The purpose of the LDB Orders microservice is to parse monthly order reports and insert them into the LDB Orders entity in MS Dynamics
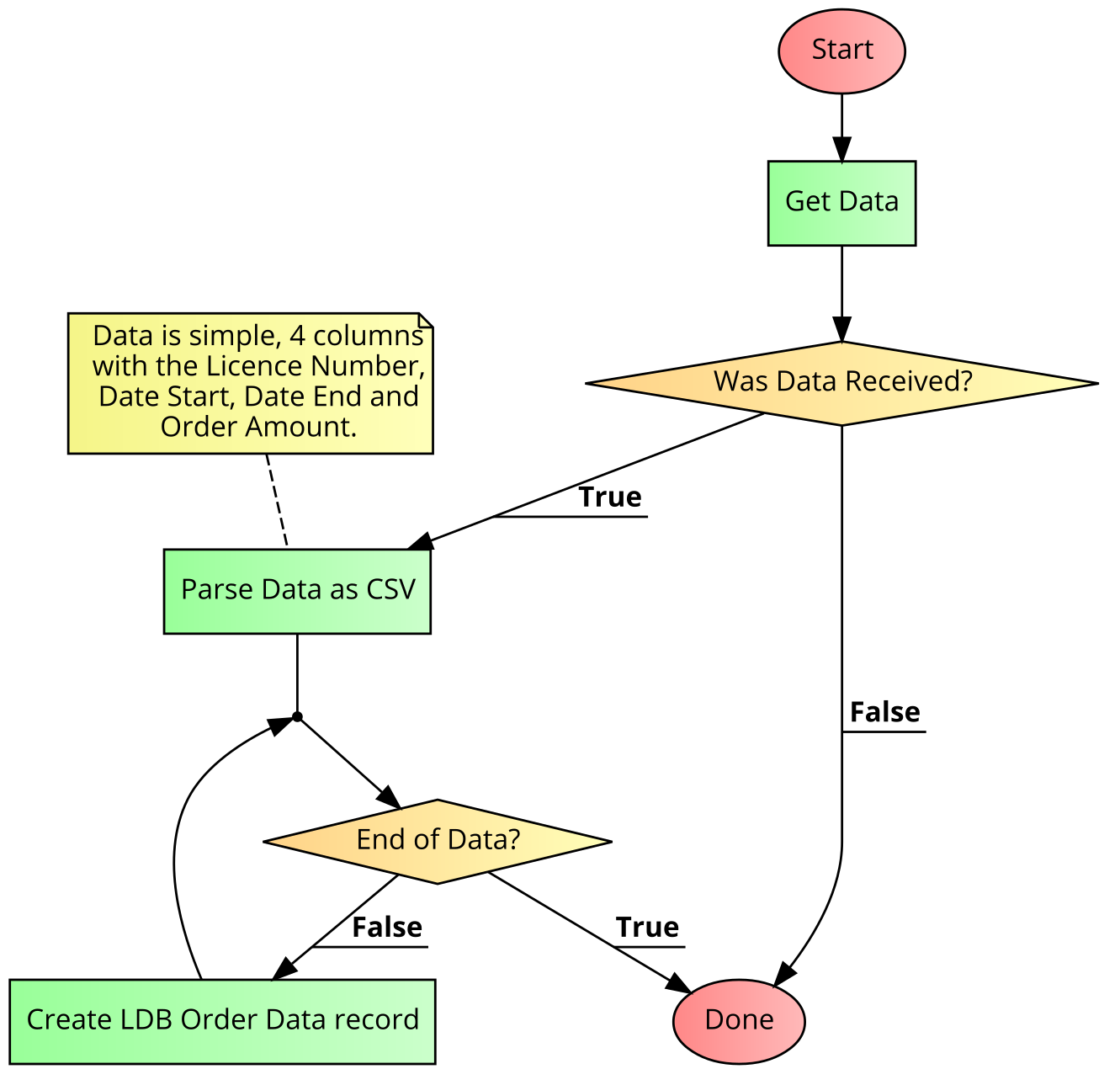 The main input to the system is a text file that is available on the LDB SCP server.
The main input to the system is a text file that is available on the LDB SCP server.
A scheduled job checks for this file, and if it is present it will import the data.
This service is a Dotnet Core 5.0 application. As such you can use a C# IDE such as Visual Studio or VS Code to edit the files.
This section describes concepts and tools necessary for testing the service.
This system uses the Hangfire system of job scheduling.
Hangfire login is restricted to those with local access. To obtain local access:
- Local development
- Run the service locally, after configuring appropriate secrets.
- Navigate to /hangfire after the application starts. If you launch from visual Studio it should go to this URL by default.
- OpenShift deployment
- Open a CLI session to the given OpenShift cluster
- Use
oc project <project>to change to the project namespace containing the instance of the service you wish to control - Use
oc get podsto get a list of running pods. - Use
oc port-forward <podname> 8080:8080to forward port 8080 from the container running the service to localhost. Note that you must not have an existing service using port 8080. - Navigate to
https://localhost:8080/hangfirein a browser.
Once on the hangfire console you may view the status of jobs, and trigger a new job.
###Secrets
The following secrets can be used to adjust the configuration of the service:
| Secret | Purpose |
|---|---|
| DEBUG_MODE | Enables extra logging |
| LDB_URL | Host used for SCP connection to LDB |
| LDB_USERNAME | Username for LDB |
| LDB_PASSWORD | Password for LDB |
| DYNAMICS_ODATA_URI | ODATA URI for MS Dynamics. Leave blank to disable Dynamics portion of the service |
| SPLUNK_COLLECTOR_URL | Full URL for the Splunk collector | | SPLUNK_TOKEN | Splunk access token | | SPLUNK_CHANNEL | Splunk channel | | ENABLE_HANGFIRE_JOBS | Controls whether or not the hangfire job runs. |