Lending is by far one of the most popular use case in the currently booming Decentralised Finance sector. The second-generation lending protocols like Aave and Compound allow users to deposit and borrow from a lending pool automatically setting the interest rates to balance capital supply and demand. However, both of them suffer from liquidity crunch as borrowers need to provide collateral that significantly exceeds their loan size. It causes the collateral funds to remain idle in the pool. From the macroeconomic perspective, it means that approximately 70% of the funds stay unproductive and is not used for assets investment, trading or staking activity.
PrimeLoans are the next generation lending platform on Avalanche that will allow under-collateral borrowing from pooled deposits. The core innovation is lending funds not to a personal account but a special purpose smart-contract. The contract automatically guards solvency and every activity needs to undergo a series of checks. This mechanism blocks transactions which could cause the smart-loan valuation to drop below a safe threshold. The insolvency risk is further mitigated by a decentralised liquidation mechanism allowing anyone to forcibly repay part of the loan due to assets price movements caused by external factors. Wrapping loans with smart contracts reduces the collateral need, improving the money supply in the entire Avalanche ecosystem. Patient capital holders will earn interest on the funds provided, while borrowers could use extra capital for investment in high-grow assets.
The core idea of DeltaPrime protocol is similar to current lending protocols. There is a common lending pool, to which some users can deposit their funds collecting deposit rate, while the others use it to borrow funds and pay borrowing rate. Rates depend on a current utilisation of a pool.
The main innovation is that borrowed funds are not sent straight to a borrowers' wallets, but to a special purpose smart-contracts which they can use to operate their loans. In that way they can experience Prime Brokerage like experience with additional liquidity and cross-margin for their investments. Every Prima Account is a separate smart contract deployed to network.
One way to use the protocol is to deposit tokens in a lending pool (passive investing). It immediately starts to accumulate interest based on the current rates. The rates depend on a current utilisation of a pool, the higher it is the higher the rates. This way the usage of a pool balances according to supply and demand.
Another way to use the protocol is to create a Prime Account (active investing). Prime Account is a dedicated smart contract deployed to a blockchain that only an owner can control. By means of his account a user can borrow funds from the pool and provide his collateral. Then he can use both to invest in assets thanks to integrations with DEXs. In that way LTV up to 500% can be obtained.
The first features available for Prime Brokerage Account users will be:
- Trading on DEXs
- Leveraged staking
- Leveraged liquidity mining
The interest are accumulated on every interaction with the pool. To save the gas costs the Pool contract uses a helper contract which manages the balances using virtual indices and updates the state only after user interaction.
Borrowing interest is higher than deposit interest. Flexible borrowing/deposit rates give a possibility of adjusting pool for a demand and optimize it for better performance. Total deposited value in a pool must be always lower or equal to total borrowed value plus a current pool balance.
The main concern of lending protocols in DeFi space is ensuring that the loans will be repaid. Usually two main principles are implemented:
- Overcollateralization of loans (so there is always enough assets to repay the loan)
- Liquidation mechanism (to repay partly/fully a loan if it's in a dangerous state)
In DeltaPrime protocol the first one can be omitted. By managing all borrowed funds and collateral in a single smart contract it's much easier to control the state of a loan. The current value of all assets in Prime Account is calculated on every user's operation that could affect solvency, as well as is constantly checked by liquidation bots. In the event of crossing solvency threshold (LTV of 5), the account can be liquidated, which means that everyone can resell part of tokens and repay part of a loan to bring it back to a solvent state. At the same time smart contract checks whether the liquidation is not too unfavorable for a borrower and blocks such operations.
It's crucial for such a protocol to calculate solvency of an account based on proper asset prices. To avoid exploits based on price manipulation on DEXs, current price feeds are delivered by RedStone oracle and used in every transaction that could affect solvency.
