
欢迎来到PyPOTS
一个使用机器学习建模部分观测时间序列(POTS)的Python算法工具库
















⦿ `开发背景`: 由于传感器故障、通信异常以及不可预见的未知原因,在现实环境中收集的时间序列数据普遍存在缺失值,
这使得部分观测时间序列(partially-observed time series,简称为POTS)成为现实世界数据的建模中普遍存在的问题。
数据缺失会严重阻碍数据的高级分析、建模、与后续应用,所以如何直接面向POTS建模成为一个亟需解决的问题。
尽管关于在POTS上进行不同任务的机器学习算法已经有了不少的研究,但当前没有专门针对POTS建模开发的工具箱。
因此,旨在填补该领域空白的“PyPOTS”工具箱应运而生。
⦿ `应用意义`: PyPOTS(发音为"Pie Pots")是一个易上手的工具箱,工程师和研究人员可以通过PyPOTS轻松地处理POTS数据建模问题,
进而将注意力更多地聚焦在要解决的核心问题上。PyPOTS会持续不断的更新关于部分观测多变量时间序列的经典算法和先进算法。
除此之外,PyPOTS还提供了统一的应用程序接口,详细的算法学习指南和应用示例。
🤗 如果你认为PyPOTS有用,请星标🌟该项目来帮助更多人注意到PyPOTS的存在。
如果PyPOTS对你的研究有帮助,请在你的研究中[引用PyPOTS](#-引用pypots)。
这是对我们开源研究工作的最大支持,谢谢!
该说明文档的后续内容如下:
[**❖ 支持的算法**](#-支持的算法),
[**❖ PyPOTS生态系统**](#-pypots生态系统),
[**❖ 安装教程**](#-安装教程),
[**❖ 使用案例**](#-使用案例),
[**❖ 引用PyPOTS**](#-引用pypots),
[**❖ 贡献声明**](#-贡献声明),
[**❖ 社区组织**](#-社区组织)。
## ❖ 支持的算法
PyPOTS当前支持多变量POTS数据的插补,预测,分类,聚类以及异常检测五类任务。下表描述了当前PyPOTS中所集成的算法以及对应不同任务的可用性。
符号 ✅ 表示该算法当前可用于相应的任务(注意,目前模型尚不支持的任务在未来版本中可能会逐步添加,敬请关注!)。
算法的参考文献以及论文链接在该文档底部可以找到。
🌟 自**v0.2**版本开始, PyPOTS中所有神经网络模型都支持超参数调优。该功能基于[微软的NNI](https://github.com/microsoft/nni)框架实现。
你可以通过参考我们的时间序列插补综述项目的代码[Awesome_Imputation](https://github.com/WenjieDu/Awesome_Imputation)来了解如何使用PyPOTS调优模型的超参。
🔥 请注意:Transformer, iTransformer, FreTS, Crossformer, PatchTST, DLinear, ETSformer, FiLM, FEDformer, Informer, Autoformer模型
在它们的原始论文中并未用作插补方法,因此这些模型的输入中不能带有缺失值, 所以无法接受POTS数据作为输入。
**为了使上述模型能够适用于POTS数据,我们采用了与[SAITS论文](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.08516)中相同的embedding策略和训练方法(ORT+MIT)对它们进行改进**。
| **类型** | **算法** | **插补** | **预测** | **分类** | **聚类** | **异常检测** | **年份 - 刊物** |
|:--------------|:-----------------------------------|:--------:|:--------:|:---------:|:--------:|:------------:|:-----------------|
