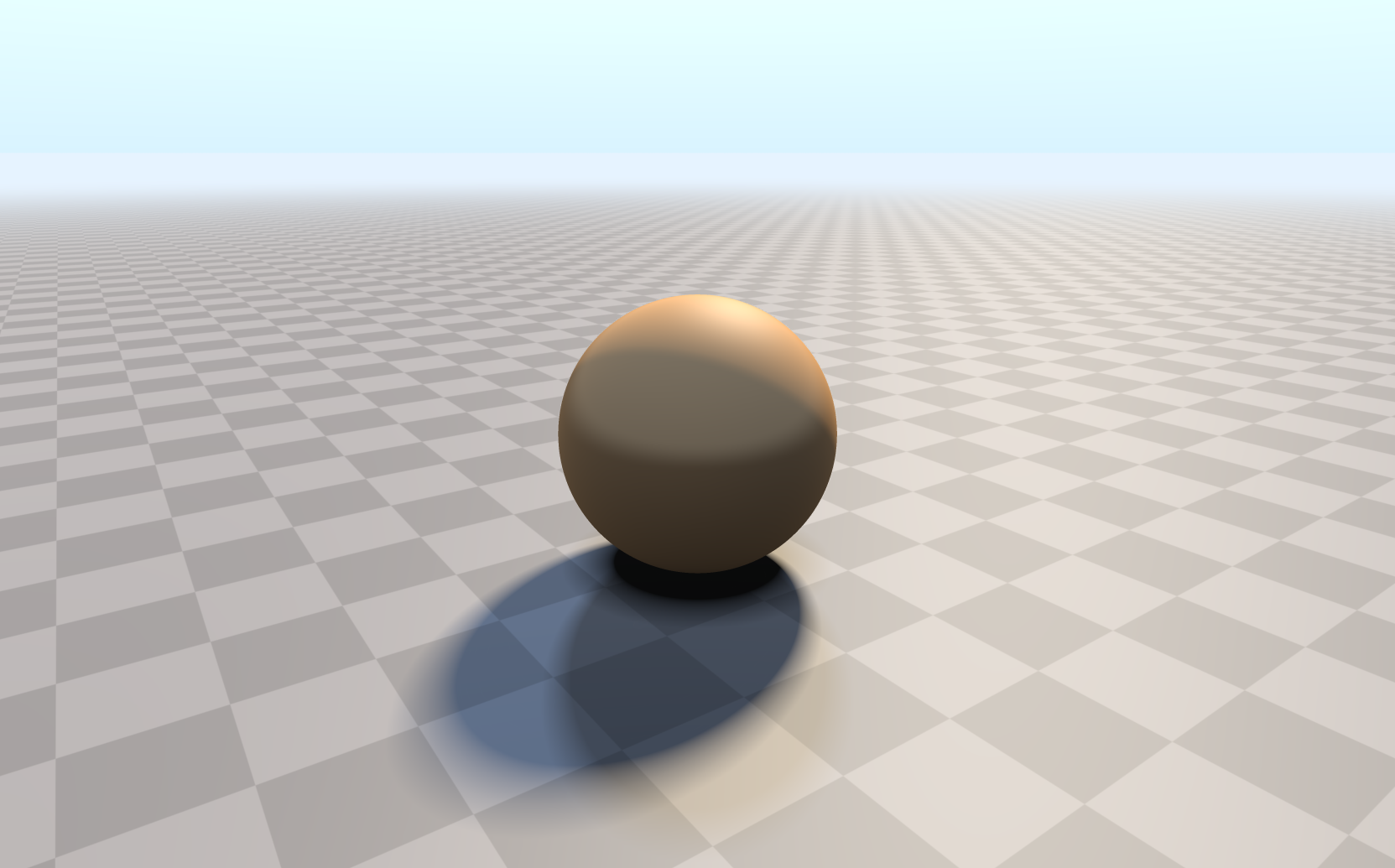
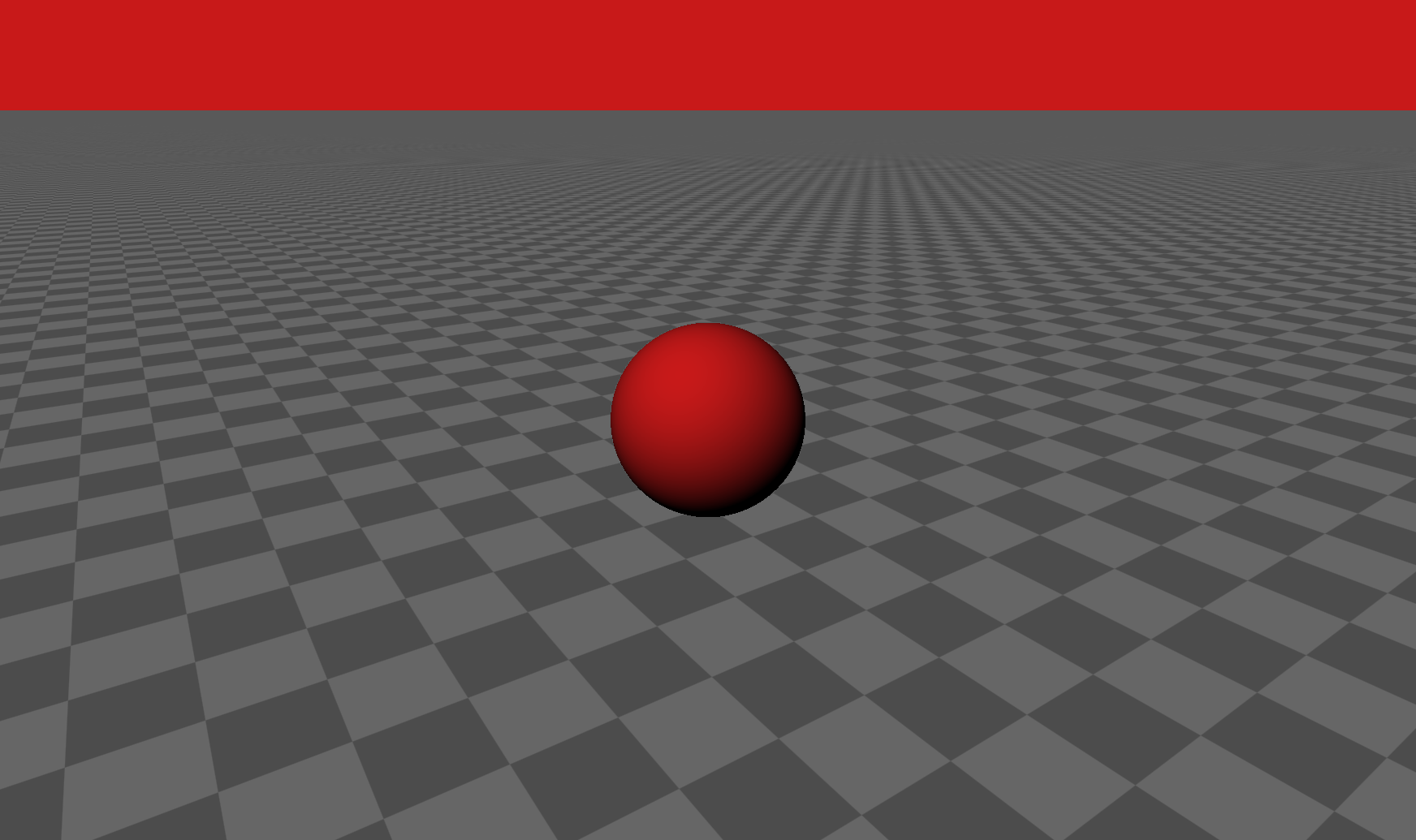
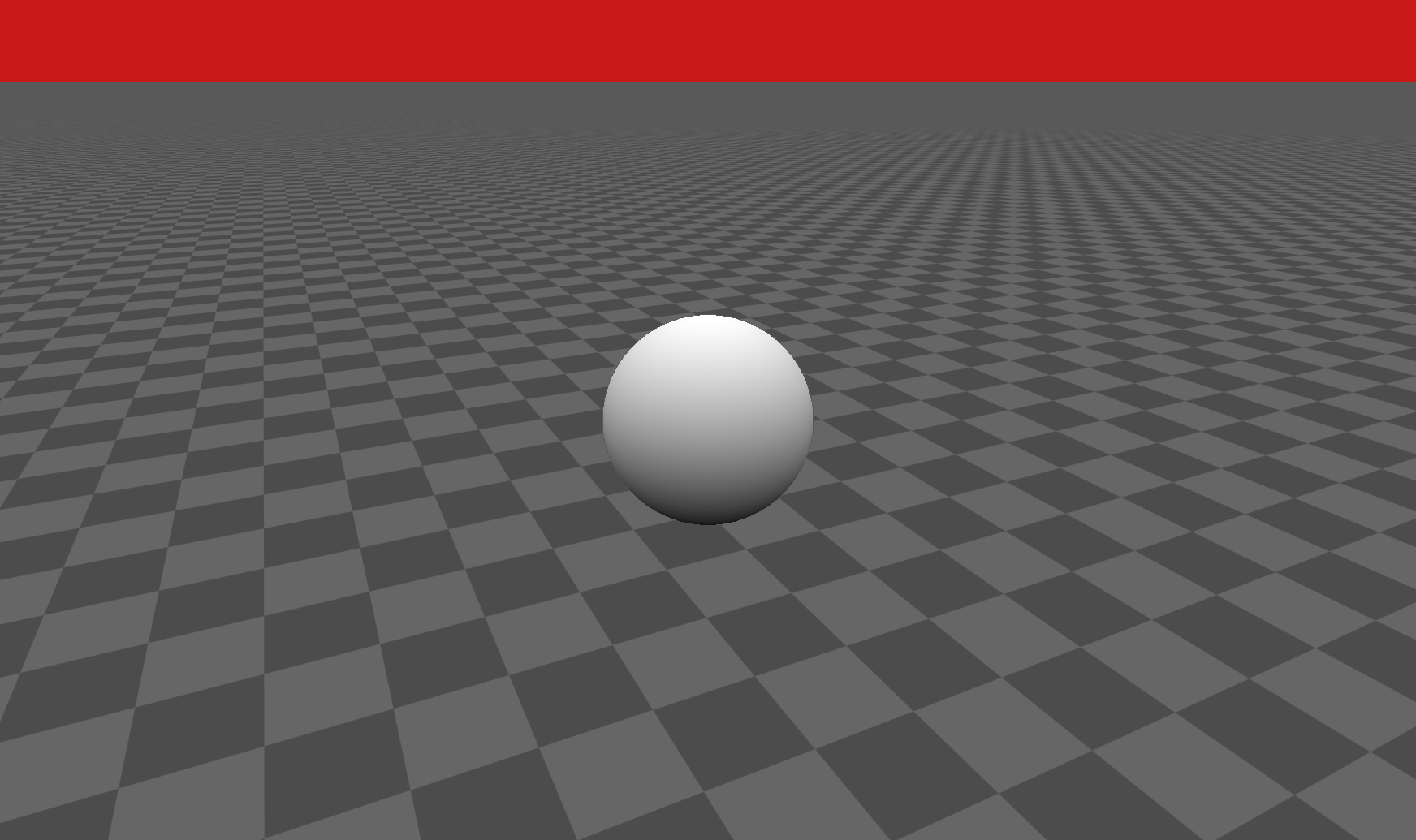
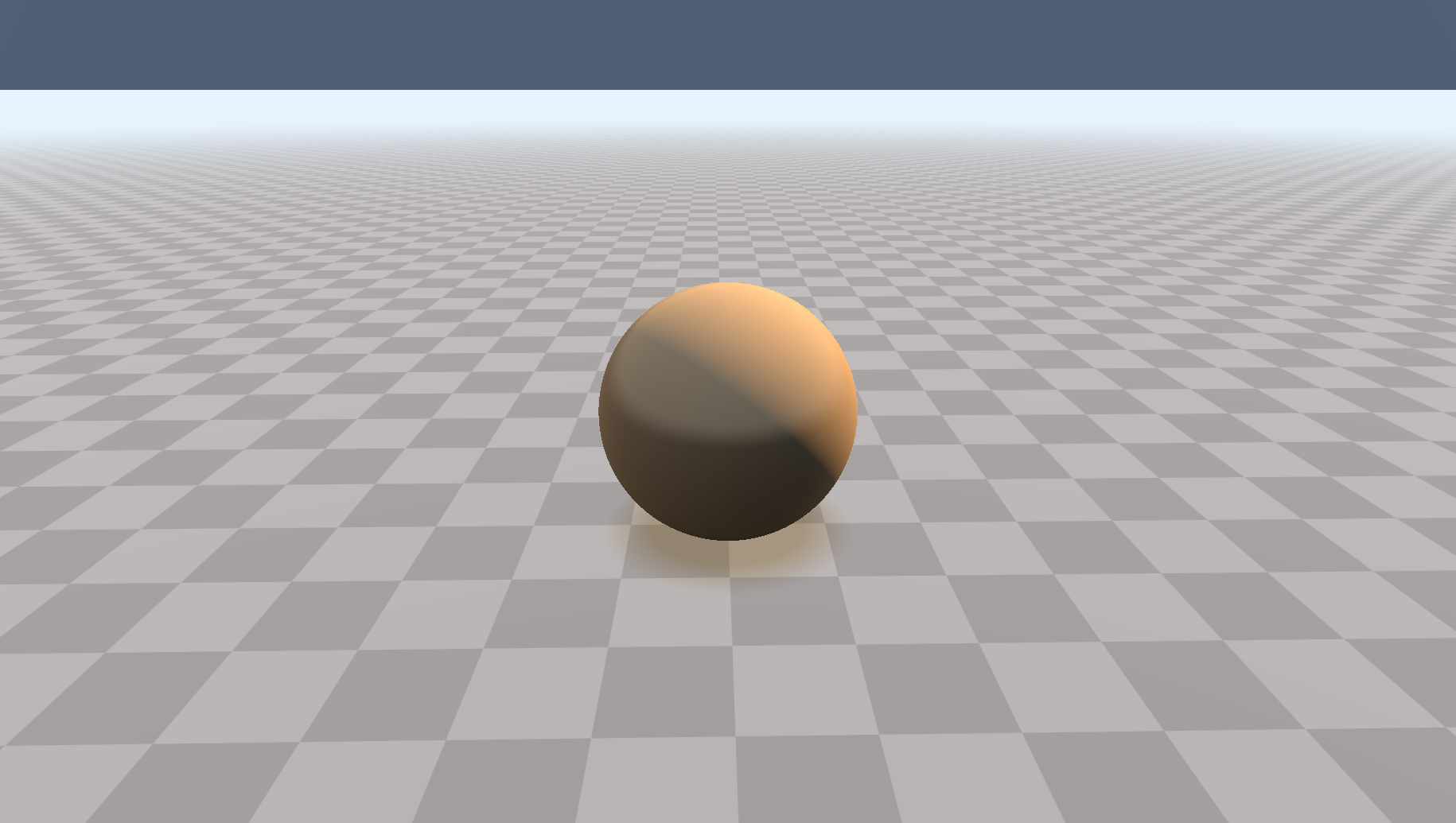
最终图像,内容来自iq大神的sahdertoy
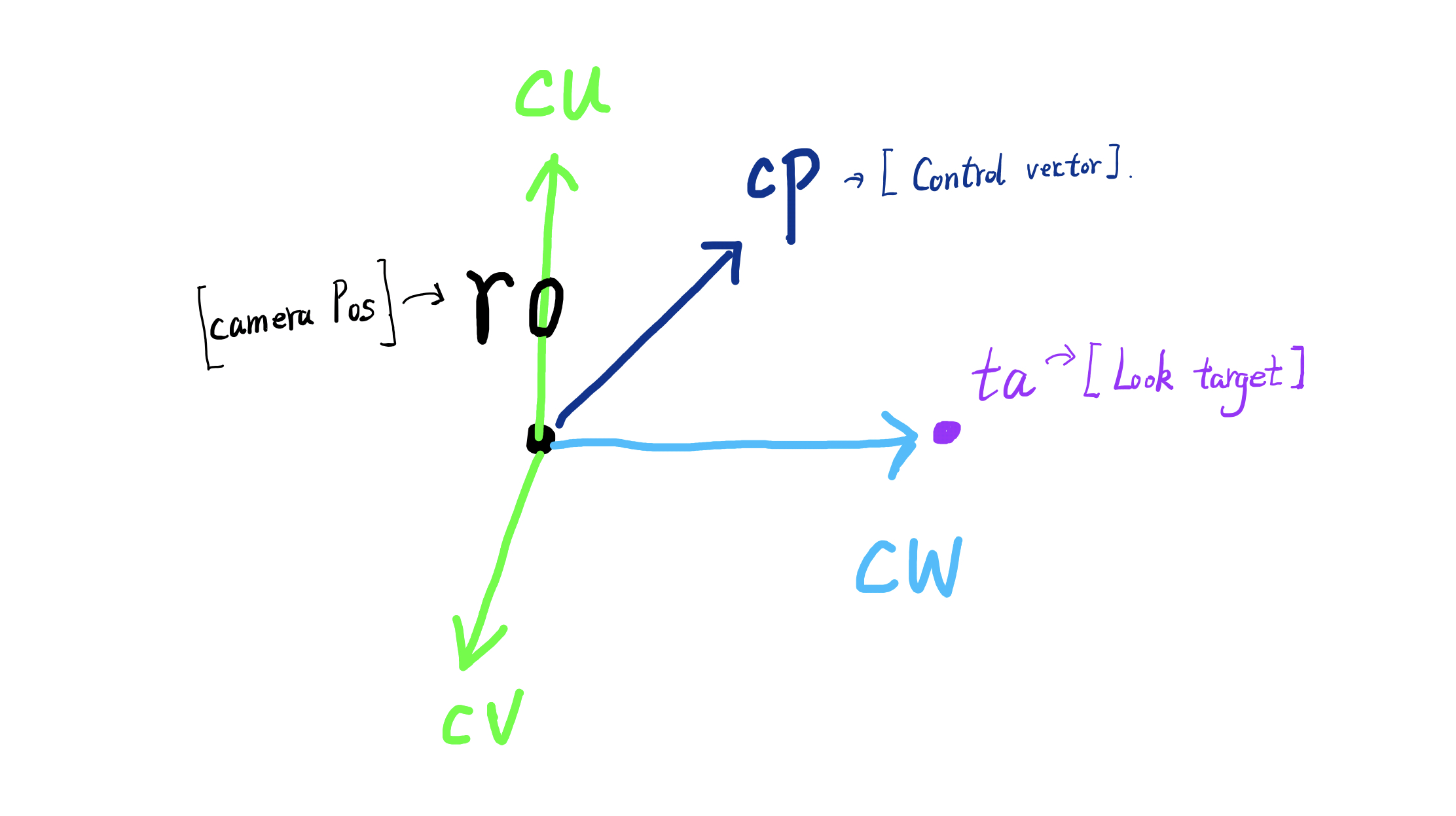
mat3 setCamera( in vec3 ro, in vec3 ta, float cr )
{
vec3 cw = normalize(ta-ro);
vec3 cp = vec3(sin(cr), cos(cr),0.0);
vec3 cu = normalize( cross(cw,cp) );
vec3 cv = normalize( cross(cu,cw) );
return mat3( cu, cv, cw );
}
这个方法设置了一个转化矩阵,根据摄像机的空间位置,我们需要把摄像机转化到世界坐标系
在main()中调用 :
void main() {
// camera, ro:摄像机圆心,ta:目标点
vec3 ro = vec3( 2 , 2 , 4 );
vec3 ta = vec3( 0, 0, 0 );
// camera-to-world transformation
mat3 ca = setCamera( ro, ta, 0.0 );
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
为了更加可控,可以增加鼠标控制:
vec2 mo = iMouse.xy/iResolution.xy;
获得鼠标的空间坐标点 那么我们可以直接使用这个值进行对camera的位置更改
// 鼠标控制的摄像机位置
vec3 ro = vec3( cos(mo.x), mo.y, sin(mo.x) );
// 测试
gl_FragColor = vec4(ro,1.0);
我们把屏幕的坐标从 0-1 ,改到 -0.5 到 0.5
vec2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*gl_FragCoord.xy)/iResolution.y;
// 测
gl_FragColor = vec4(p,1.0,1.0); vec3 rd = ca * normalize( vec3(p.xy,2.0) );
// 测试
gl_FragColor = vec4(rd,1.0);
ca * viewSpace ,把坐标空间从 viewspace 转化到世界空间
// p是球心位置,s是球的半径
float sdSphere( vec3 p, float s )