The UI was designed to be as simple and intuitive as possible. It contains of two main sections:
In the top section the dashboard contains a bar showing global state of the pool:
- APR - current APR in the pool
- Your deposits - sum of user's deposits
- Your profit - profit gained by user
- All deposits - sum of deposits of all users
In the middle of the screen, there is a widget allowing user to make one of actions:
- Deposit
- Withdraw
Below user can see deposits history chart and lists of all his deposit-related actions.
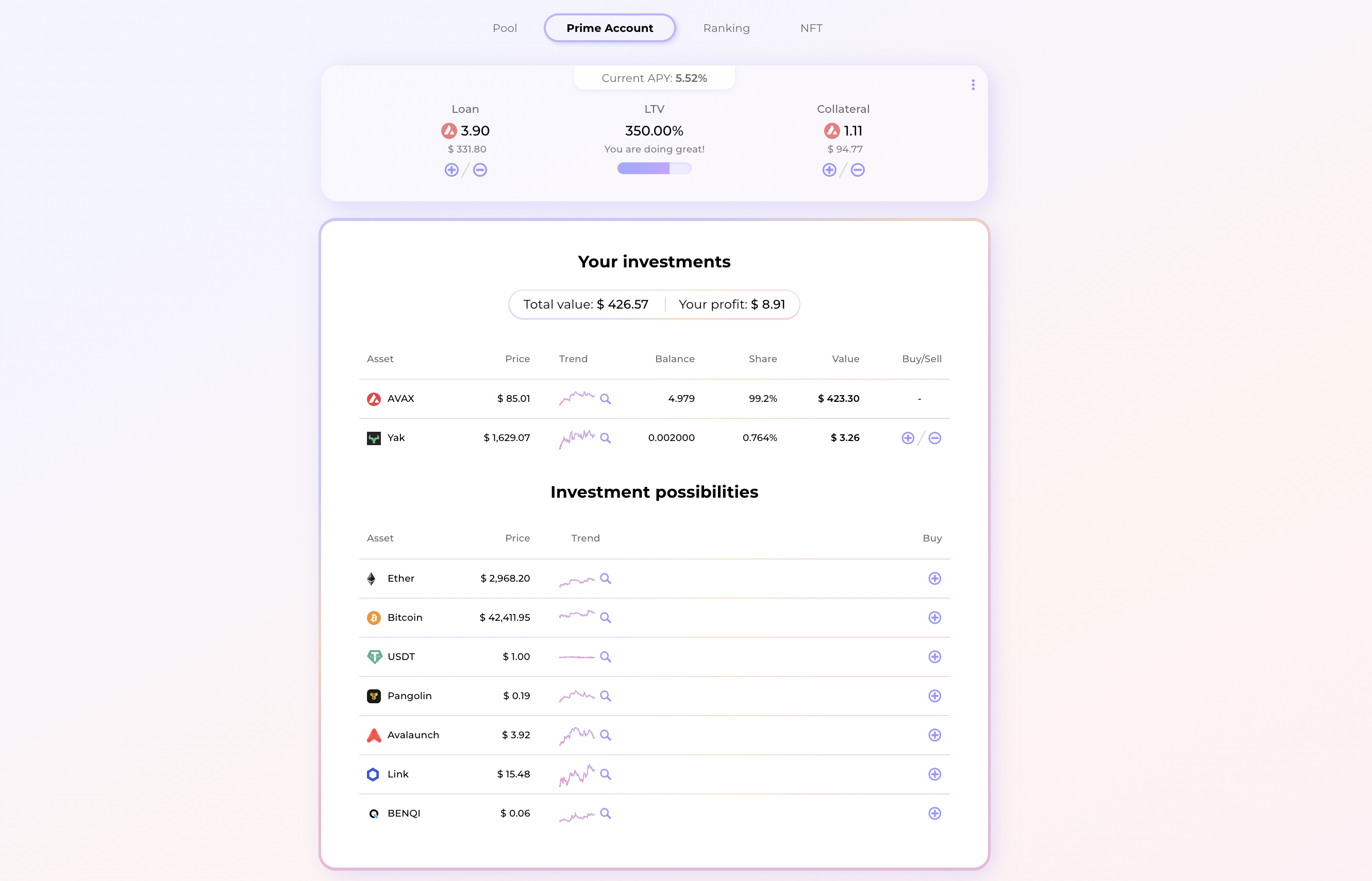
In the top section there are 4 main information show:
- APY - current APY of the pool
- Loan - the amount of funds borrowed by this loan from the pool denominated in AVAX / USD and the current borrowing costs (APR)
- LTV - shows a ratio between the total loan value and the collateral (total assets value minus debt)
- Collateral - the current value of user collateral (total assets value minus debt)
In the bottom section, there is a table showing the current allocation of the borrowed funds and investment possibilities. It lists assets available for investment, their price and current holdings displayed in absolute values and as portfolio percentage. Every asset can be bought and sold by simply clicking on plus or minus buttons. There is also an option to see the asset's historical performance by clicking on the "magnifier" button.
