对中文进行分类demo,分成0/1/2
可以理解为0是一般,1是好,2是差。模型代码、数据集都在我的网盘里,链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/18vPGelYCXGqp5OCWZWz36A 提取码:de0f
我们使用的是Google官方开源的中文BERT预训练模型
vocab.txt里把常用的中文基本覆盖了
class MyDataProcessor(object):
"""Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
raise NotImplementedError()
def get_dev_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
raise NotImplementedError()
def get_test_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for prediction."""
raise NotImplementedError()
def get_labels(self):
"""Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
raise NotImplementedError()这是完全照搬class DataProcessor的类,只是类名改成MyDataProcessor
读取数据的类get_train_examples
class MyDataProcessor(DataProcessor):
"""Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_sentiment.txt')
f = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 读取数据,并指定中文常用的utf-8
train_data = []
index = 0 # ID值
for line in f.readlines(): # 参考XnliProcessor
guid = "train-%d" % index
line = line.replace('\n', '').split('\t') # 处理换行符,原数据是以tab分割
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(str(line[1])) # 第0位置是索引,第1位置才是数据,可以查看train_sentiment.txt
label = str(line[2]) # 我们的label里没有什么东西,只有数值,所以转字符串即可
train_data.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=None, label=label)) # 这里我们没text_b,所以传入None
index += 1 # index每次不一样,所以加等于1
return train_data # 这样数据就读取完成参照XnliProcessor
class XnliProcessor(DataProcessor):
"""Processor for the XNLI data set."""
def __init__(self):
self.language = "zh"
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
"""See base class."""
lines = self._read_tsv(
os.path.join(data_dir, "multinli",
"multinli.train.%s.tsv" % self.language))
examples = []
for (i, line) in enumerate(lines):
if i == 0:
continue
guid = "train-%d" % (i) # 获取样本ID
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(line[0])
text_b = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(line[1]) # 获取text_a和b,我们只有a所以把b去掉
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(line[2]) # 获取标签
if label == tokenization.convert_to_unicode("contradictory"):
label = tokenization.convert_to_unicode("contradiction")
examples.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=text_b, label=label)) # 把读进来的东西传到InputExample,这个类可以点进去,里面什么都没做,只不过是模板,我们也照着做
return examples获取label
# 也是参考XnliProcessor,把return改成0,1,2即可
def get_labels(self):
"""Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
return ["0", "1", "2"]
以下是完整的
class MyDataProcessor(DataProcessor):
"""Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
def get_train_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train_sentiment.txt')
f = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') # 读取数据,并指定中文常用的utf-8
train_data = []
index = 0 # ID值
for line in f.readlines(): # 参考XnliProcessor
guid = "train-%d" % index
line = line.replace("\n", "").split("\t") # 处理换行符,原数据是以tab分割
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(str(line[1])) # 第0位置是索引,第1位置才是数据,可以查看train_sentiment.txt
label = str(line[2]) # 我们的label里没有什么东西,只有数值,所以转字符串即可
train_data.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=None, label=label)) # 这里我们没text_b,所以传入None
index += 1 # index每次不一样,所以加等于1
return train_data # 这样数据就读取完成
def get_dev_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_sentiment.txt')
f = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
dev_data = []
index = 0
for line in f.readlines():
guid = "dev-%d" % index
line = line.replace('\n', '').split('\t')
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(str(line[1]))
label = str(line[2])
dev_data.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=None, label=label))
index += 1
return dev_data
def get_test_examples(self, data_dir):
"""Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for prediction."""