{
return length(p)-s;
}我们已经有了两个基本值,一个是相机原点 ro ,一个是光线方向 rd
我们定义一个场景来存放所有marching的内容
float map( in vec3 pos )
{
return sdSphere( pos , 1.0 );
}- 光线的位置更新: ro + rd * t ,从初始点ro开始,朝着方向rd ,走t倍的距离
- 我们循环 Max_Step 次,代表我们最多marching 步数 ,
- 还要满足t被距离之后,不能超过我们预定的Max_Dist。
- 就算SDF函数,我们每一次都得到一个 最小 距离 h
- 然后我们每一步都用 h 更新 t
- 最后,当我们得到的最小距离h很接近表面时,我们就知道他已经时表面的点,我们更新一个res返回
vec3 castRay( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 res = vec3(0.0,0.0,0.0);
float t = 0.0 ;
for( int i = 0 ; i < Max_Step && t < Max_Dist ; i++ )
{
float h = map( ro+rd*t );
if( abs(h)<( Surf_Dist * t ))
{
res = vec3(t,h,1.0);
break;
}
t += h;
}
return res;
}当然我么还要define 这些值
#define Max_Step 250
#define Max_Dist 100.0
#define Surf_Dist 0.000001
最后,我们希望对这个图进行渲染,我们为了综合,开一个单独的函数,为了以后反射,高光,阴影等计算
vec3 render( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
return vec3(res.x);
}
测试:
vec3 ro = vec3( cos(mo.x)-5.0, mo.y, sin(mo.x) );
vec3 col = render(ro,rd);
gl_FragColor = vec4(col,1.0);
至此,我么已经渲染出一个球,我们再来回顾一下整个过程:顺便我还加入一些其他步骤
- 更新设置鼠标和摄像机
void mainImage( out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord )
{
vec2 mo = iMouse.xy/iResolution.xy;
float time = 15.0 + iTime;
//cam
