A contribution to Haystack tutorials may be anything from a suggestion for edits or a new tutorial request to adding a new tutorial or editing an existing one yourself.
To make a request for a new tutorial or to suggest edits and fixes, submit an issue and choose the appropriate type:
-
Bug report: For any edit suggestions or bug reports.
-
New Tutorial Request 📓: To suggest that we create a new tutorial.
All of the Haystack tutorials live in the tutorials folder in this repo. Each tutorial is an interactive .ipynb file and we generate a Markdown file to accompany it.
Here's what you need to do to add or edit tutorials 👇:
- Prepare your environment:
- Install the Python requirements with
pip install -r requirements.txt - Install the pre-commit hooks with
pre-commit install. This utility will run some formatting/checking tasks right before all git commit operations.
- Install the Python requirements with
- If you're creating a new tutorial:
- Follow the naming convention for file names.
- Add your new tutorial to index.toml. Here,
weightis the order in which your tutorial appears. For example, a tutorial withweight = 15comes after a tutorial withweight = 10and before20. Each tutorial comes with a Google Colab link andOpen in Colabbutton on the top of the tutorial by default. If your new tutorial cannot be run on Google Colab, setcolab = falsenot to displayOpen in Colabbutton on top the tutorial.
- Edit an existing tutorial or copy the tutorial template to create a new tutorial.
- Pre-commit hooks will ensure the
markdownsfolder reflects your changes but you can update the docs at any time:- Run
python scripts/generate_markdowns.py --index index.toml --notebooks tutorials/your-tutorial.ipynb --output markdowns/. This generates or updates the relevant markdown file in/markdowns.
- Run
- Create a pull request.
- Wait for the CI checks to pass. These checks pass if the relevant markdown files are created.
- Update the README, if necessary.
- Wait for a review and merge 🎉. Thank you for contributing 💙.
The default behaviour for markdown files is that it gets the same name as the corresponfing .ipynb notebook of that tutorial. The name of the markdown file is also the location at which the tutorial will appear on the website.
For example, "01_Basic_QA_Pipeline" will be on https://haystack.deepset.ai/tutorials/01_basic_qa_pipeline
In index.toml you have the option of adding an optional slug entry for a tutorial which will generate the correspoinding markdown under the name you give for the slug. This is useful for scenarios where you are updating a tutorial to the point where it makes sense that the name of the .ipynb file changes, but you would still like people to access the tutorial on the same URL.
We use a GitHub action for our Continuous Integration tasks. This means that as soon as you open a PR, GitHub starts executing some workflows on your code. Here, the workflow checks that you've generated the required .md files for the tutorials you've edited or created.
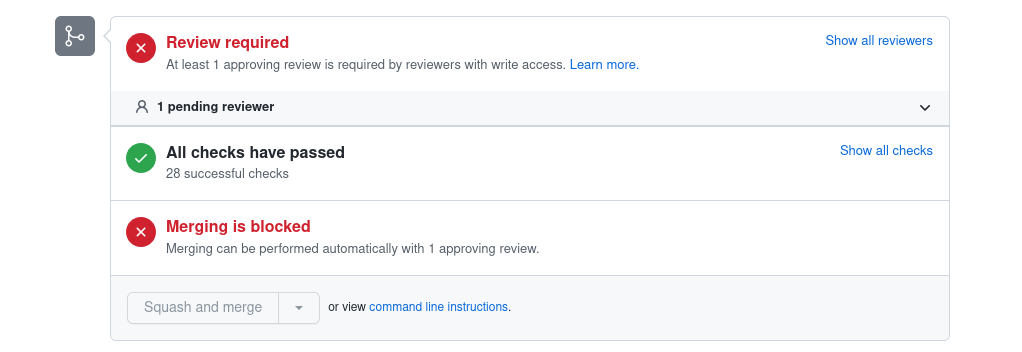
If all goes well, at the bottom of your PR page, you should see something like this, where all checks are green.
If you see some red checks, then something didn't work and you need to take some action. The most likely reason is that the .md file accompanying the .ipynb tutorial hasn't been updated or created. You can try to run repeat step 4 in Contributing to Haystack Tutorials.
- Each tutorial name starts with a number. If you create a new tutorial, its name should start with the number following the last tutorial.
- Separate words in the title with an
_underscore. - Use a short descriptive name for the filename, for example: 22_creating_a_summarizer_pipeline.
- Generated markdown files only have the number of the tutorial (use the
scripts/generate_markdowns.pyscript for this).