Stormi is a fast and simple, hash-based file-server written in Rust
Stormi accepts multipart/form-data form with media payload, writes the data to disk and automatically infers the mimetype of the uploaded files.
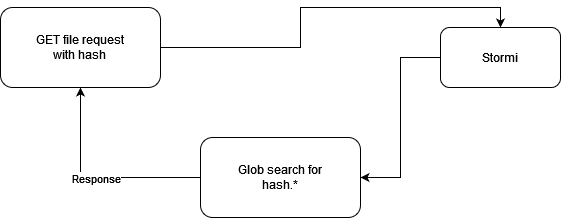
When GETting files Stormi uses a glob search with a given hash and wildcard(*) extension match(hash.*).
Stormi has 3 endpoints:
/:hash- GET - For getting a file with its hash/upload- POST - For uploading a set of files/remove- POST - For removing items from Stormi
{
"hashes": ["hash1", "hash2", "hash3"]
}Create a base64 encoded string with your credentials in the following format: username:password, replace credentials with the output and change file.png to the filename you want to upload.
Send the request curl:
$ curl -X POST --form file='file.png' https://127.0.0.1:6345/upload -H 'Authorization: credentials'Response structure of /upload and /remove is the same:
{
"skipped": [],
"hashes": []
}skipped- the hases that have been skippedhashes- the hashes that have been added, modified or removed
Here is a list of different wrapper implementations around the Stormi API
To configure Stormi, you will need to create a config.yaml file and add at least one user with its password and permissions to users. Check out the configuration example.
You can compile Stormi locally using the following command:
$ cargo build --releaseand start it using:
$ ./target/release/stormiYou can also create a Stormi instance using Docker
Pull the image:
$ docker pull ghcr.io/polygon-isecure/stormi:latestCreate an instance:
$ docker run -dp 6435:6435 --name stormi ghcr.io/polygon-isecure/stormi:latest