| Neural Net | iTransformer[^24] | ✅ | | | | | 2024 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | FreTS[^23] | ✅ | | | | | 2024 - NeurIPS |
| Neural Net | SAITS[^1] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - ESWA |
| Neural Net | Crossformer[^16] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | TimesNet[^14] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | PatchTST[^18] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | ETSformer[^19] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | DLinear[^17] | ✅ | | | | | 2023 - AAAI |
| Neural Net | FiLM[^22] | ✅ | | | | | 2022 - NeurIPS |
| Neural Net | Raindrop[^5] | | | ✅ | | | 2022 - ICLR |
| Neural Net | FEDformer[^20] | ✅ | | | | | 2022 - ICML |
| Neural Net | Autoformer[^15] | ✅ | | | | | 2021 - NeurIPS |
| Neural Net | CSDI[^12] | ✅ | ✅ | | | | 2021 - NeurIPS |
| Neural Net | Informer[^21] | ✅ | | | | | 2021 - AAAI |
| Neural Net | US-GAN[^10] | ✅ | | | | | 2021 - AAAI |
| Neural Net | CRLI[^6] | | | | ✅ | | 2021 - AAAI |
| Probabilistic | BTTF[^8] | | ✅ | | | | 2021 - TPAMI |
| Neural Net | GP-VAE[^11] | ✅ | | | | | 2020 - AISTATS |
| Neural Net | VaDER[^7] | | | | ✅ | | 2019 - GigaSci. |
| Neural Net | M-RNN[^9] | ✅ | | | | | 2019 - TBME |
| Neural Net | BRITS[^3] | ✅ | | ✅ | | | 2018 - NeurIPS |
| Neural Net | GRU-D[^4] | ✅ | | ✅ | | | 2018 - Sci. Rep. |
| Neural Net | Transformer[^2] | ✅ | | | | | 2017 - NeurIPS |
| Naive | LOCF/NOCB | ✅ | | | | | |
| Naive | Mean | ✅ | | | | | |
| Naive | Median | ✅ | | | | | |
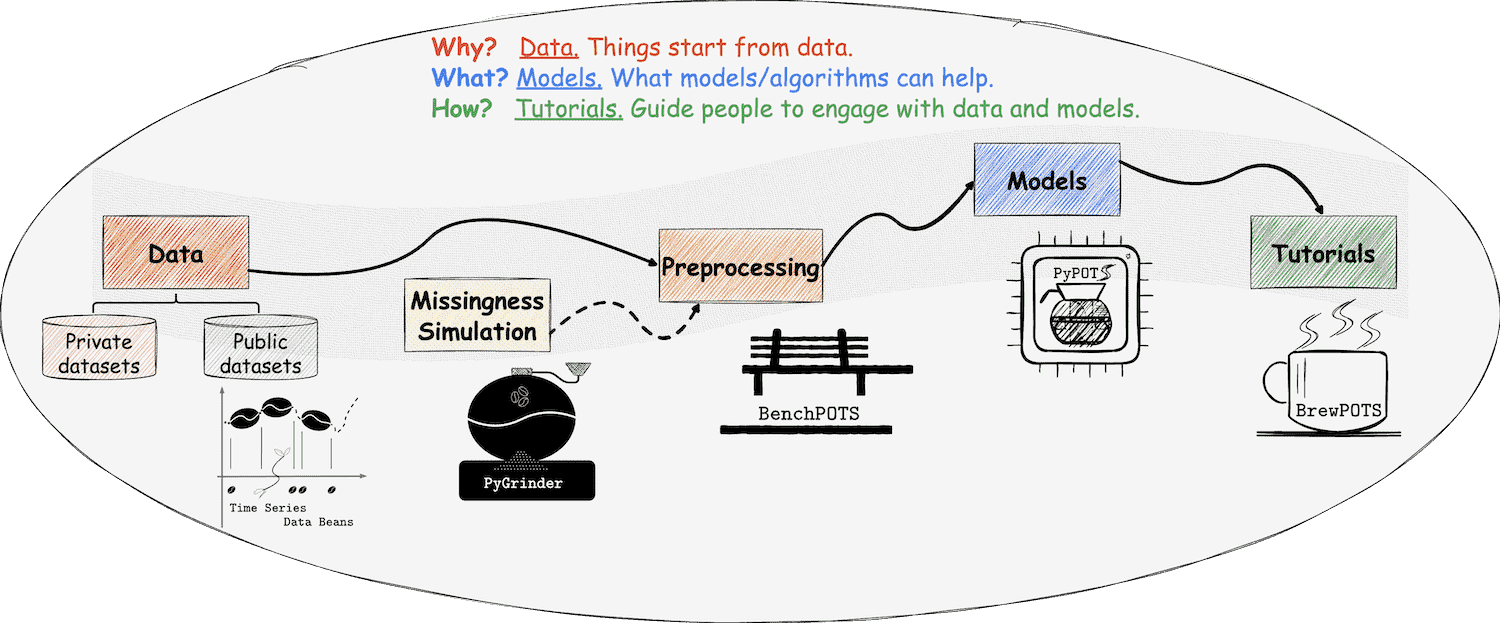
## ❖ PyPOTS生态系统
在PyPOTS生态系统中,一切都与我们熟悉的咖啡息息相关,甚至可以将其视为一杯咖啡的诞生过程!