file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_sentiment.txt') # 我们直接用验证集来输出结果
print(file_path)
f = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8')
test_data = []
index = 0
for line in f.readlines():
guid = "test-%d" % index
line = line.replace('\n', '').split('\t')
text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(str(line[1]))
label = '0' # 这里的label随机使用即可,只是为了传入
test_data.append(
InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=None, label=label))
index += 1
return test_data
def get_labels(self):
"""Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
return ["0", "1", "2"] # 参考XnliProcessor,改成返回0,1,2main函数增加运行内容
def main(_):
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
processors = {
"cola": ColaProcessor,
"mnli": MnliProcessor,
"mrpc": MrpcProcessor,
"xnli": XnliProcessor,
'my':MyDataProcessor, # 这是增加的部分,这样运行参数task_name才能对应上
}参数
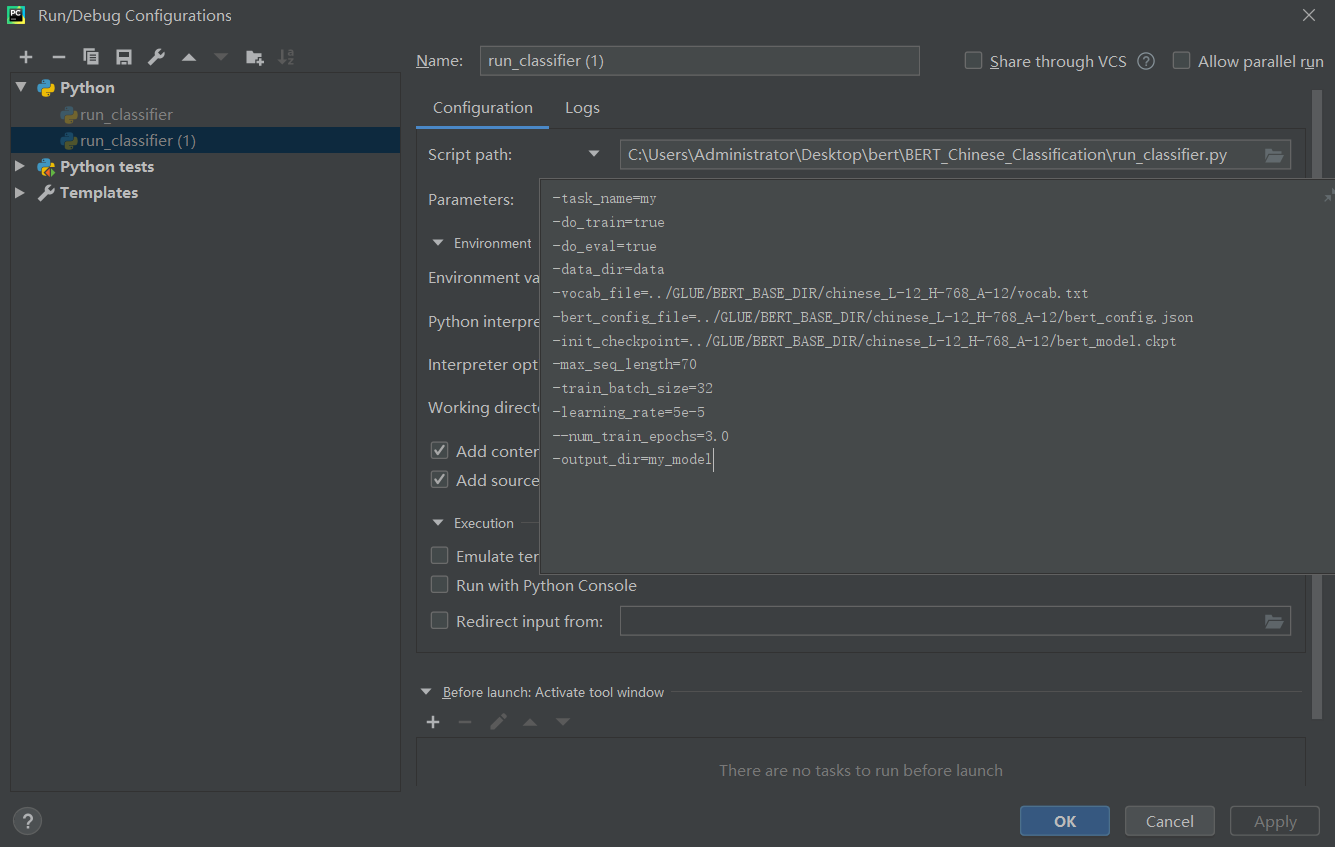
-task_name=my
-do_train=true
-do_eval=true
-data_dir=data
-vocab_file=../GLUE/BERT_BASE_DIR/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt
-bert_config_file=../GLUE/BERT_BASE_DIR/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json
-init_checkpoint=../GLUE/BERT_BASE_DIR/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_model.ckpt
-max_seq_length=70
-train_batch_size=32
-learning_rate=5e-5
--num_train_epochs=3.0
-output_dir=my_model
task_name:运行的模块,在main里指定了名字对应的类
do_train:是否训练
do_eval:是否验证
data_dir:数据地址
vocab_file:词库表
bert_config_file:bert参数
init_checkpoint:初始化参数
max_seq_length:最长字符限制
