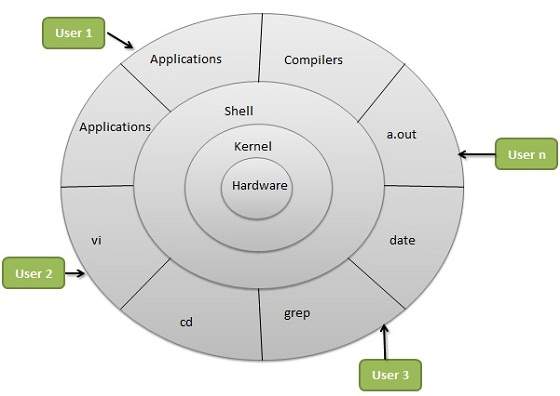
An OS is made up of 2 components, known as,
- Shell
- Kernel
The kernel is the core of an OS which manages the entire system resources The shell acts as an interface between kernel and end user or application.
In UNIX OS, the shell is very protective – hence it is more secure. Whereas, in WINDOWS, the shell is less protective and more good in usability.
UNIX was originally called MULTICS (Multiplexed Information & Computing Systems).
Then it changed to UNICS (Uniplexed Information & Computing Systems). Then it changed to UNIX – Extended version of UNICS.
UNIX is a character based OS. It has been modified into a GUI based OS called LINUX. LINUX was developed by a person named Linus Torvalds.
- Red Hat
- Mandrake (HP)
- Fedora Core
- Ubuntu
- SUSE
All files in UNIX are related to one another. The file system in UNIX is a collection of all these related files organized in a hierarchical (inverted tree like structure).
Every UNIX file system has a top, which serves as the reference point for all files. This top is called
rootand is represented by a frontslash (/). Root is actually a directory.
The root directory has a number of subdirectories under it. These subdirectories in turn have other sub directories under them.
Every file, apart from the root , must have a parent and thus it should be possible to trace the ultimate parentage of a file to a root.
-
Root– it is the starting directory for Unix OS. Denoted by / -
Etc– contains all configuration files of Unix OS. -
Dev– contains all device files like drivers.- A device file or special file is an interface for a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special device files in MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows. They allow software to interact with a device driver using standard input/output system calls, which simplifies many tasks and unifies user-space I/O mechanisms. Device files often provide simple interfaces to peripheral devices, such as printers.
-
Bin– stands for ‘binary’. Contains binary files. Binary files are files which can be run i.e, they are executable files. -
Lib– stands for ‘library files’. It contains all re-usable programs/data. -
Temp– just for temporary storage. Similar to recycle bin where we can store unwanted files. -
Lost & found– same as ‘restore’. Lost files or directories are stored here. When we are working on Unix and there is a power shutdown. If we wish to recover the documents we were earlier working on, then they can be found in lost&found directory. -
Mnt– stands for ‘mount’. Used for mounting external devices. It is also used for connecting external storage devices like – HDD(hard disk drive), USB, DVD, C etc.
UNIX OS supports multiple users at any given point of time. The users of UNIX will be assigned a separate directory known as home directory.
Each user of UNIX OS has their own username & password and separate home directory.
When a user is logged into UNIX OS, the default working directory will be user home directory.
A user directory is used for installation of a s/w which can be used by all the users of the UNIX OS.