如你所见,PyPOTS的标志中有一个咖啡壶。除此之外还需要什么呢?请接着看下去、
 👈 在PyPOTS中,数据可以被看作是咖啡豆,而写的携带缺失值的POTS数据则是不完整的咖啡豆。
为了让用户能够轻松使用各种开源的时间序列数据集,我们创建了开源时间序列数据集的仓库 Time Series Data Beans (TSDB)(可以将其视为咖啡豆仓库),
TSDB让加载开源时序数据集变得超级简单!访问 [TSDB](https://github.com/WenjieDu/TSDB),了解更多关于TSDB的信息,目前总共支持169个开源数据集!
👈 在PyPOTS中,数据可以被看作是咖啡豆,而写的携带缺失值的POTS数据则是不完整的咖啡豆。
为了让用户能够轻松使用各种开源的时间序列数据集,我们创建了开源时间序列数据集的仓库 Time Series Data Beans (TSDB)(可以将其视为咖啡豆仓库),
TSDB让加载开源时序数据集变得超级简单!访问 [TSDB](https://github.com/WenjieDu/TSDB),了解更多关于TSDB的信息,目前总共支持169个开源数据集!
 👉 为了在真实数据中模拟缺失进而获得不完整的咖啡豆,我们创建了生态系统中的另一个仓库[PyGrinder](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyGrinder)(可以将其视为磨豆机),
帮助你在数据集中模拟缺失数据,用于评估机器学习算法。根据Robin的理论[^13],缺失模式分为三类:
完全随机缺失(missing completely at random,简称为MCAR)、随机缺失(missing at random,简称为MAR)和非随机缺失(missing not at random,简称为MNAR )。
PyGrinder支持以上所有模式并提供与缺失相关的其他功能函数。通过PyGrinder,你可以仅仅通过一行代码就将模拟缺失引入你的数据集中。
👉 为了在真实数据中模拟缺失进而获得不完整的咖啡豆,我们创建了生态系统中的另一个仓库[PyGrinder](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyGrinder)(可以将其视为磨豆机),
帮助你在数据集中模拟缺失数据,用于评估机器学习算法。根据Robin的理论[^13],缺失模式分为三类:
完全随机缺失(missing completely at random,简称为MCAR)、随机缺失(missing at random,简称为MAR)和非随机缺失(missing not at random,简称为MNAR )。
PyGrinder支持以上所有模式并提供与缺失相关的其他功能函数。通过PyGrinder,你可以仅仅通过一行代码就将模拟缺失引入你的数据集中。
 👈 现在我们有了咖啡豆、磨豆机和咖啡壶,那么如何萃取一杯咖啡呢?冲泡教程是必不可少的!
考虑到未来的工作量,PyPOTS的相关教程将发布在一个独立的仓库[BrewPOTS](https://github.com/WenjieDu/BrewPOTS)中。
点击访问查看教程,学习如何萃取你的POTS数据!
👈 现在我们有了咖啡豆、磨豆机和咖啡壶,那么如何萃取一杯咖啡呢?冲泡教程是必不可少的!
考虑到未来的工作量,PyPOTS的相关教程将发布在一个独立的仓库[BrewPOTS](https://github.com/WenjieDu/BrewPOTS)中。
点击访问查看教程,学习如何萃取你的POTS数据!
☕️ 欢迎来到 PyPOTS 生态系统 !