train_batch_size:训练次数
learning_rate:学习率
num_train_epochs:循环训练次数
output_dir:输出路径
设置参数完成,run即可
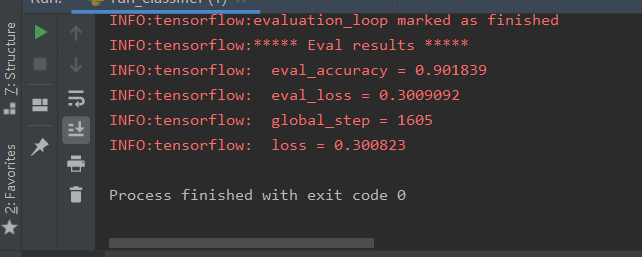
最终模型结果
进行预测的参数
-task_name=my
-do_predict=true
-data_dir=data
-vocab_file=../GLUE/BERT_BASE_DIR/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12/vocab.txt
-bert_config_file=../GLUE/BERT_BASE_DIR/chinese_L-12_H-768_A-12/bert_config.json
-init_checkpoint=my_model
-max_seq_length=70
-output_dir=my_model_predictinit_checkpoint:使用的初始化参数已经是我们训练过的了
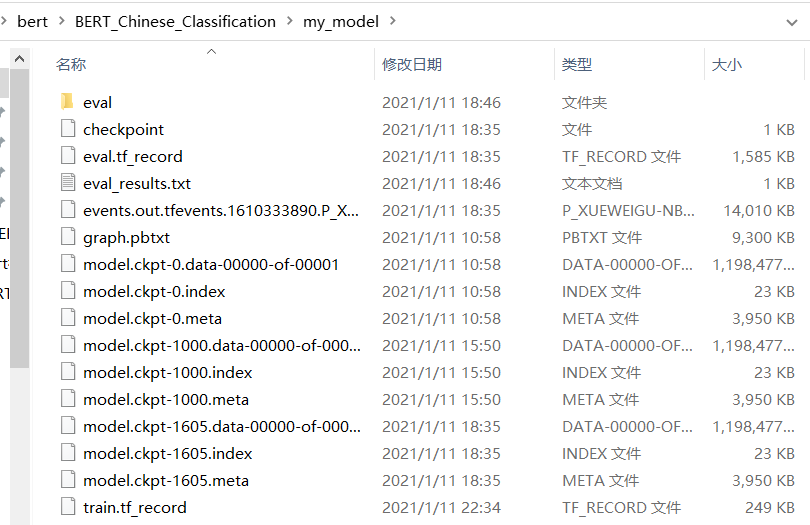
RUN完后有如下文件
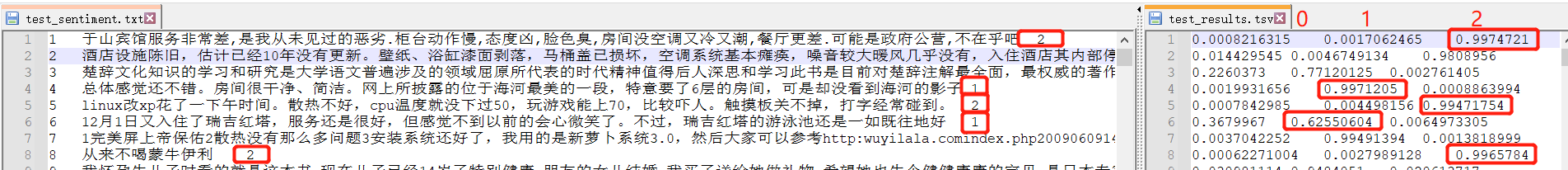
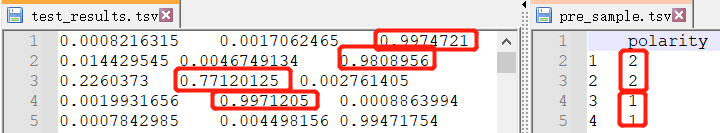
打开与原文件对比,是准确的,不过现在是概率,我们转成值
添加get_results.py
import os
import pandas as pd
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = "my_model_predict"
pd_all = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(path, "test_results.tsv"), sep='\t', header=None)
data = pd.DataFrame(columns=['polarity'])
print(pd_all.shape)
for index in pd_all.index:
neutral_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[0]
positive_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[1]
negative_score = pd_all.loc[index].values[2]
if max(neutral_score, positive_score, negative_score) == neutral_score:
data.loc[index+1] = ["0"]
elif max(neutral_score, positive_score, negative_score) == positive_score:
data.loc[index+1] = ["1"]
else:
data.loc[index+1] = ["2"]
data.to_csv(os.path.join(path, "pre_sample.tsv"), sep='\t')运行完后,同个目录下会出现pre_sample.tsv文件,对比结果
正确
至此,我们完成了中文情感分类实战,写了函数训练、验证,并输出预测结果,BERT也算正式使用了起来,给在做的你点个赞👍。