vec3 ro = vec3( 4.6*cos(0.1*time + 6.0*mo.x), 1.0 + 2.0*mo.y, 0.5 + 4.6*sin(0.1*time + 6.0*mo.x) );
vec3 ta = vec3( -0.5, -0.4, 0.5 );
mat3 ca = setCamera( ro, ta, 0.0 );
}- 初始化Ray,并且调用render进行marching,加入了gamma 和 tot 总量
vec3 tot = vec3(0.0);
vec2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*gl_FragCoord.xy)/iResolution.y;
vec3 rd = ca * normalize( vec3(p.xy,2.0) );
vec3 col = render(ro,rd);
// gamma
col = pow( col, vec3(0.4545) );
tot += col;
gl_FragColor = vec4(tot,1.0);
- 在render函数中,我们只是简单的做了一个castRay,并没有做光照渲染。
- castRay中,我们根据ro 和 rd ,利用sdf的sphere公式,绘制出了一个球
- 方法一 : 来自 iq 的网站 : normalsSDF
vec3 calcNormal( in vec3 pos )
{
vec2 e = vec2(1.0,-1.0)*0.5773*0.0005;
return normalize( e.xyy*map( pos + e.xyy ) +
e.yyx*map( pos + e.yyx ) +
e.yxy*map( pos + e.yxy ) +
e.xxx*map( pos + e.xxx ) );
}
2.方法二 : 来自 klems
vec3 calcNormal( in vec3 pos )
{
vec3 n = vec3(0.0);
for( int i=ZERO; i<4; i++ )
{
vec3 e = 0.5773*(2.0*vec3((((i+3)>>1)&1),((i>>1)&1),(i&1))-1.0);
n += e*map(pos+0.0005*e).x;
}
return normalize(n);
}我们要在render方法中计算他的法线:
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
vec3 pos = ro + res.x * rd;
vec3 normal = calcNormal( pos );
既然我们法线也有了,我们现在就可以模拟一个灯光,然后做一个漫反射材质了 :
vec3 render( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 col = vec3(0, 0, 0);