## ❖ 安装教程
你可以参考PyPOTS文档中的 [安装说明](https://docs.pypots.com/en/latest/install.html) 以获取更详细的指南。
PyPOTS可以在 [PyPI](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pypots) 和 [Anaconda](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pypots) 上安装。
你可以按照以下方式安装PyPOTS(同样适用于TSDB以及PyGrinder):
```bash
# 通过pip安装
pip install pypots # 首次安装
pip install pypots --upgrade # 更新为最新版本
# 利用最新源代码安装最新版本,可能带有尚未正式发布的最新功能
pip install https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/archive/main.zip
# 通过conda安装
conda install -c conda-forge pypots # 首次安装
conda update -c conda-forge pypots # 更新为最新版本
```
## ❖ 使用案例
除了[BrewPOTS](https://github.com/WenjieDu/BrewPOTS)之外, 你还可以在Google Colab
 上找到一个简单且快速的入门教程。如果你有其他问题,请参考[PyPOTS文档](https://docs.pypots.com)。
你也可以在我们的[社区](#-community)中提问,或直接[发起issue](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/issues)。
下面,我们为你演示使用PyPOTS进行POTS数据插补的示例:
上找到一个简单且快速的入门教程。如果你有其他问题,请参考[PyPOTS文档](https://docs.pypots.com)。
你也可以在我们的[社区](#-community)中提问,或直接[发起issue](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/issues)。
下面,我们为你演示使用PyPOTS进行POTS数据插补的示例:
点击此处查看 SAITS 模型应用于 PhysioNet2012 数据集插补任务的简单案例:
``` python
# 数据预处理,使用PyPOTS生态帮助完成繁琐的数据预处理
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from pygrinder import mcar
from pypots.data import load_specific_dataset
data = load_specific_dataset('physionet_2012') # PyPOTS将自动下载并加载和处理数据
X = data['X']
num_samples = len(X['RecordID'].unique())
X = X.drop(['RecordID', 'Time'], axis = 1)
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X.to_numpy())
X = X.reshape(num_samples, 48, -1)
X_ori = X # keep X_ori for validation
X = mcar(X, 0.1) # 随机掩盖观测值的10%,作为基准数据
dataset = {"X": X} # X用于模型输入
print(X.shape) # X的形状为(11988, 48, 37), 即11988个样本,每个样本有48个步长(time steps)和37个特征(features)
# 模型训练。PyPOTS的好戏上演了!
from pypots.imputation import SAITS
from pypots.utils.metrics import calc_mae
saits = SAITS(n_steps=48, n_features=37, n_layers=2, d_model=256, n_heads=4, d_k=64, d_v=64, d_ffn=128, dropout=0.1, epochs=10)
# 因为基准数据对模型不可知,将整个数据集作为训练集, 也可以把数据集分为训练/验证/测试集
saits.fit(dataset) # 基于数据集训练模型
imputation = saits.impute(dataset) # 插补数据集中原始缺失部分和我们上面人为遮蔽缺失的基准数据部分
indicating_mask = np.isnan(X) ^ np.isnan(X_ori) # 用于计算插补误差的掩码矩阵
mae = calc_mae(imputation, np.nan_to_num(X_ori), indicating_mask) # 计算人为遮掩部分数据的平均绝对误差MAE
saits.save("save_it_here/saits_physionet2012.pypots") # 保存模型
saits.load("save_it_here/saits_physionet2012.pypots") # 你随时可以重新加载保存的模型文件以进行后续的插补或训练
```
## ❖ 引用PyPOTS
> [!TIP]
> **[2024年2月更新]** 😎 我们的综述论文[Deep Learning for Multivariate Time Series Imputation: A Survey](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.04059)
> 已在 arXiv 上发布,代码也在GitHub项目([Awesome_Imputation](https://github.com/WenjieDu/Awesome_Imputation))上开源。
> 我们全面调研总结了最新基于深度学习的时间序列插补方法文献并对现有的方法进行分类,除此之外,还讨论了该领域当前的挑战和未来发展方向。
>
> **[2023年6月更新]** 🎉 PyPOTS的5页短版论文已被第9届SIGKDD international workshop on
Mining and Learning from Time Series ([MiLeTS'23](https://kdd-milets.github.io/milets2023/))收录。
> 此外,PyPOTS也已被纳入[PyTorch Ecosystem](https://pytorch.org/ecosystem/)。
介绍PyPOTS的论文可以通过[该链接](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.18811)在arXiv上获取,我们正在努力将其发表在更具影响力的学术刊物上,
例如JMLR (track for [Machine Learning Open Source Software](https://www.jmlr.org/mloss/))。
如果你在工作中使用了PyPOTS,请按照以下格式引用我们的论文并为将项目设为星标🌟,以便让更多人关注到它,对此我们深表感谢🤗。
据不完全统计,该[列表](https://scholar.google.com/scholar?as_ylo=2022&q=%E2%80%9CPyPOTS%E2%80%9D&hl=en>)为当前使用PyPOTS并在其论文中引用PyPOTS的科学研究项目
```bibtex
@article{du2023pypots,
title={{PyPOTS: a Python toolbox for data mining on Partially-Observed Time Series}},
author={Wenjie Du},
year={2023},
eprint={2305.18811},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.18811},
doi={10.48550/arXiv.2305.18811},
}
```
或者
> Wenjie Du. (2023).
