dijkstra算法总结- 常用模板解决
- 其他写法
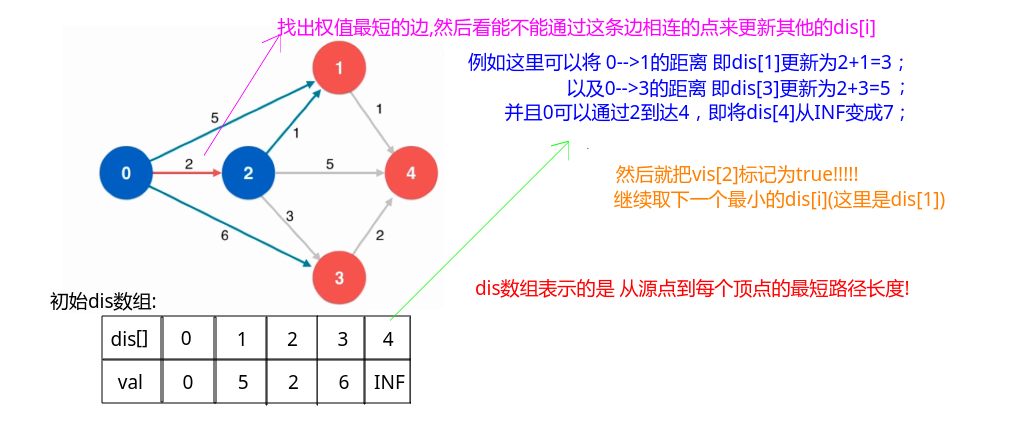
总结一下dijkstra算法大致的流程:
- 一开始有一个
dist[]数组(也可以是map)来保存从start(起点)到每个点的最短路径(一开始的话,如果start和某个点没有边,就为INF(或者为null),如果有连线的话就是边的权值); - 然后每次从
dist数组中取出一个dist[i]最小的i(不能取已经用过的顶点(vis数组标记)),也就是start距离某个结点最近的一个; - 取出这个结点之后,用这个结点更新和它相连的边的
dist数组; - 直到把所有的
dist数组都更新一遍;
注意:
dijkstra为什么不能有负权边? 因为如果有的话,我们找最小的那个结构的时候,没准它还能通过松弛变得更短,例如上面我们一开始选出0~2这条边的时候,试想如果2~1的那条边权值为-4,那一开始我们找的0~2这条边就是错的,所以不能有负权边。
推荐的写法
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int m;
static boolean[] vis;
static ArrayList<Edge> G[];
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int to;
public int w;
public Edge(int to, int w) {
this.to = to;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return w - o.w;
}
}
static int[] dijkstra(int start) {
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dis = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) dis[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //初始标记(不是-1(因为是求最小的))
dis[start] = 0;
// G.vis[start] = true; //第一个访问 start, 不能将start标记为true
pq.add(new Edge(start, 0)); //将第一条边加入 pq, 自环边
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge curEdge = pq.poll();
int to = curEdge.to;
if (vis[to])
continue;
vis[to] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < G[to].size(); i++) { //更新相邻的边
int nxtNode = G[to].get(i).to;
int nxtW = G[to].get(i).w;
if (!vis[nxtNode] && dis[nxtNode] > dis[to] + nxtW) {
dis[nxtNode] = dis[to] + nxtW;
pq.add(new Edge(nxtNode, dis[nxtNode])); //将这个新的dis[nxtNode]加入优先队列,没准它是下一个(很小)
}
}
}
return dis;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
while (cin.hasNext()) {
n = cin.nextInt();
m = cin.nextInt();
G = new ArrayList[n]; // 0~n-1
vis = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
G[i] = new ArrayList<>();
vis[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int from = cin.nextInt();
int to = cin.nextInt();
int w = cin.nextInt();
G[from].add(new Edge(to, w));
G[to].add(new Edge(from, w));
}
int s = cin.nextInt();
int e = cin.nextInt();
int[] dis = dijkstra(s);
System.out.println(dis[e] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dis[e]);
}
}
}没有使用堆优化,也就是说找出当前最小的dist所在的结构的时候,遍历了一遍当前的dist。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static class Node{
public int value;
public ArrayList<Edge>edges;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
private static class Edge{
public int weight;
public Node from;
public Node to;
public Edge( Node from, Node to,int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
private static class Graph{
public HashMap<Integer,Node>nodes;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
}
}
//没有使用堆优化的 O(n^2)
public static HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra(Node head){
HashMap<Node,Integer>dist = new HashMap<>();
dist.put(head,0);
for(Edge edge : head.edges){
dist.put(edge.to,edge.weight);
}
HashSet<Node>set = new HashSet<>();
for(Node minNode = getMinAndUnSelect(dist,set); minNode != null ; minNode = getMinAndUnSelect(dist,set)){
int distance = dist.get(minNode);
for(Edge edge : minNode.edges){
Node toNode = edge.to;
if(set.contains(toNode))continue;
if(!dist.containsKey(toNode)){
dist.put(toNode,distance + edge.weight);
}
dist.put(toNode,Math.min(dist.get(toNode),distance + edge.weight));
}
set.add(minNode); //使用过这个之后就标记
}
return dist;
}
//找出dist中最小且没有选择的结点
private static Node getMinAndUnSelect(HashMap<Node, Integer> dist, HashSet<Node> set) {
Node minNode = null;