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
vec3 normal = calcNormal(res.x * rd + ro);
col = sin( vec3(0.9,0.1,0.1));
vec3 lig = normalize( vec3(-0.4, 0.7, -0.6) );
float dif = clamp( dot( normal, lig ), 0.0, 1.0 );
return dif * col ;
}
当然除了diffue ,还有其他光照计算 这里我们一共计算了
- vertex positon
- vertex normal
- vertex refect
- light direction
- half vector
- ambient color
- back Color
- cubemap Color
- Rim Color
- Diffuse
vec3 render( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 col = vec3(0, 0, 0);
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
vec3 pos = res.x * rd + ro ;
vec3 normal = calcNormal(pos);
vec3 ref = reflect( rd, normal );
col = sin( vec3(0.9,0.1,0.1));
vec3 lig = normalize( vec3(-0.4, 0.7, -0.6) );
// Half vector
vec3 hal = normalize( lig-rd );
// ambient
float amb = clamp( 0.5+0.5*normal.y, 0.0, 1.0 );
// back
float bac = clamp( dot( normal, normalize(vec3(-lig.x,0.0,-lig.z))), 0.0, 1.0 )*clamp( 1.0-pos.y,0.0,1.0);
// cube map rel
float dom = smoothstep( -0.2, 0.2, ref.y );
// rim
float fre = pow( clamp(1.0+dot(normal,rd),0.0,1.0), 2.0 );
// diffuse
float dif = clamp( dot( normal, lig ), 0.0, 1.0 );
return vec3(fre);
}可以逐个的输出测试:
我们在castray的时候指定一个范围来当作地面
float tmax = Max_Dist ;