> PyPOTS: a Python toolbox for data mining on Partially-Observed Time Series.
> arXiv, abs/2305.18811.https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.18811
## ❖ 贡献声明
非常欢迎你为这个激动人心的项目做出贡献!
通过提交你的代码,你将:
1. 把你开发完善的模型直接提供给PyPOTS的所有用户使用,让你的工作更加广为人知。
请查看我们的[纳入标准](https://docs.pypots.com/en/latest/faq.html#inclusion-criteria)。
你也可以利用项目文件中的模板`template`(如:
[pypots/imputation/template](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/tree/main/pypots/imputation/template))快速启动你的开发;
2. 成为[PyPOTS贡献者](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/graphs/contributors)之一,
并在[PyPOTS网站](https://pypots.com/about/#volunteer-developers)上被列为志愿开发者;
3. 在我们发布新版本的[更新日志](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/releases)中被提及;
你也可以通过为该项目设置星标🌟,帮助更多人关注它。你的星标🌟既是对PyPOTS的认可,也是对PyPOTS发展所做出的重要贡献!
👏 点击这里可以查看PyPOTS当前的星标者和分支者
我们为拥有越来越多的出色用户以及更多的星标✨而感到自豪:


👀请在[PyPOTS网站](https://pypots.com/users/)上查看我们用户所属机构的完整列表!
## ❖ 社区组织
我们非常关心用户的反馈,因此我们正在建立PyPOTS社区:
- [Slack](https://join.slack.com/t/pypots-org/shared_invite/zt-1gq6ufwsi-p0OZdW~e9UW_IA4_f1OfxA):你可以在这里进行日常讨论、问答以及与我们的开发团队交流;
- [领英](https://www.linkedin.com/company/pypots):你可以在这里获取官方公告和新闻;
- [微信公众号](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sNgZmgAyxDn2sZxXoWJYMA):你可以关注官方公众号并加入微信群聊参与讨论以及获取最新动态;
如果你有任何建议、想法、或打算分享与时间序列相关的论文,欢迎加入我们!
PyPOTS社区是一个开放、透明、友好的社区,让我们共同努力建设并改进PyPOTS!
[//]: # (Use APA reference style below)
[^1]: Du, W., Cote, D., & Liu, Y. (2023). [SAITS: Self-Attention-based Imputation for Time Series](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119619). *Expert systems with applications*.
[^2]: Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N.M., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). [Attention is All you Need](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/hash/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Abstract.html). *NeurIPS 2017*.
[^3]: Cao, W., Wang, D., Li, J., Zhou, H., Li, L., & Li, Y. (2018). [BRITS: Bidirectional Recurrent Imputation for Time Series](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2018/hash/734e6bfcd358e25ac1db0a4241b95651-Abstract.html). *NeurIPS 2018*.
[^4]: Che, Z., Purushotham, S., Cho, K., Sontag, D.A., & Liu, Y. (2018). [Recurrent Neural Networks for Multivariate Time Series with Missing Values](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-24271-9). *Scientific Reports*.
[^5]: Zhang, X., Zeman, M., Tsiligkaridis, T., & Zitnik, M. (2022). [Graph-Guided Network for Irregularly Sampled Multivariate Time Series](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05357). *ICLR 2022*.
[^6]: Ma, Q., Chen, C., Li, S., & Cottrell, G. W. (2021). [Learning Representations for Incomplete Time Series Clustering](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17070). *AAAI 2021*.
[^7]: Jong, J.D., Emon, M.A., Wu, P., Karki, R., Sood, M., Godard, P., Ahmad, A., Vrooman, H.A., Hofmann-Apitius, M., & Fröhlich, H. (2019). [Deep learning for clustering of multivariate clinical patient trajectories with missing values](https://academic.oup.com/gigascience/article/8/11/giz134/5626377). *GigaScience*.
[^8]: Chen, X., & Sun, L. (2021). [Bayesian Temporal Factorization for Multidimensional Time Series Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.06366). *IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence*.
[^9]: Yoon, J., Zame, W. R., & van der Schaar, M. (2019). [Estimating Missing Data in Temporal Data Streams Using Multi-Directional Recurrent Neural Networks](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8485748). *IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering*.
[^10]: Miao, X., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Gao, Y., Mao, X., & Yin, J. (2021). [Generative Semi-supervised Learning for Multivariate Time Series Imputation](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17086). *AAAI 2021*.
