This document describes a basic workflow for deploying and testing Red Hat AMQ Broker with MicroShift.
Use the instructions in the Install MicroShift on RHEL for Edge document to configure a virtual machine running MicroShift.
Log into the virtual machine and run the following commands to configure the MicroShift access and check if the PODs are up and running.
mkdir ~/.kube
sudo cat /var/lib/microshift/resources/kubeadmin/kubeconfig > ~/.kube/config
oc get pods -A
Log into the virtual machine and run the following commands to create the AMQ Broker deployment in the amq-broker namespace.
oc apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openshift/microshift/main/docs/config/amq-broker.yamlVerify that the application started successfully in the amq-broker namespace.
oc get pods -n amq-brokerThe deployment exposes the AMQ Broker Web Interface and amqp protocol ports that can be accessed via the NodePort type services.
Run the following command to see the mapped port numbers.
oc get service -n amq-broker
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
amq-web NodePort 10.43.109.135 <none> 8161:31715/TCP 7m5s
amqp NodePort 10.43.241.87 <none> 5672:30322/TCP 7m4sIn the current deployment, use ports 31715 and 30322 to access Web and
amqpservices respectively. Note that port mapping may be different in other deployments.
Log into the hypervisor host to test connection and functionality of the AMQ Broker.
Run the following commands to login into the Red Hat Container Registry and download the Red Hat AMQ Broker image.
podman login registry.redhat.io
podman pull registry.redhat.io/amq7/amq-broker:7.8The artemis utility from the image can be used to test the AMQ Broker by producing and consuming messages.
podman run --rm -it amq-broker:7.8 /opt/amq/bin/artemis
usage: artemis <command> [<args>]
The most commonly used artemis commands are:
address Address tools group (create|delete|update|show) (example ./artemis address create)
browser It will browse messages on an instance
check Check tools group (node|queue) (example ./artemis check node)
consumer It will consume messages from an instance
create creates a new broker instance
data data tools group (print) (example ./artemis data print)
help Display help information
mask mask a password and print it out
migrate1x Migrates the configuration of a 1.x Artemis Broker
producer It will send messages to an instance
queue Queue tools group (create|delete|update|stat|purge) (example ./artemis queue create)
See 'artemis help <command>' for more information on a specific command.Start by setting the queue name and connection string variables.
AMQ_QUEUE=microshift-queue
AMQ_CONNECT="--url tcp:https://VM_IP:AMPQ_PORT --protocol amqp"
Make sure to use the current virtual machine IP and service port:
- Replace
VM_IPwith the current IP address of the MicroShift virtual machine (i.e. 192.168.122.32)- Replace
AMPQ_PORTwith the currentNodePortof theamqpservice (i.e. 30332)
Run the following commands to produce and consume data using the microshift-queue queue. One these operations complete successfully, fifty messages should remain in the queue to be consumed.
podman run --rm -it amq-broker:7.8 /opt/amq/bin/artemis producer --destination $AMQ_QUEUE $AMQ_CONNECT --message-count 100
podman run --rm -it amq-broker:7.8 /opt/amq/bin/artemis consumer --destination $AMQ_QUEUE $AMQ_CONNECT --message-count 50Open a browser at the http:https://VM_IP:AMQ_WEB_PORT URL, click on the Management Console link and log in using redhat:redhat credentials.
Make sure to use the current virtual machine IP and service port:
- Replace
VM_IPwith the current IP address of the MicroShift virtual machine (i.e. 192.168.122.32)- Replace
AMPQ_WEB_PORTwith the currentNodePortof theamq-webservice (i.e. 31715)
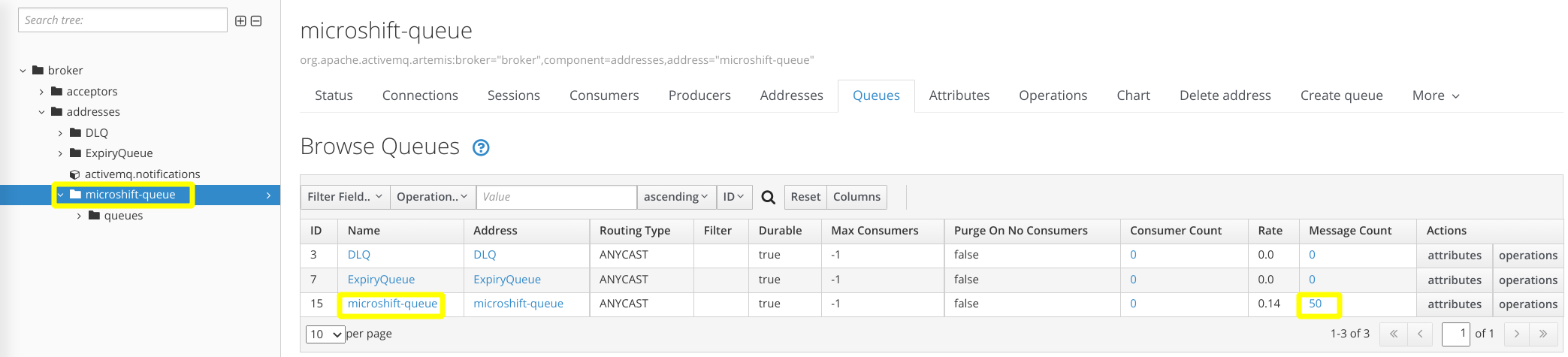
Navigate to broker > addresses > microshift-queue in the tree and select the Queues tab. Review the Message Count column in the table, noting that there are fifty messages remaining to be consumed in the queue.
See Producing and consuming test messages for more information.
The AMQ Broker deployment is configured to mount a 1GB volume at the /data directory and set the AMQ_DATA_DIR environment variable to point to that location. All the messages sent to the AMQ Broker are persisted on the volume until their expiry or retrieval.
Run the following command to delete the running AMQ Broker pod instance.
oc delete pods -n amq-broker -l app=amq-brokerWait until a new AMQ Broker pod is started and check the message queue in the Management Console as described in the Web Interface section. Note that there are still fifty messages remaining to be consumed in the queue.
Log into the virtual machine and run the following command to delete the AMQ Broker deployment.
oc delete namespaces amq-broker