This guide describes how to design a new FPGA Configuration with a custom Intel Quartus Prime project. That FPGA Configuration can be written during boot or during runtime by Linux.
For each board the used default FPGA Configuration and a version with an Intel NIOS II Soft-Core processor inside this repository are available. The Intel Quartus Prime Project with the Intel NIOS II Soft-Core processor is connected via the FPGA-to-HPS-Bridge to the Hard-IP of the HPS. This allows to use Hard-IP components, such as CAN with the NIOS II processor.
-
Instal Intel Quartus Prime (18.1 or later)
-
A step-by-step guide how to install Intel Quartus Prime on Linux is available here (Of cause NIOS II support is only for a NIOS II Project required)
-
Use a demo project
- Clone the Intel Quartus Prime archive file (.qar) from this repository for your project
- Start Intel Quartus Prime and choose "
Project/Archive Project" to select the archive file - Start the compilation of the Quartus Prime project
-
Design your own FPGA Configuration file
- I wrote a guide to show in steps how to design a custom Intel Quartus Prime project and how to use FPGA I/O with the HPS and Linux
rsyocto allows with its BSP (board support package) layer meta-intelfpga to change the FPGA Configuration with a single Linux command as shown in chapter two:
FPGA-writeConfig -f gpiConf.rbfNote: The new build system can do these steps automatically!