[^11]: Fortuin, V., Baranchuk, D., Raetsch, G. & Mandt, S. (2020). [GP-VAE: Deep Probabilistic Time Series Imputation](https://proceedings.mlr.press/v108/fortuin20a.html). *AISTATS 2020*.
[^12]: Tashiro, Y., Song, J., Song, Y., & Ermon, S. (2021). [CSDI: Conditional Score-based Diffusion Models for Probabilistic Time Series Imputation](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/hash/cfe8504bda37b575c70ee1a8276f3486-Abstract.html). *NeurIPS 2021*.
[^13]: Rubin, D. B. (1976). [Inference and missing data](https://academic.oup.com/biomet/article-abstract/63/3/581/270932). *Biometrika*.
[^14]: Wu, H., Hu, T., Liu, Y., Zhou, H., Wang, J., & Long, M. (2023). [TimesNet: Temporal 2d-variation modeling for general time series analysis](https://openreview.net/forum?id=ju_Uqw384Oq). *ICLR 2023*
[^15]: Wu, H., Xu, J., Wang, J., & Long, M. (2021). [Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/hash/bcc0d400288793e8bdcd7c19a8ac0c2b-Abstract.html). *NeurIPS 2021*.
[^16]: Zhang, Y., & Yan, J. (2023). [Crossformer: Transformer utilizing cross-dimension dependency for multivariate time series forecasting](https://openreview.net/forum?id=vSVLM2j9eie). *ICLR 2023*.
[^17]: Zeng, A., Chen, M., Zhang, L., & Xu, Q. (2023). [Are transformers effective for time series forecasting?](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/26317). *AAAI 2023*
[^18]: Nie, Y., Nguyen, N. H., Sinthong, P., & Kalagnanam, J. (2023). [A time series is worth 64 words: Long-term forecasting with transformers](https://openreview.net/forum?id=Jbdc0vTOcol). *ICLR 2023*
[^19]: Woo, G., Liu, C., Sahoo, D., Kumar, A., & Hoi, S. (2023). [ETSformer: Exponential Smoothing Transformers for Time-series Forecasting](https://openreview.net/forum?id=5m_3whfo483). *ICLR 2023*
[^20]: Zhou, T., Ma, Z., Wen, Q., Wang, X., Sun, L., & Jin, R. (2022). [FEDformer: Frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting](https://proceedings.mlr.press/v162/zhou22g.html). *ICML 2022*.
[^21]: Zhou, H., Zhang, S., Peng, J., Zhang, S., Li, J., Xiong, H., & Zhang, W. (2021). [Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17325). *AAAI 2021*.
[^22]: Zhou, T., Ma, Z., Wen, Q., Sun, L., Yao, T., Yin, W., & Jin, R. (2022). [FiLM: Frequency improved Legendre Memory Model for Long-term Time Series Forecasting](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2022/hash/524ef58c2bd075775861234266e5e020-Abstract-Conference.html). *NeurIPS 2022*.
[^23]: Yi, K., Zhang, Q., Fan, W., Wang, S., Wang, P., He, H., An, N., Lian, D., Cao, L., & Niu, Z. (2024). [Frequency-domain MLPs are More Effective Learners in Time Series Forecasting](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/hash/f1d16af76939f476b5f040fd1398c0a3-Abstract-Conference.html). *NeurIPS 2024*.
[^24]: Liu, Y., Hu, T., Zhang, H., Wu, H., Wang, S., Ma, L., & Long, M. (2024). [iTransformer: Inverted Transformers Are Effective for Time Series Forecasting](https://openreview.net/forum?id=JePfAI8fah). *ICLR 2024*.
🏠 访问量

















 上找到一个简单且快速的入门教程。如果你有其他问题,请参考[PyPOTS文档](https://docs.pypots.com)。
你也可以在我们的[社区](#-community)中提问,或直接[发起issue](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/issues)。
下面,我们为你演示使用PyPOTS进行POTS数据插补的示例:
上找到一个简单且快速的入门教程。如果你有其他问题,请参考[PyPOTS文档](https://docs.pypots.com)。
你也可以在我们的[社区](#-community)中提问,或直接[发起issue](https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyPOTS/issues)。
下面,我们为你演示使用PyPOTS进行POTS数据插补的示例: