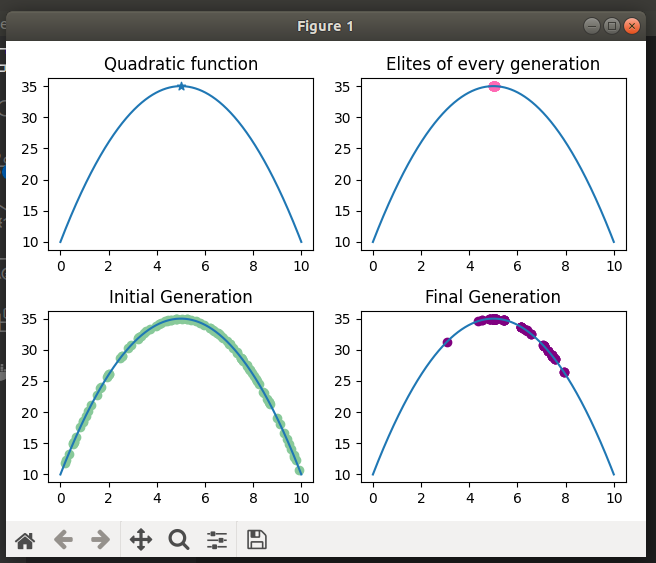
Given a function f and a domain [a, b], find the maximum value of the function by implementing a genetic algorithm.
class Variables:
def __init__(self, length: int, bounds: Bounds, parameters: Parameters, precision: int) -> None:
self.length = length
self.bounds = bounds
self.parameters = parameters
self.precision = precisionwhere
Bounds = Tuple[int, int]
Parameters = Tuple[int, int, int]A chromosome will be a binary representation of the float solution - lower bound
Chromosome = List[int]A population is a list of Chromosomes
Population = List[Chromosome]For generating a new chromosome, we will generate a random uniform number between the upper and lower bound and convert it into binary, then into a list.
# * function that generates chromosome
def generate_chromosome(vars: Variables) -> Chromosome:
float_number = round(uniform(vars.bounds[0], vars.bounds[1]) - vars.bounds[0], vars.precision)
float_number = int(float_number * 10 ** vars.precision)
float_number = format(float_number, '0' + str(vars.length) + 'b')
binary_chromosome = [int(i) for i in float_number]
return binary_chromosomeFor generating a new population, we use the function above in a list comprehension.
# * function that generates population
def generate_population(dimension: int, vars: Variables) -> Population:
return [generate_chromosome(vars) for _ in range(dimension)]Another important and useful function is one that performs the reverse operation of formatting a float number into a binary list.
# * function that returns the float value of the chormosome
def binary_to_float(binary_chromosome: Chromosome, vars: Variables) -> float:
binary = ''.join([str(item) for item in binary_chromosome])
float_number = int(binary, 2)
return round(float_number * 10 ** (- vars.precision), vars.precision)Given the function to generate solutions, we have a guarantee that the solutions are between the bounds. Also, having in mind that some chromosomes can mutate and then maybe have a worse solution, the fitness function will verify if the solution is still between the bounds. If yes, it will compute the value of the function f.
# * the FITNESS FUNCTION
def fitness(binary_chromosome: Chromosome, vars: Variables) -> float:
number = binary_to_float(binary_chromosome, vars)
if number > vars.bounds[1] - vars.bounds[0]:
return - 1
return function(number, vars)# * quadratic function
def function(x: float, vars: Variables) -> float:
return vars.parameters[0] * x ** 2 + vars.parameters[1] * x + vars.parameters[2]This function uses the roulette method to select the intermediate population for a later crossover.
# * the SELECTION FUNCTION
def roulette_selection(population: Population, ret_dimension: int, vars: Variables) -> Population:
intervals = [0]
sum = 0
for i in range(len(population)):
sum += selection_prob(population[i], population, vars)
intervals.append(sum)
intermediate_population = []
for i in range(ret_dimension):
u = random()
index = search(u, intervals)
intermediate_population.append(population[index])
return intermediate_populationThe binary search function:
# * the search function
def search(u: float, intervals: List[float]) -> int:
i = 0
step = 1
length = len(intervals)
while step < length:
step *= 2
while step:
if i + step < length and intervals[i + step] < u:
i += step
step //= 2
return iSingle point crossover function
# * the CROSSOVER FUNCTION
def single_point_crossover(a: Chromosome, b: Chromosome) -> Tuple[Chromosome, Chromosome]:
length = len(a)
if length < 2:
return a, b
point = randint(1, length - 1)
offspring_a, offspring_b = a[0 : point] + b[point : ], b[0 : point] + a[point : ]
return offspring_a, offspring_b# * the mutation function
def mutation(a: Chromosome, mutation_prob: float, show: bool = False) -> Chromosome:
index = randrange(1, len(a))
a[index] = a[index] if random() > mutation_prob else abs(a[index] - 1)
return a# * the evolution function
def evolution(vars: Variables, dimension: int, generations: int, crossover_prob: float, mutation_prob: float) -> Population:
population = generate_population(dimension, vars)
selected = ceil(crossover_prob * dimension / 2 * 2) # selected for crossover
members = dimension - selected - 2 # memnbers going to next gen
show_function(vars)
show_initial_population(population, vars)
elite = [ ]
for i in range(generations):
population = sorted(population, key = lambda chromosome: fitness(chromosome, vars), reverse = True)
# todo 1 elitistic selection
next_generation = population[0 : 2]
elite.append(binary_to_float(population[0], vars))
# todo 2 copy
# * select (1 - cp) * dimension
next_generation += choices(population = population, k = members)
# todo 3 crossover
# * select (cp * dimension) members, pair them and produce offspring
intermediate_population = roulette_selection(population, selected, vars, i == 1)
for _ in range(selected // 2):
parents = random_selection(intermediate_population)
offspring_a, offspring_b = single_point_crossover(parents[0], parents[1], i == 1)
next_generation += [offspring_a, offspring_b]
# todo 3 mutation
next_generation = [mutation(item, mutation_prob, i == 1) for item in next_generation]
population = next_generation
show_elite(elite, vars)
show_final_population(population, vars)For the input below:
dimension: int = 100
bounds: Bounds = (0, 10)
parameters: Parameters = (-1, 10, 10)
precision: int = 3
nr_generations: int = 20
crossover_probability = 0.25
mutation_probability = 0