-
For the Arria 10 SX SoC-FPGA:
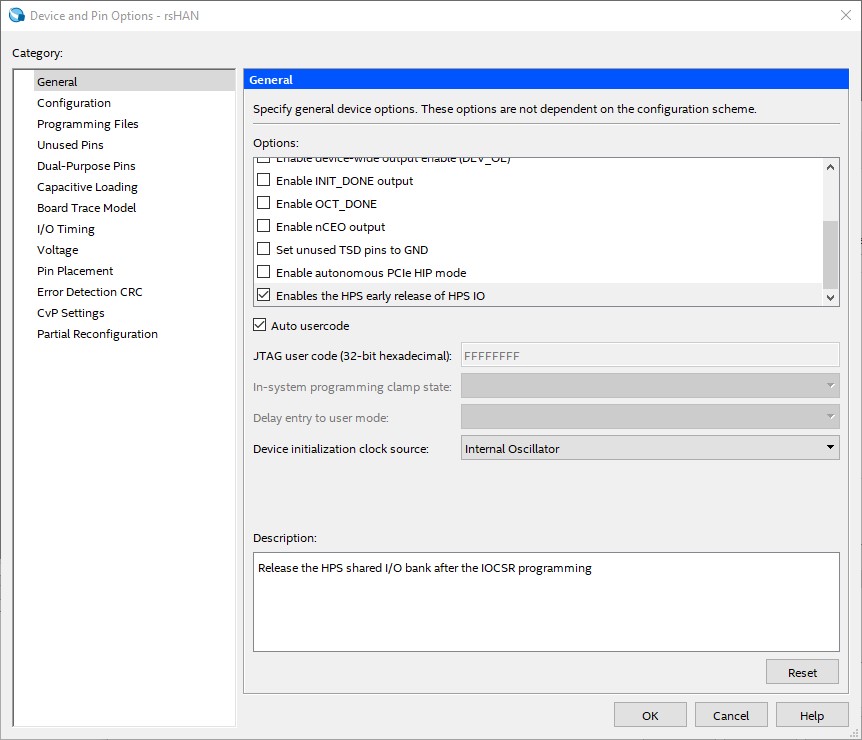
- Be sure that "
Enables the HPS early release of HPS IO" is enabled in the Intel Quartus Prime- and HPS- Settings- To split the FPGA Configuration in a peripheral- and core- FPGA Configuration
- This allows to hold for example the memory configuration of the HPS during FPGA Configuration changes (EMIF= external memory interface controller of the Intel Arria 10 SX is part of the FPGA Fabric and need a connection over the FPGA Interconnect before the secondary bootloader (u-boot) can use the SDRAM)
- For more information please visit the Intel Arria 10 documentation page
- Execute the following Intel SoC-EDS-Shell command:
quartus_cpf -c --hps -o bitstream_compression=on rsHAN.sof socfpga.rbf
- SOF here: "
rsHAN.sof" - RBF here: "
socfpga.rbf"
- SOF here: "
- With this command two FPGA Configuration files for the HPS- and Memory-System (e.g. HPS PLL, HPS I/O, HPS Core voltage,...) and for everything else are generated
- Output:
socfpga.periph.rbf" and "socfpga.core.rbf"
- Output:
- Be sure that "
-
For the Cyclone V SoC-FPGA:
-
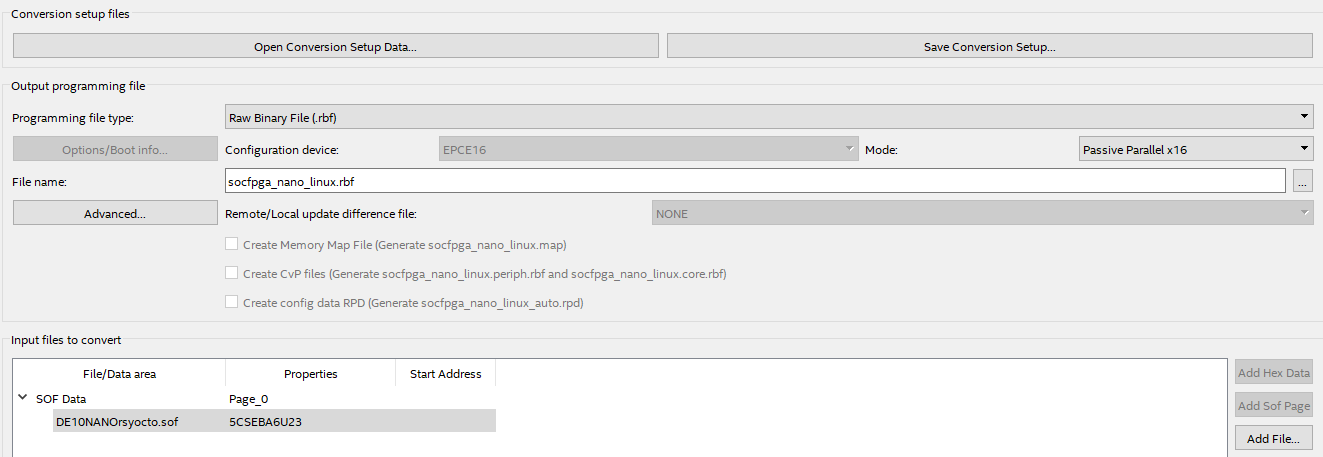
For FPGA Configuration of the FPGA with Linux use these export settings:
-
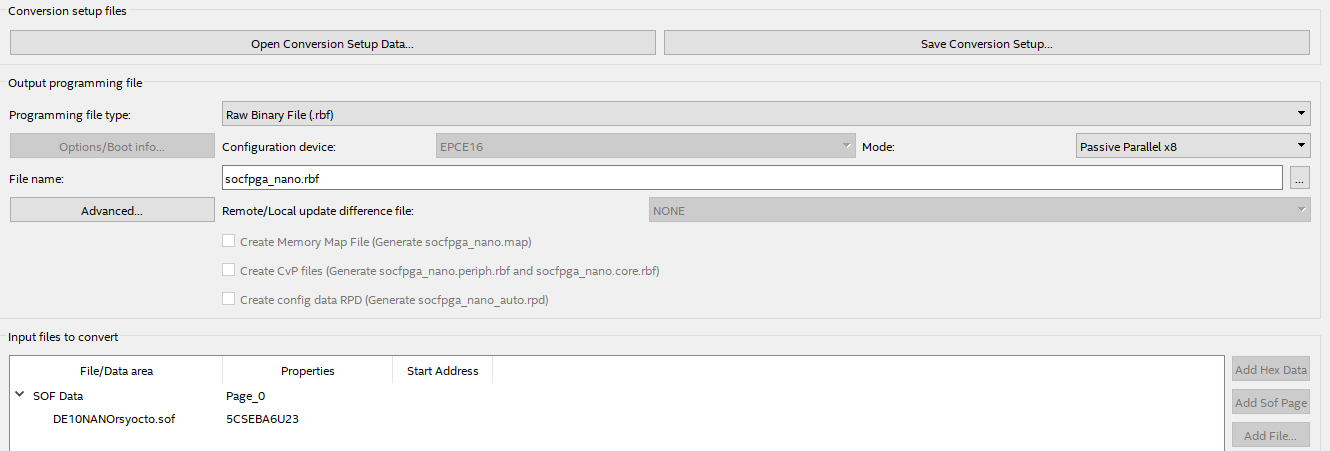
For FPGA Configuration of the FPGA during the boot use these export settings:
-