Below user can see an account history chart and lists of all his loan-related actions.
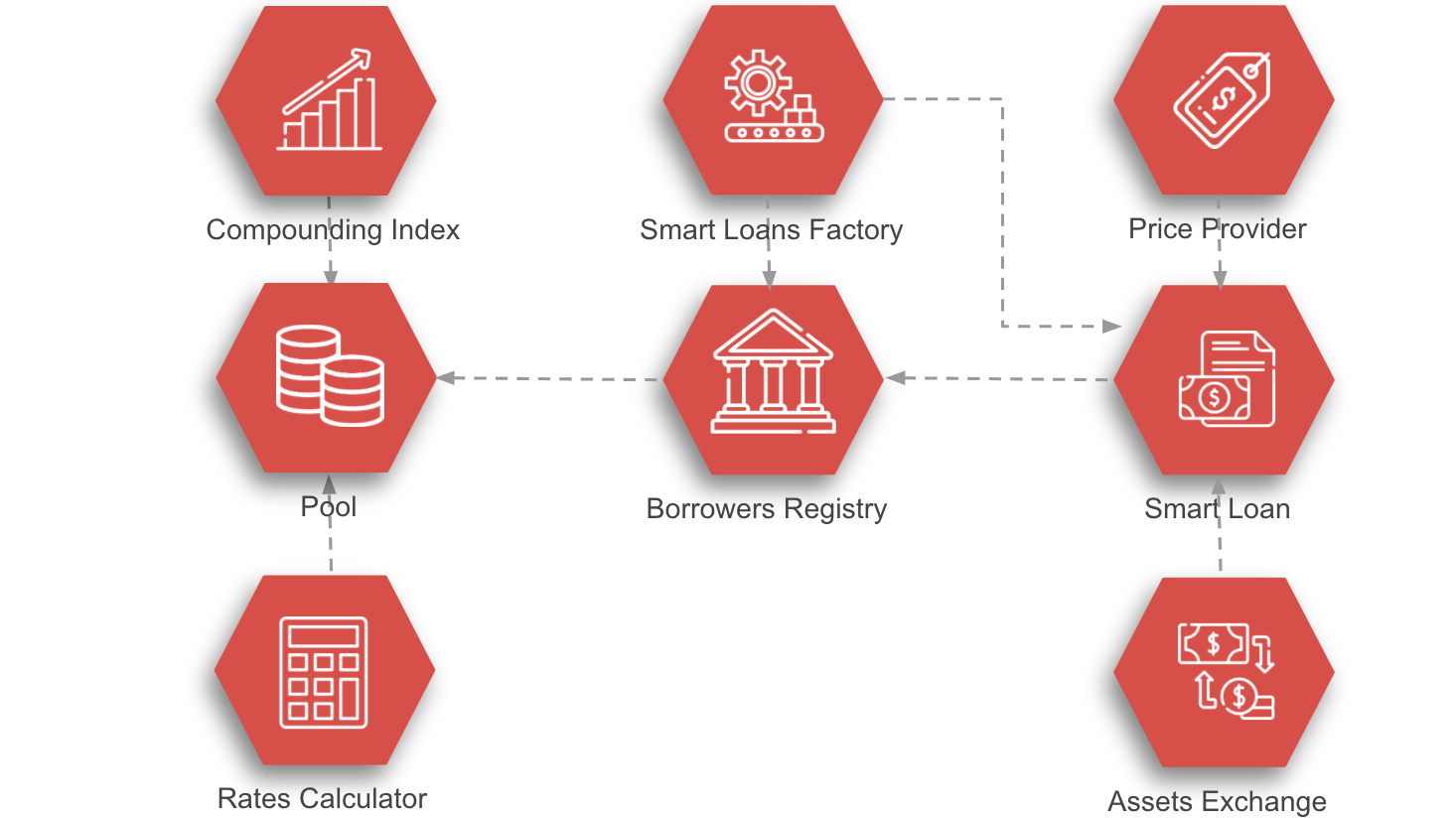
The smart contracts could be divided into two main groups:
-
Pool.sol - a contract that aggregates deposits and borrowings. It keeps track of the balance and liabilities of every user. It accumulates the interest in the real-time based on the rates model connected by the setRatesCalculator. The borrowers are verified by the linked contract.
