A tool to identify unused code in Swift projects.
- Installation
- How To Use
- How It Works
- Analysis
- Comment Commands
- Xcode Integration
- Excluding Files
- Continuous Integration
- Platforms
- Troubleshooting
Homebrew (macOS only)
Install Homebrew:
You can skip this step if you already have Homebrew installed.
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
Now install Periphery itself:
brew tap peripheryapp/periphery && brew install periphery
Add Periphery to your Package.swift dependencies:
.package(url: "https://github.com/peripheryapp/periphery", from: "2.0.0")Now run periphery via Swift:
swift run periphery scan ...
CocoaPods (macOS only)
Add the following to your Podfile:
pod 'Periphery'
Now run pod install, the Periphery executable will be downloaded and placed at Pods/Periphery/periphery.
mint install peripheryapp/periphery
The scan command is Periphery's primary function. To begin a guided setup, simply change to your project directory and run:
periphery scan --setup
After answering a few questions, Periphery will print out the full scan command and execute it.
The guided setup is only intended for introductory purposes, once you are familiar with Periphery you can try some more advanced options, all of which can be seen with periphery help scan.
To get coherent results from Periphery, it's crucial to understand the implications of the build targets you choose to analyze. For example, imagine a project consisting of three targets: App, Lib and Tests. The App target imports Lib, and the Tests targets imports both App and Lib. If you were to provide all three to the --targets option then Periphery will be able to analyze your project as a whole. However, if you only choose to analyze App and Lib, but not Tests, Periphery may report some instances of unused code that are only referenced by Tests. Therefore when you suspect Periphery has provided an incorrect result, it's important to consider the targets that you have chosen to analyze.
If your project consists of one or more standalone frameworks that do not also contain some kind of application that consume their interfaces, then you'll need to tell Periphery to assume that all public declarations are in fact used by including the --retain-public option.
For projects that are mixed Objective-C & Swift, it's highly recommend you read about the implications this can have on your results.
Once you've settled upon the appropriate options for your project, you may wish to persist them in a YAML configuration file. The simplest way to achieve this is to run Periphery with the --verbose option. Near the beginning of the output you will see the [configuration] section with your configuration formatted as YAML below. Copy & paste the configuration into .periphery.yml in the root of your project folder. You can now simply run periphery scan and the YAML configuration will be used.
Periphery first builds your project. For Xcode projects the schemes provided via the --schemes option are built using xcodebuild. For Swift Package Manager projects, the individual targets provided via the --targets option are built using swift build. The Swift compiler employs a technique called index-while-building to populate an index store that contains information about the structure of your project's source code.
After your project is built, Periphery performs an indexing phase. For every source file that is a member of the targets provided via the --targets option, Periphery obtains its structural information from the index store and builds its own internal graph representation of your project. Periphery also analyzes each file's abstract syntax tree (AST) to fill in some details not provided by the index store.
Once indexing is complete, Periphery analyzes the graph to identify unused code. This phase consists of a number of steps that mutate the graph to make it easier to identify specific scenarios of unused code. The final step walks the graph from its roots to identify declarations that are no longer referenced.
The goal of Periphery is to report instances of unused declarations. A declaration is a class, struct, protocol, function, property, constructor, enum, typealias, associatedtype, etc. As you'd expect, Periphery is able to identify simple unreferenced declarations, e.g a class that is no longer used anywhere in your codebase.
Periphery can also identify more advanced instanced of unused code. The following section explains these in detail.
Periphery can identify unused function parameters. Instances of unused parameters can also be identified in protocols and their conforming declarations, as well as parameters in overridden methods. Both of these scenarios are explained further below.
An unused parameter of a protocol function will only be reported as unused if the parameter is also unused in all implementations.
protocol Greeter {
func greet(name: String)
func farewell(name: String) // 'name' is unused
}
class InformalGreeter: Greeter {
func greet(name: String) {
print("Sup " + name + ".")
}
func farewell(name: String) { // 'name' is unused
print("Cya.")
}
}Tip
You can ignore all unused parameters from protocols and conforming functions with the
--retain-unused-protocol-func-paramsoption.
Similar to protocols, parameters of overridden functions are only reported as unused if they're also unused in the base function and all overriding functions.
class BaseGreeter {
func greet(name: String) {
print("Hello.")
}
func farewell(name: String) { // 'name' is unused
print("Goodbye.")
}
}
class InformalGreeter: BaseGreeter {
override func greet(name: String) {
print("Sup " + name + ".")
}
override func farewell(name: String) { // 'name' is unused
print("Cya.")
}
}Unused parameters of protocols or classes defined in foreign modules (e.g Foundation) are always ignored, since you do not have access to modify the base function declaration.
