### Forms
#### CSRF Protection
In Laravel 5.7 you create form by simple HTML
```
```
[CSRF](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-site_request_forgery) protection is enabled by default, so you need to include a CSRF token with each form sent
Token can be included by adding a `@csrf` directive inside the `
```
The token is then verified inside Laravel using the `VerifyCsrfToken` middleware.
### Middleware
Middleware is a mechanism that filter requests going through your application.
Simply put - each middleware is a chunk of code that runs BEFORE or AFTER the request is handled by `Controller Action` or a `Closure`.
Below is an example flow of the request going through your application:
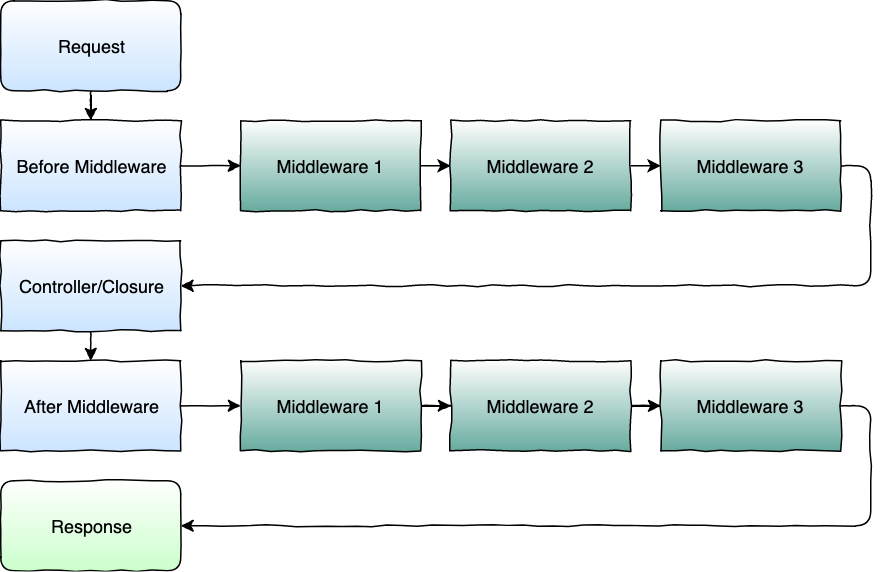
An example AFTER middleware from [Laravel Docs](https://laravel.com/docs/5.7/middleware#defining-middleware)
```
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
class AfterMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
// Calling $next with $request parameter
$response = $next($request);
// Do something here after the request is handled by Controller/Closure
return $response;
}
}
```
An example BEFORE middleware
```
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
class BeforeMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
// Do something here before the request is handled by Controller/Closure...
// Calling $next with $request parameter
return $next($request);
}
}
```
Middleware should call the passed `Closure` `$next` with the `$request` parameter to allow further processing, or `throw` an `Exception` or do a redirect to stop further processing of the `Request`.
Middleware examples:
* Authentication (veryfying if user is authenticated)
* CSRF protection
* CORS middleware
### Request
Obtaining data sent with request
```
class PostController extends Controller
{
public function store(Request $request)
{
$title = $request->input('title');
}
}
```
Reading all input as an `array`
```
$input = $request->all();
```
Reading an individual value with default provided
```
$name = $request->input('title', 'Draft post');
```
Retrieving all of the input values as an `array`
```
$input = $request->input();
```
The `input()` method can read data regardless of the HTTP verb used (works for `GET` query parameters or input fields sent through `