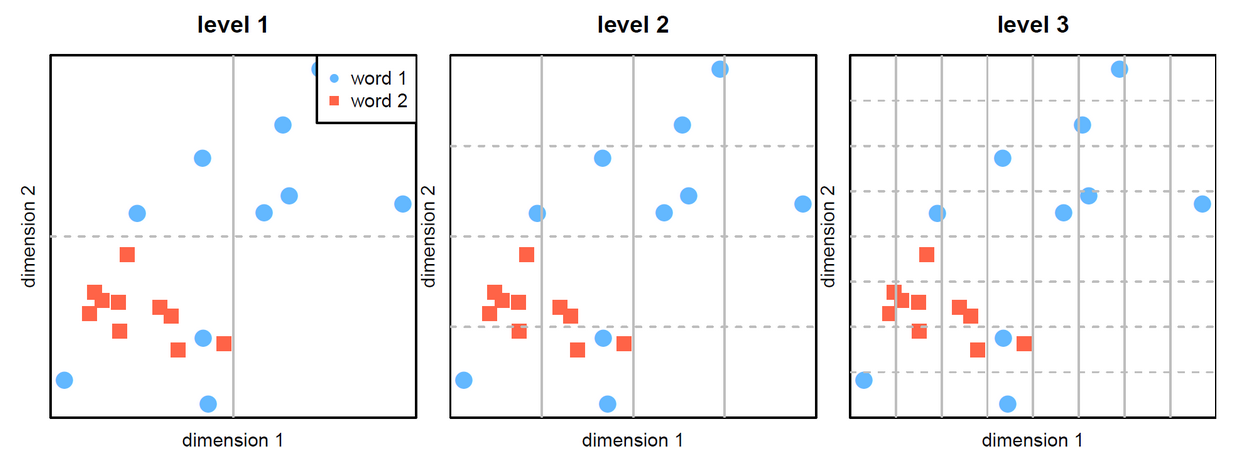
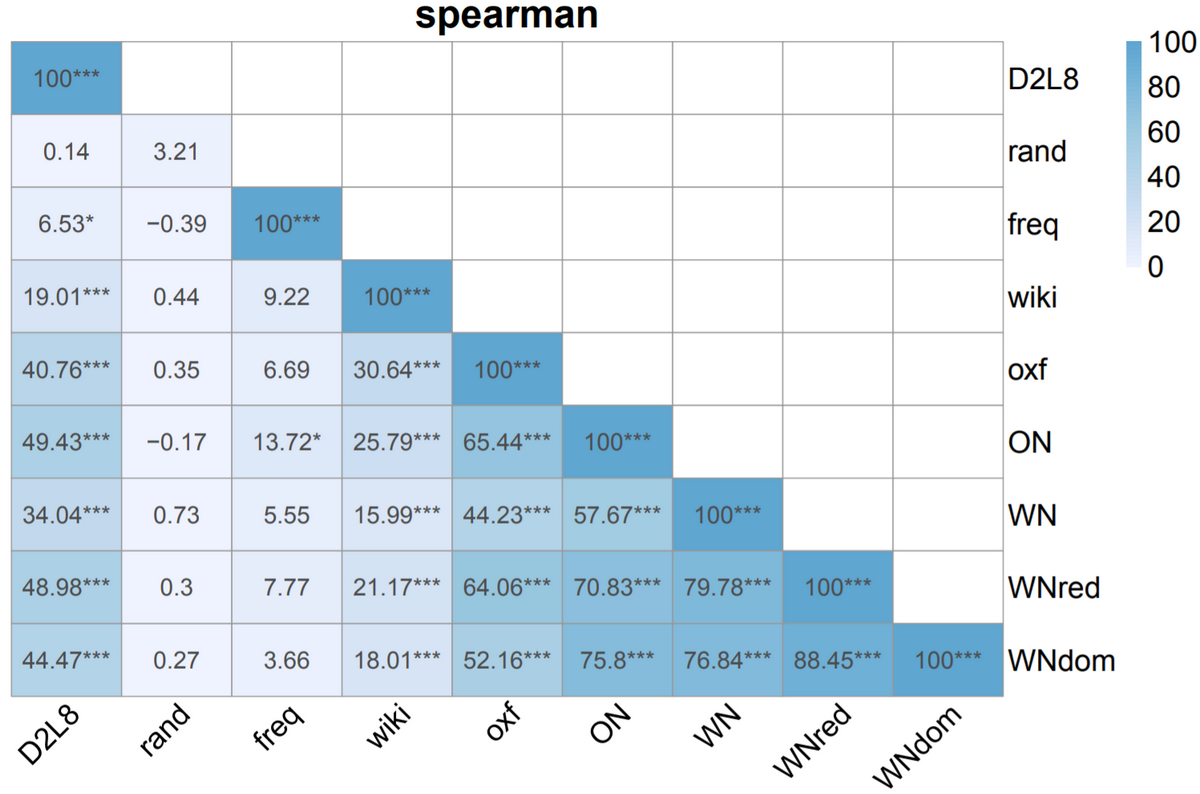
This repository contains code and data to reproduce the results presented in the paper: Unsupervised Word Polysemy Quantification with Multiresolution Grids of Contextual Embeddings (Xypolopoulos et al. 2020). link to arXiv
-
The number of senses of a given word, or polysemy, is a very subjective notion, which varies widely across annotators and resources.
-
We propose a novel method to estimate polysemy, based on simple geometry in the contextual embedding space. Our approach is fully unsupervised and purely data-driven, which makes it applicable to any language.
-
We show through rigorous experiments that our rankings are well correlated (with strong statistical significance) with 6 different rankings derived from famous human-constructed resources such as WordNet, OntoNotes, Oxford, Wikipedia etc., for 6 different standard metrics. We also visualize and analyze the correlation between the human rankings.
-
A valuable by-product of our method is the ability to sample, at no extra cost, sentences containing different senses of a given word.
- WordNet
- Wikipedia
- Ontonotes (requires application)
- WordNet-Domains (requires application)
- Deep contextualized word embeddings
We used AllenAI's Embeddings from Language Models (ELMo) and specifically the command line tool provided by the authors.
If you use some of the code in this repository, or simply if you want to refer to our paper, please cite:
@article{xypolopoulos2020unsupervised,
title={Unsupervised Word Polysemy Quantification with Multiresolution Grids of Contextual Embeddings},
author={Christos Xypolopoulos and Antoine J. -P. Tixier and Michalis Vazirgiannis},
year={2020},
eprint={2003.10224},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}Xypolopoulos, Christos, Antoine J-P. Tixier, and Michalis Vazirgiannis. "Unsupervised Word Polysemy Quantification with Multiresolution Grids of Contextual Embeddings." arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10224 (2020).
-
We thank Giannis Nikolentzos for helpful discussions about pyramid matching.
-
This work was supported by the LinTo project.
-
We gratefully acknowledge the support of NVidia Corporation that donated the Titan V GPU used for this research.