Unused parameters of functions that simply call fatalError are also ignored. Such functions are often unimplemented required initializers in subclasses.
class Base {
let param: String
required init(param: String) {
self.param = param
}
}
class Subclass: Base {
init(custom: String) {
super.init(param: custom)
}
required init(param: String) {
fatalError("init(param:) has not been implemented")
}
}A protocol which is conformed to by an object is not truly used unless it's also used as an existential type, or to specialize a generic method/class. Periphery is able to identify such redundant protocols whether they are conformed to by one, or even multiple objects.
protocol MyProtocol { // 'MyProtocol' is redundant
func someMethod()
}
class MyClass1: MyProtocol { // 'MyProtocol' conformance is redundant
func someMethod() {
print("Hello from MyClass1!")
}
}
class MyClass2: MyProtocol { // 'MyProtocol' conformance is redundant
func someMethod() {
print("Hello from MyClass2!")
}
}
let myClass1 = MyClass1()
myClass1.someMethod()
let myClass2 = MyClass2()
myClass2.someMethod()Here we can see that despite both implementations of someMethod are called, at no point does an object take on the type of MyProtocol. Therefore the protocol itself is redundant, and there's no benefit from MyClass1 or MyClass2 conforming to it. We can remove MyProtocol along with each redundant conformance, and just keep someMethod in each class.
Just like a normal method or property of a object, individual properties and methods declared by your protocol can also be identified as unused.
protocol MyProtocol {
var usedProperty: String { get }
var unusedProperty: String { get } // 'unusedProperty' is unused
}
class MyConformingClass: MyProtocol {
var usedProperty: String = "used"
var unusedProperty: String = "unused" // 'unusedProperty' is unused
}
class MyClass {
let conformingClass: MyProtocol
init() {
conformingClass = MyConformingClass()
}
func perform() {
print(conformingClass.usedProperty)
}
}
let myClass = MyClass()
myClass.perform()Here we can see that MyProtocol is itself used, and cannot be removed. However, since unusedProperty is never called on MyConformingClass, Periphery is able to identify that the declaration of unusedProperty in MyProtocol is also unused and can be removed along with the unused implementation of unusedProperty.
Along with being able to identify unused enumerations, Periphery can also identify individual unused enum cases. Plain enums that are not raw representable, i.e that don't have a String, Character, Int or floating-point value type can be reliably identified. However, enumerations that do have a raw value type can be dynamic in nature, and therefore must be assumed to be used.
Let's clear this up with a quick example:
enum MyEnum: String {
case myCase
}
func someFunction(value: String) {
if let myEnum = MyEnum(rawValue: value) {
somethingImportant(myEnum)
}
}There's no direct reference to the myCase case, so it's reasonable to expect it might no longer be needed, however if it were removed we can see that somethingImportant would never be called if someFunction were passed the value of "myCase".
Properties that are assigned but never used are identified as such, e.g:
class MyClass {
var assignOnlyProperty: String // 'assignOnlyProperty' is assigned, but never used
init(value: String) {
self.assignOnlyProperty = value
}
}In some cases this may be the intended behavior, so to silence these results you can either disable this analysis technique entirely with --retain-assign-only-properties, or ignore individual properties using Comment Commands.
Periphery cannot analyze Objective-C code since types may be dynamically typed.
By default Periphery does not assume that declarations accessible by the Objective-C runtime are in use. If your project is a mix of Swift & Objective-C, you can enable this behavior with the --retain-objc-accessible option. Swift declarations that are accessible by the Objective-C runtime are those that are explicitly attributed with @objc or @objcMembers, and classes that inherit NSObject either directly or indirectly via another class.
For whatever reason, you may want to keep some unused code. Source code comment commands can be used to instruct Periphery to ignore specific declarations, and exclude them from the results.
An ignore comment command can be placed directly on the line above any declaration to ignore it, and all descendent declarations:
// periphery:ignore
class MyClass {}You can also ignore specific unused function parameters:
// periphery:ignore:parameters unusedOne,unusedTwo
func someFunc(used: String, unusedOne: String, unusedTwo: String) {
print(used)
}The // periphery:ignore:all command can be placed at the top of the source file to ignore the entire contents of the file. Note that the comment must be placed above any code, including import statements.
Before setting up Xcode integration, we highly recommend you first get Periphery working in a terminal, as you will be using the exact same command via Xcode.
Select your project in the Project Navigator and click the + button at the bottom left of the Targets section. Select Cross-platform and choose Aggregate. Hit Next.
Choose a name for the new target, e.g "Periphery" or "Unused Code".