float tp1 = (0.0-ro.y)/rd.y;
if( tp1>0.0 )
{
tmax = min( tmax, tp1 );
res = vec3( tp1, 1.0 ,1.0);
}
我们需要一种方法来区分不同的问题,地板还是sphere? 所以我们把map函数改一下,我们增加一个通道来区分他们
vec2 map( in vec3 pos )
{
return vec2(sdSphere( pos, 1.0 ),40) ;
}第二个通道随便指定一个值就行
此外我们就很多地方需要修改一下 calcNormal函数中返回指定x通道 castRay函数中,判断指定x通道,res指定y通道
for( int i = 0 ; i < Max_Step && t < Max_Dist ; i++ )
{
vec2 h = map( ro+rd*t );
if( abs(h.x)<( Surf_Dist * t ))
{
res = vec3(t,h.y,1.0);
break;
}
t += h.x;
}
return res;
同样报错的地方,比如法线计算,我们也要指定到x通道
这样我们就可以根据res的y通道来区分材质了
vec3 render( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 col = vec3(0, 0, 0);
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
float m = res.y;
vec3 pos = res.x * rd + ro ;
vec3 normal = calcNormal(pos);
vec3 ref = reflect( rd, normal );
// light dir
vec3 lig = normalize( vec3(-0.4, 0.7, -0.6) );
// Half vector
vec3 hal = normalize( lig-rd );
// ambient
float amb = clamp( 0.5+0.5*normal.y, 0.0, 1.0 );
// back
float bac = clamp( dot( normal, normalize(vec3(-lig.x,0.0,-lig.z))), 0.0, 1.0 )*clamp( 1.0-pos.y,0.0,1.0);
// cube map rel
float dom = smoothstep( -0.2, 0.2, ref.y );
// rim
float fre = pow( clamp(1.0+dot(normal,rd),0.0,1.0), 2.0 );
// diffuse
float dif = clamp( dot( normal, lig ), 0.0, 1.0 );