-
LinearIndex.sol - a helper contract that facilitates the calculation of deposits and loans interest rates. It uses a global index, that has a snapshot on every user interaction to achieve a O(1) complexity balance updates.
-
VariableUtilisationRatesCalculator.sol - an interest rates calculation model that automatically adjust the rates based on the current pool utilisation defined as a ratio between borrowed and deposited funds. The mechanism helps to balance the capital supply and demand because a higher need for loans means that the users will need to pay higher interest rates which should reduce the borrowers' appetite.
-
IBorrowersRegistry.sol - an interface that keeps track of borrowers and their loans by maintaining a bidirectional mapping. It also answers if an account is allowed to borrow funds by calling the canBorrow method.
-
SmartLoan.sol - a core loan contract that manages borrowings, investments and guards solvency. Borrowing activity is performed by the borrow and the repay methods which interact with the Pool contract. Investment activity is implemented in the invest and the redeem methods which interact with the Assets Exchange contract. All of the methods mentioned are wrapped by the remainsSolvent modifier which doesn't allow the solvency to exceed the specified maximum ltv. The solvency level is calculated as the ratio between the debt value and the current collateral value in the real-time using the getLTV function. If the solvency ratio exceeds a safe level anyone could liquidate the loan calling the liquidate function. This pays back part of the debt and a percentage of the liquidated amount is transferred to the caller as a reward for monitoring the loan status. A user can reduce the liquidation risk adjusting amount of personal funds deposited to the loan (margin) by calling the fund method. If the LTV ratio is considerably low, a user may withdraw part of the funds calling the withdraw function.
-
SmartLoansFactory.sol - a helper contract that orchestrates loans creation and initial funding in one transaction. It also manages data about loan creators acting as a Borrowers Registry.
-
PangolinIntermediary.sol - an exchange contract that allows investing AVAX into other popular crypto-tokens on Pangolin DEX.
-
To build the application please install first all of the dependencies by running:
yarn install
-
Create a
.secretfile in the root of the project with a mnemonic phrase of your account. -
Make sure that all of the smart-contracts are compiled before trying to deploy the dApp:
npx truffle compile
-
Setup your local network (e.g. like here) and migrate contracts
-
Depending on your environment set a proper
chainIdinsrc/config.js. It must match the chain id returned by the network and be set up in your Metamask configuration of network as well. -
To deploy the front-end on your local machine please type in your command line:
yarn serve
-
The application needs a Metamask plugin active and connected to a proper network. Remember to reset your account nonce if you restart or change your network.
-
Run a forked node
yarn forked-test-node
-
Migrate contracts (in a separate terminal window)
npx truffle migrate --network local
Your default chain id is 31337. Set it up in the UI application and your Metamask account.
-
Smart contracts test could be executed by typing:
npx hardhat test
This project was funded by the Avalanche-X grant programme.