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(Entry<Node,Integer> entry : dist.entrySet()){ // map遍历方式 https://www.cnblogs.com/fqfanqi/p/6187085.html
Node node = entry.getKey();
int distance = entry.getValue();
if(!set.contains(node) && distance < minDistance){
minDistance = distance;
minNode = node;
}
}
return minNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
while(cin.hasNext()){
int n = cin.nextInt();
int m = cin.nextInt();
Graph G = new Graph();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)G.nodes.put(i,new Node(i));
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
int w = cin.nextInt();
Node from = G.nodes.get(a);
Node to = G.nodes.get(b);
from.edges.add(new Edge(from,to,w));
to.edges.add(new Edge(to,from,w));
}
int start = cin.nextInt();
int end = cin.nextInt();
HashMap<Node, Integer> dist = dijkstra(G.nodes.get(start));//从start开始
Integer res = dist.get(G.nodes.get(end));
System.out.println((res == null) ? -1 : res);
}
}
}堆优化,其他写法(建图稍有不同):
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class Main {
static class Node{
public int value;
public ArrayList<Edge>edges;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
static class Edge{
public int weight;
public Node from;
public Node to;
public Edge( Node from, Node to,int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static class Graph{
public HashMap<Integer,Node>nodes;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
}
}
static class NodeRecord {
public Node node;
public int distance;
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
static class EdgeComparator implements Comparator<NodeRecord>{
@Override
public int compare(NodeRecord o1, NodeRecord o2) {
return o1.distance - o2.distance;
}
}
static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra(Node head){
HashMap<Node,Integer>dist = new HashMap<>();
dist.put(head,0);
for(Edge edge : head.edges){//这个不能少
dist.put(edge.to,edge.weight);
}
PriorityQueue<NodeRecord>priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new EdgeComparator());
priorityQueue.add(new NodeRecord(head,0));
HashSet<Node>set = new HashSet<>();
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
NodeRecord poll = priorityQueue.poll();
Node cur = poll.node;
int distance = poll.distance;
if(set.contains(cur))continue;
set.add(cur);
for(Edge edge : cur.edges){
int w = edge.weight;
Node toNode = edge.to;
if(set.contains(toNode))continue;
if(!dist.containsKey(toNode))dist.put(toNode,distance + w);
dist.put(toNode,Math.min(dist.get(toNode),distance + w));
priorityQueue.add(new NodeRecord(toNode,dist.get(toNode)));
}
}
return dist;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
while(cin.hasNext()){
int n = cin.nextInt();
int m = cin.nextInt();
Graph G = new Graph();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)G.nodes.put(i,new Node(i));
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
int w = cin.nextInt();
Node from = G.nodes.get(a);
Node to = G.nodes.get(b);
from.edges.add(new Edge(from,to,w));
to.edges.add(new Edge(to,from,w)); //注意无向图
}
int start = cin.nextInt();
int end = cin.nextInt();
HashMap<Node, Integer> dist = dijkstra(G.nodes.get(start));//从start开始
Integer res = dist.get(G.nodes.get(end));
System.out.println((res == null) ? -1 : res);
}
}
}手写堆解决写法。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Node{
public int value;
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
static class Edge{
public int weight;
public Node from;
public Node to;
public Edge( Node from, Node to,int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