if( m>-0.5 ){
if(m<1.5)
return vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0);
col = sin( vec3(0.9,0.1,0.1));
}
return col ;
}
同样来自iq大神的文章 checkerfiltering
//
float checkersGradBox( in vec2 p )
{
// filter kernel
vec2 w = fwidth(p) + 0.001;
// analytical integral (box filter)
vec2 i = 2.0*(abs(fract((p-0.5*w)*0.5)-0.5)-abs(fract((p+0.5*w)*0.5)-0.5))/w;
// xor pattern
return 0.5 - 0.5*i.x*i.y;
}
在地板选择材质中调用他 :
if(m<1.5)
{
float f = checkersGradBox( 5.0*pos.xz );
col = 0.3 + f*vec3(0.1);
return col ;
}
我们在更新一下球:
vec2 map( in vec3 pos )
{
return vec2(sdSphere( pos - vec3(0.0,0.25,0.0), 0.25 ),40) ;
}
float calcAO( in vec3 pos, in vec3 nor )
{
float occ = 0.0;
float sca = 1.0;
for( int i=0; i<5; i++ )
{
float hr = 0.01 + 0.12*float(i)/4.0;
vec3 aopos = nor * hr + pos;
float dd = map( aopos ).x;
occ += -(dd-hr)*sca;
sca *= 0.95;
}
return clamp( 1.0 - 3.0*occ, 0.0, 1.0 ) * (0.5+0.5*nor.y);
}
// lighting
float occ = calcAO( pos, normal );
我们回过头去重新看代码,我重新理了一下render函数,使他看起来更加流畅:
vec3 render( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd )
{
vec3 col = vec3(0.7, 0.9, 1.0) + rd.y * 0.8 ;
vec3 res = castRay(ro,rd) ;
float t = res.x;
float m = res.y;
if( m>-0.5 ){
vec3 pos = t * rd + ro ;
