Vehicle Detection Project
The goals/steps of this project are the following:
- Perform a Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) feature extraction on a labeled training set of images and train an SVM classifier
- Optionally, you can also apply a color transform and append binned color features, as well as histograms of color, to your HOG feature vector.
- Note: for those first two steps don't forget to normalize your features and randomize a selection for training and testing.
- Implement a sliding-window technique and use your trained classifier to search for vehicles in images.
- Run your pipeline on a video stream (start with the test_video.mp4 and later implement on full project_video.mp4) and create a heat map of recurring detections frame by frame to reject outliers and follow detected vehicles.
- Estimate a bounding box for vehicles detected.
Rubric Points
In this writeup I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
Provide a Writeup / README that includes all the rubric points and how you addressed each one. You can submit your writeup as markdown or pdf. Here is a template writeup for this project you can use as a guide and a starting point.
You're reading it!
1. Explain how (and identify where in your code) you extracted HOG features from the training images.
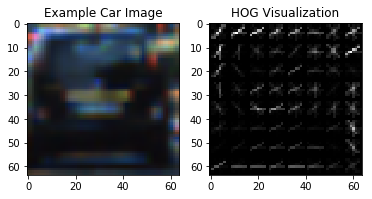
I started by reading in all the vehicle and non-vehicle images. Here is an example of one of each of the vehicle and non-vehicle classes:
Vehicles
Non-vehicles
I then explored different color spaces and different skimage.hog() parameters (orientations, pixels_per_cell, and cells_per_block). I grabbed random images from each of the two classes and displayed them to get a feel for what the skimage.hog() output looks like.
Here is an example using the HLS color space and HOG parameters of orientations=8, pixels_per_cell=(8, 8) and cells_per_block=(2, 2):
2. Explain how you settled on your final choice of HOG parameters.
I tried various combinations of parameters and found that orientations=9, pixels_per_cell=(12, 12) and cells_per_block=(4, 4) show the best performance.
3. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you trained a classifier using your selected HOG features (and color features if you used them).
I trained an SVM classifier using HOG and color (histogram binning) features.
As GridSearchCV shows, the classifier should perform better with rbf kernel, C=100 and gamma=0.001
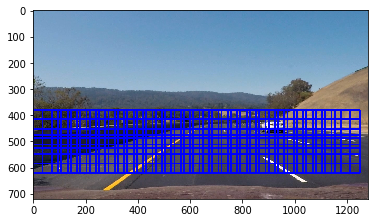
1. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you implemented a sliding window search. How did you decide what scales to search and how much to overlap windows?
I decided to implement the sliding window search as following:
- Choose the search window scale, where, e. g.
scale=1defines a(8, 8)window,scale=2defines a(16, 16)window, etc. - Choose the vertical search range
ystartandystop - Choose stepping stride and iterate through the windows
cells_per_step - Extract HOG features for the full image.
- For each window, extract HOG sub-sample and color features
- Run classifier to make a prediction
The scale=1.5 and cells_per_step=2 was showing the best prediction result and less amount of false positives.
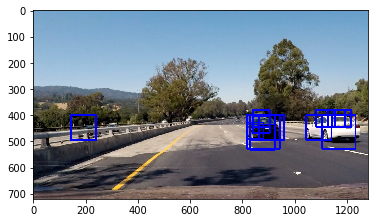
2. Show some examples of test images to demonstrate how your pipeline is working. What did you do to optimize the performance of your classifier?
Ultimately I searched on scales 1, 1.5 and 2, using HLS 3-channel HOG and color features in the feature vector, which provided a nice result. Here is some example image:
1. Provide a link to your final video output. Your pipeline should perform reasonably well on the entire project video (somewhat wobbly or unstable bounding boxes are ok as long as you are identifying the vehicles most of the time with minimal false positives.)
Here's a link to my video result (the same on YouTube)
2. Describe how (and identify where in your code) you implemented some kind of filter for false positives and some method for combining overlapping bounding boxes.
I recorded the positions of positive detections in a set of frames. From the positive detections I created a heatmap and then thresholded that map to identify vehicle positions. I then used scipy.ndimage.measurements.label() to identify individual blobs in the heatmap. I then assumed each blob corresponded to a vehicle. I constructed bounding boxes to cover the area of each blob detected.
Here's an example result showing heatmaps of a series of frames, the result of scipy.ndimage.measurements.label() and the bounding boxes then overlaid on the last frame of video:
Resulting scipy.ndimage.measurements.label() labels and detection bounding boxes:
1. Briefly discuss any problems / issues you faced in your implementation of this project. Where will your pipeline likely fail? What could you do to make it more robust?
Though, the SVC classifier performs reasonably well, it tends to overfit. It's clearly visible on the project video, that it has many false positives in complex conditions. To eliminate overfitting, we could try to train classifier on a larger data set or apply image pre-processing algorithms. To improve the detection pipeline, in general, we could try to use classifier ensembles, for example, or use much more sophisticated classifiers as convolution neural networks.
Another big disadvantage of the chosen naive approach, is a very low performance - the pipeline works at 0.4 FPS