static class Graph{
public HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
}
}
static class NodeRecord {
public Node node;
public int distance;
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
static class NodeHeap {
private Node[] nodes;
private HashMap<Node, Integer> indexMap;//堆的下标
private HashMap<Node, Integer> distMap; //堆里面Node对应的distance
private int size;
public NodeHeap(int size) {
nodes = new Node[size];
indexMap = new HashMap<>();
distMap = new HashMap<>();
this.size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {//堆是否为空
return size == 0;
}
public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node, int distance) {
//如果在堆中已经有了这个结点,就要更新 -1表示的是被访问过了
if (indexMap.containsKey(node) && indexMap.get(node) != -1) { //update contain and index != -1
distMap.put(node, Math.min(distMap.get(node), distance));
insertHeapify(node, indexMap.get(node));
}
//如果 堆中没有这个结点 就创建一个
if (!indexMap.containsKey(node)) {//if isEntered --> ignore
nodes[size] = node;
indexMap.put(node, size);
distMap.put(node, distance);
insertHeapify(node, size++);
}
}
//从堆中取一个
public NodeRecord poll() {
NodeRecord top = new NodeRecord(nodes[0], distMap.get(nodes[0]));//取出堆顶
swap(0, size - 1); //和最后一个交换
indexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1); //标记已经用过,相当于 Hashset作用
distMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]); //距离数组中李处
nodes[size - 1] = null; //结点数组中设置为null
heapify(0, --size);
return top;
}
private void insertHeapify(Node node, int index) { //插入并调整
while (distMap.get(nodes[index]) < distMap.get(nodes[(index - 1) / 2])) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
private void heapify(int index, int size) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < size) {
int minIndex = left + 1 < size && distMap.get(nodes[left + 1]) < distMap.get(nodes[left])
? left + 1 : left;
minIndex = distMap.get(nodes[minIndex]) < distMap.get(nodes[index]) ? minIndex : index;
if (minIndex == index) break;
swap(minIndex, index);
index = minIndex;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
private void swap(int a, int b) {
indexMap.put(nodes[a], b);//交换各自的下标
indexMap.put(nodes[b], a);
Node tmp = nodes[a];
nodes[a] = nodes[b];
nodes[b] = tmp;
}
}
static HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra(Graph G,int start){
NodeHeap heap = new NodeHeap(G.nodes.size());
heap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(G.nodes.get(start),0);
HashMap<Node,Integer>dist = new HashMap<>();
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
NodeRecord poll = heap.poll();
Node cur = poll.node;
int distance = poll.distance;
for(Edge edge : cur.edges){
heap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to, distance + edge.weight);
}
dist.put(cur,distance);
}
return dist;
}
static Graph createGraph(Scanner cin,int n,int m){
Graph G = new Graph();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)G.nodes.put(i,new Node(i));
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
int w = cin.nextInt();
Node from = G.nodes.get(a);
Node to = G.nodes.get(b);
from.edges.add(new Edge(from,to,w));
to.edges.add(new Edge(to,from,w));
}
return G;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
while(cin.hasNext()){
int n = cin.nextInt();
int m = cin.nextInt();
Graph G = createGraph(cin,n,m);
int start = cin.nextInt();
int end = cin.nextInt();
HashMap<Node, Integer> dist = dijkstra(G,start);//从start开始
Integer res = dist.get(G.nodes.get(end));
System.out.println((res == null) ? -1 : res);
}
}
}