vec3 nor = (m<1.5) ? vec3(0.0,1.0,0.0) : calcNormal( pos );
vec3 ref = reflect( rd, nor );
col = 0.45 + 0.35*sin( vec3(0.05,0.08,0.10)*(m-1.0) );
if( m<1.5 )
{
float f = checkersGradBox( 5.0*pos.xz );
col = 0.3 + f*vec3(0.1);
}
// lighting
float occ = calcAO( pos, nor );
vec3 lig = normalize( vec3(-0.4, 0.7, -0.6) );
vec3 hal = normalize( lig-rd );
float amb = clamp( 0.5+0.5*nor.y, 0.0, 1.0 );
float dif = clamp( dot( nor, lig ), 0.0, 1.0 );
float bac = clamp( dot( nor, normalize(vec3(-lig.x,0.0,-lig.z))), 0.0, 1.0 )*clamp( 1.0-pos.y,0.0,1.0);
float dom = smoothstep( -0.2, 0.2, ref.y );
float fre = pow( clamp(1.0+dot(nor,rd),0.0,1.0), 2.0 );
}
return col ;
} vec3 lin = vec3(0.0);
lin += 1.40*dif*vec3(1.00,0.80,0.55);
lin += 0.20*amb*vec3(0.40,0.60,1.00)*occ;
lin += 0.40*dom*vec3(0.40,0.60,1.00)*occ;
lin += 0.50*bac*vec3(0.25,0.25,0.25)*occ;
lin += 0.25*fre*vec3(1.00,1.00,1.00)*occ;
col = col*lin;
col = mix( col, vec3(0.8,0.9,1.0), 1.0-exp( -0.0002*t*t*t ) );
最后返回颜色时,最好clamp一下
float spe = pow( clamp( dot( nor, hal ), 0.0, 1.0 ),16.0)*
dif *
(0.04 + 0.96*pow( clamp(1.0+dot(hal,rd),0.0,1.0), 5.0 ));
col = col*lin;
// 合并高光
col += 9.00*spe*vec3(1.00,0.90,0.70);
col = mix( col, vec3(0.8,0.9,1.0), 1.0-exp( -0.0002*t*t*t ) );
