TranReloc evaluates queueing systems with customer relocation. Consider the M/PH/c/c queue, i.e. where customers have exponentially distributed inter-arrival time, phase-type distributed service time, and c servers. The capacity of the queue is equal to the number of servers, and customers will be rejected if they arrive when none of the c servers are idle at the time of arrival to the queue. TranReloc extends the M/PH/c/c queue by considering a series of systems that may relocate customers instead completely rejecting them. Moreover, TranReloc gives the user the opportunity to evaluate the system with time-dependent parameters. This type of system reflects customer behavior in the rental industry and patient flow in hospitals.
TranReloc is written in Java, and the interface currently consists of a simple CLI and an R-script (see the section Implementing your model (using R)).
- Evaluate a time-dependent queueing system with exponentially distributed inter-arrival time, phase-type distributed service-time, and customer relocation.
- Choose the capacity and customer's arrival rate and phase-type distribution at each point in time.
- Choose how customers are relocated as function of the blocked queues in the system.
- Choose the service-time distribution of the relocated customers.
- Choose to either evaluate or optimize (i.e. minimize) the total capacity in the system.
- How does it work
- Implementing your model (using R)
- How to cite
- License
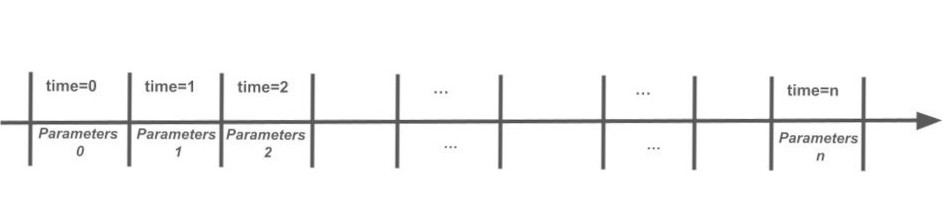
TranReloc use a Continuous-Time Markov Chain (CTMC) and a numerical approach to model the system. Consider a discretized timeline consisting of n consecutive segments. The algorithm in TranReloc use uniformization to evaluate the transient solution to the CTMC by assuming time-homogenuous (i.e. fixed) parameters within each segment. As the algorithm change segment, so does the parameters. Thus, the accuracy of the solution to the state probabilities can be controlled by adjusting the size of the segments.
The system contains a range of queues, denoted assets. Additionally, each asset is subject to a capacity, arrival intensity and range of service-time distributions. All service-times are governed by phase-type (PH) distributions. The number of assets and service distributions are fixed, but the capacity, arrival intensity and configurations of the distributions (i.e. the number of phases and parameter values) are allowed to change over time. That is, between the consecutive segments.
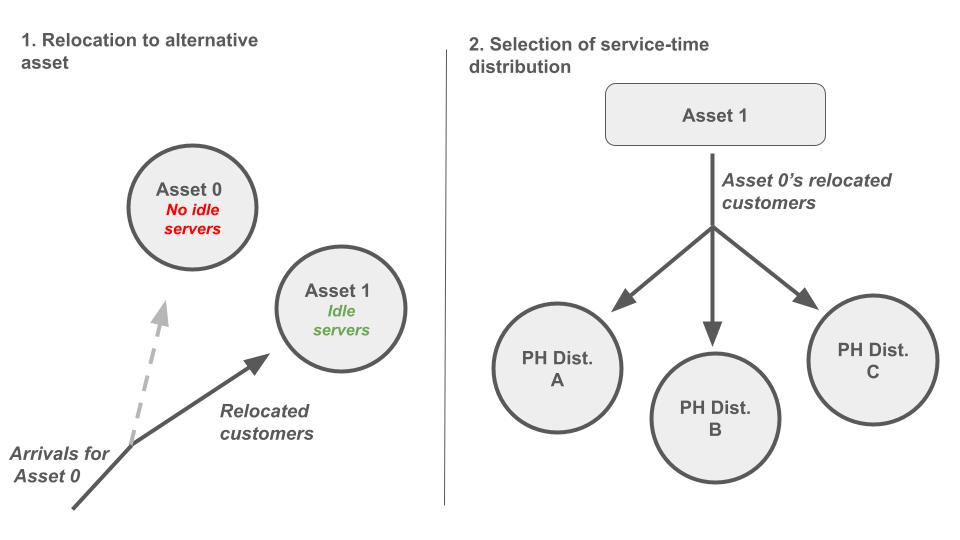
Customers arriving to an asset without idle servers can be relocated to an alternative asset instead of being lost from the system. The customers relocate to the alternative asset with a pre-specified probability, denoted the relocation probability, which is a function of the assets that are in shortage of servers at the time of arrival to the system.
As they relocate to the alternative asset, the relocated customers must be assigned a service-time distribution. The following governs the assignment process: (1) The customer's preferred asset (the one currently in shortage), and (2) a probability distribution. For instance, say customers are relocated from Asset 0 to Asset 1, and Asset 1 contains three types of service-time distributions. The service-time of the relocated customers are governed by the first distribution with a probability of 25%, the second distribution with a probability of 10%, and the third distribution with a probability of 65%.
The first service-time distribution (index 0) always governs the service-time of customers succeeding in receiving service from the preferred asset.
Coming soon.
Andersen, A. R., TranReloc: Relocation of customers in a transient queueing system with phase-type distributed service times, GitHub, URL: https://github.com/areenberg/TranReloc
Copyright 2022 Anders Reenberg Andersen.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http:https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.