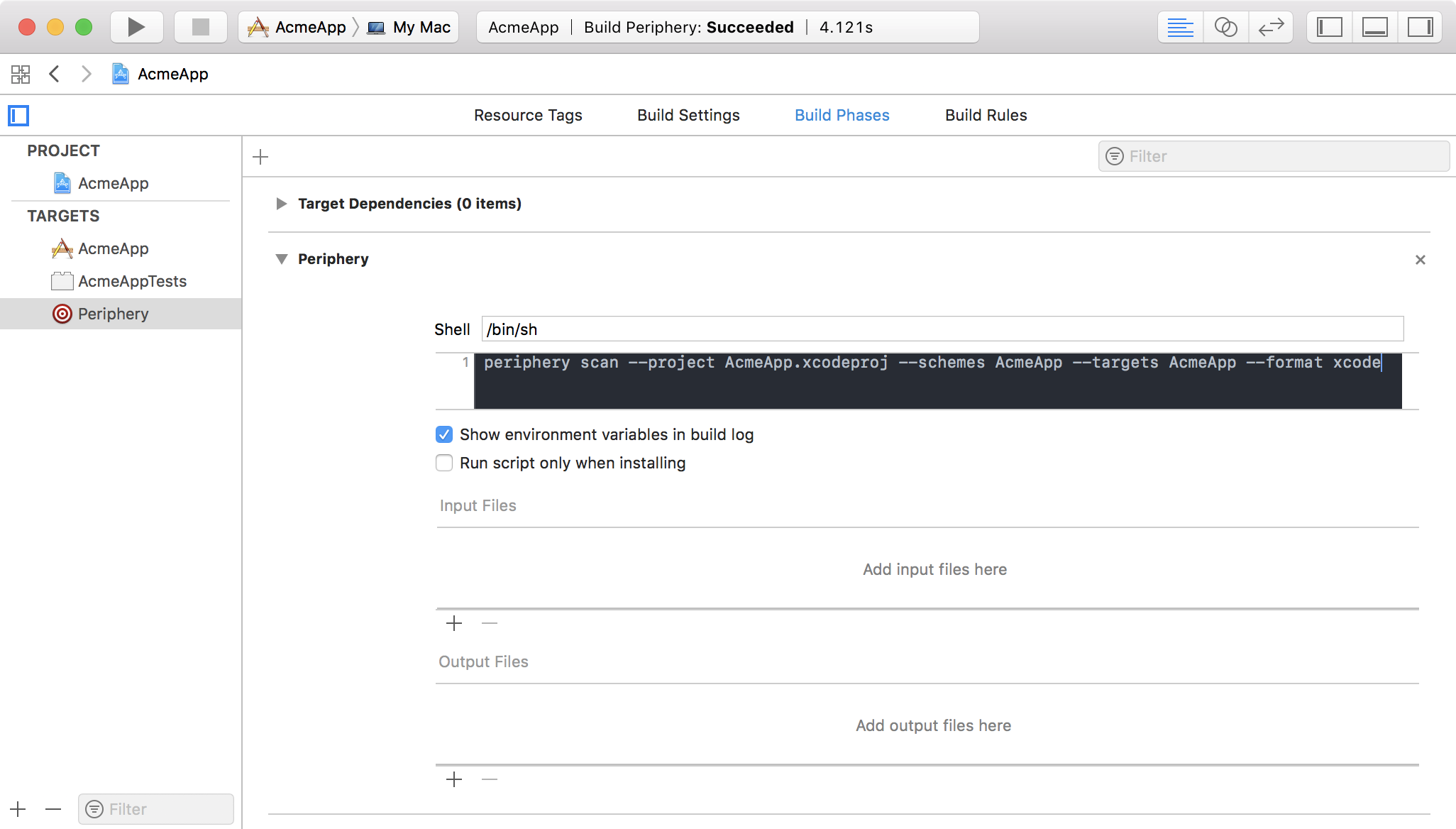
In the Build Phases section click the + button to add a new Run Script phase.
In the shell script window enter the Periphery command. Be sure to include the --format xcode option.
You're ready to roll. You should now see the new scheme in the dropdown. Select it and hit run.
Tip
If you'd like others on your team to be able to use the scheme, you'll need to mark it as Shared. This can be done by selecting Manage Schemes... and selecting the Shared checkbox next to the new scheme. The scheme definition can now be checked into source control.
Both exclusion options described below accept a path glob, either absolute or relative to your project directory. You may specify multiple globs by separating them with a pipe character, e.g "Foo.swift|{Bar,Baz}.swift|path/to/*.swift". Recursive (**) globs are not supported at this time.
To exclude the results from certain files, pass the --report-exclude <globs> option to the scan command.
To exclude files from being indexed, pass the --index-exclude <glob> option to the scan command. Excluding files from the index phase means that any declarations and references contained within the files will not be seen by Periphery. Periphery will be behave as if the files do not exist. This option can be used to exclude generated code that holds references to non-generated code.
Periphery can be used in your CI environment to ensure your project remains free of unused code. If you'd like to use Periphery immediately after running your tests, you can use the --skip-build option, provided that your build & test steps also built all of the targets you wish to analyze.
For more complex setups, you may also benefit from the --index-store-path option if your index store exists in a non-standard location.
Periphery supports both macOS and Linux. macOS supports both Xcode and Swift Package Manager (SPM) projects, whereas only SPM projects are supported on Linux.
Erroneous results in one or more files, such as false-positives and incorrect source file locations.
It's possible for the index store to become corrupt, or out of sync with the source file. This can happen, for example, if you forcefully terminate (^C) a scan. To rectify this, you can pass the --clean-build flag to the scan command to force removal of existing build artifacts.