const float maxHei = 0.8;
#define ZERO (min(iFrame,0))
float calcSoftshadow( in vec3 ro, in vec3 rd, in float mint, in float tmax )
{
// bounding volume
float tp = (maxHei-ro.y)/rd.y; if( tp>0.0 ) tmax = min( tmax, tp );
float res = 1.0;
float t = mint;
for( int i=0; i<16; i++ )
{
float h = map( ro + rd*t ).x;
res = min( res, 8.0*h/t );
t += clamp( h, 0.02, 0.10 );
if( res<0.005 || t>tmax ) break;
}
return clamp( res, 0.0, 1.0 );
}
在render中合并 :
dif *= calcSoftshadow( pos, lig, 0.02, 2.5 );
dom *= calcSoftshadow( pos, ref, 0.02, 2.5 );
在castray 初始化时:
vec3 res = vec3(0.0,-1.0,0.0);定义抗锯齿等级
#define AA 3 // make this 2 or 3 for antialiasing
在主循环中:
#if AA>1
for( int m=ZERO; m<AA; m++ )
for( int n=ZERO; n<AA; n++ )
{
// pixel coordinates
vec2 o = vec2(float(m),float(n)) / float(AA) - 0.5;
vec2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*(gl_FragCoord.xy + o))/iResolution.y;
#else
vec2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*gl_FragCoord.xy )/iResolution.y;
#endif
// ray direction
vec3 rd = ca * normalize( vec3(p.xy,2.0) );
// render
vec3 col = render( ro, rd );
// gamma
col = pow( col, vec3(0.4545) );
tot += col;
#if AA>1
}
tot /= float(AA*AA);
#endif
gl_FragColor = vec4( tot, 1.0 );