| title |
|---|
Quick Start: Run K-Means Example |
This guide will demonstrate Flink's features by example. You will see how you can leverage Flink's Iteration-feature to find clusters in a dataset using K-Means clustering. On the way, you will see the compiler, the status interface and the result of the algorithm.
Flink contains a data generator for K-Means.
# Download Flink
wget {{ site.FLINK_DOWNLOAD_URL_HADOOP_1_STABLE }}
tar xzf flink-*.tgz
cd flink-*
mkdir kmeans
cd kmeans
# Run data generator
java -cp ../examples/flink-java-examples-{{ site.FLINK_VERSION_STABLE }}-KMeans.jar org.apache.flink.example.java.clustering.util.KMeansDataGenerator 500 10 0.08
cp /tmp/points .
cp /tmp/centers .
The generator has the following arguments:
KMeansDataGenerator <numberOfDataPoints> <numberOfClusterCenters> [<relative stddev>] [<centroid range>] [<seed>]
The relative standard deviation is an interesting tuning parameter: it determines the closeness of the points to the centers.
The kmeans/ directory should now contain two files: centers and points.
Use the plotPoints.py tool to review the result of the data generator. Download Python Script
python plotPoints.py points points inputNote: You might have to install matplotlib (python-matplotlib package on Ubuntu) to use the Python script.
You can review the input data stored in the input-plot.pdf, for example with Evince (evince input-plot.pdf).
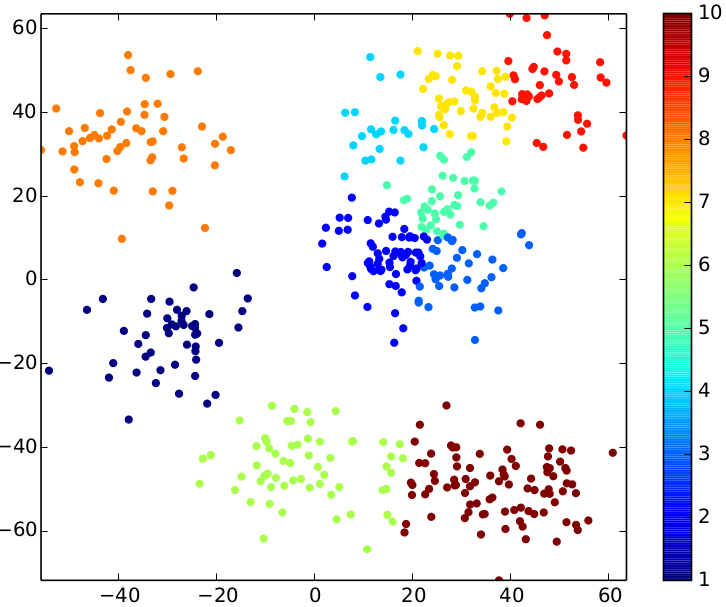
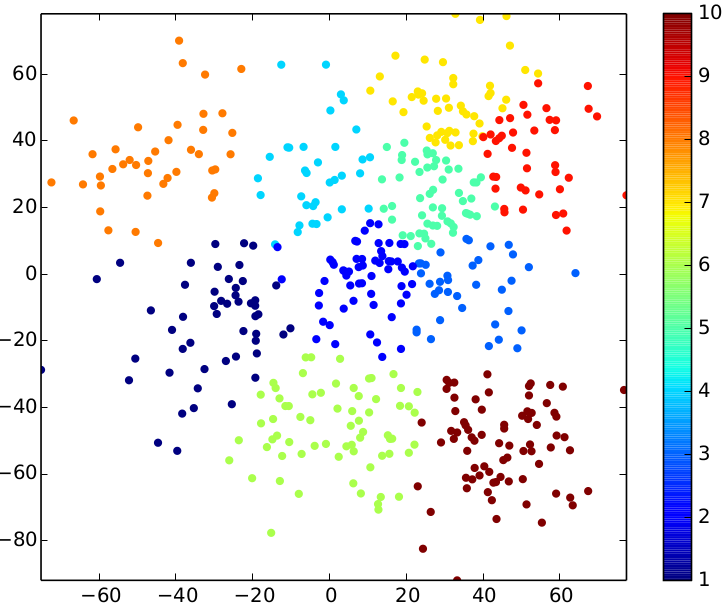
The following overview presents the impact of the different standard deviations on the input data.
| relative stddev = 0.03 | relative stddev = 0.08 | relative stddev = 0.15 |
|---|---|---|
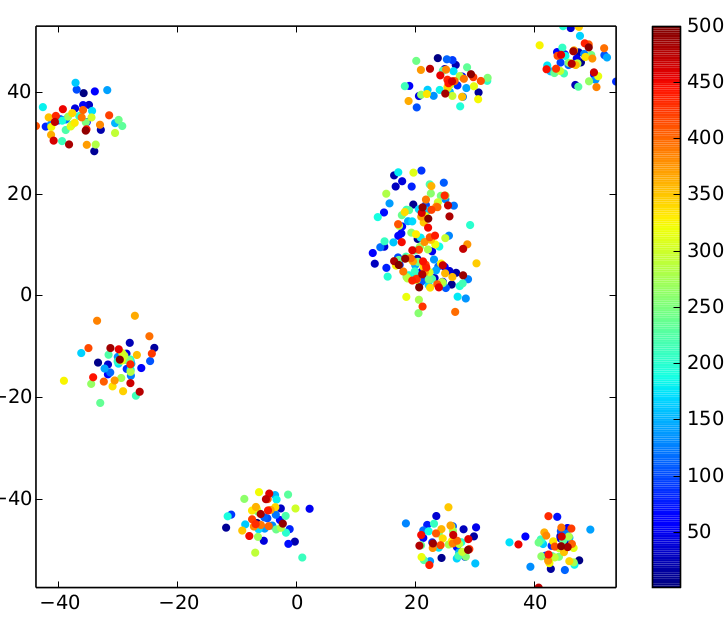 |
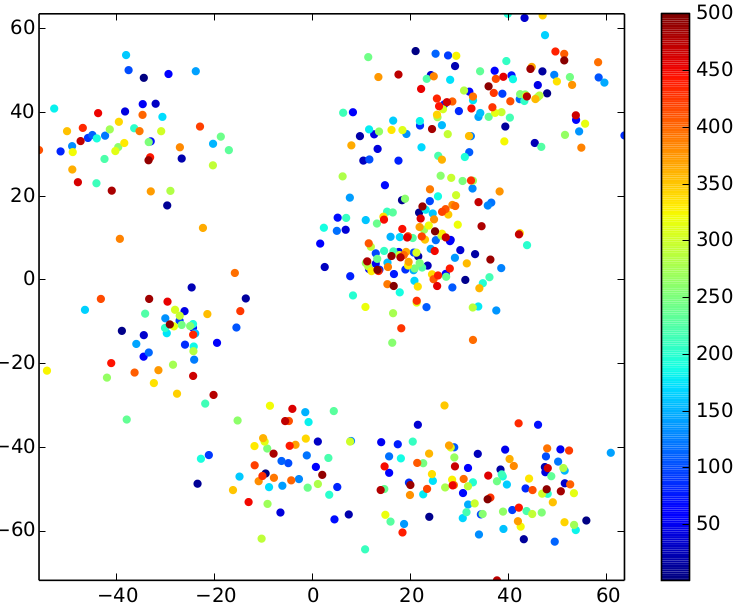 |
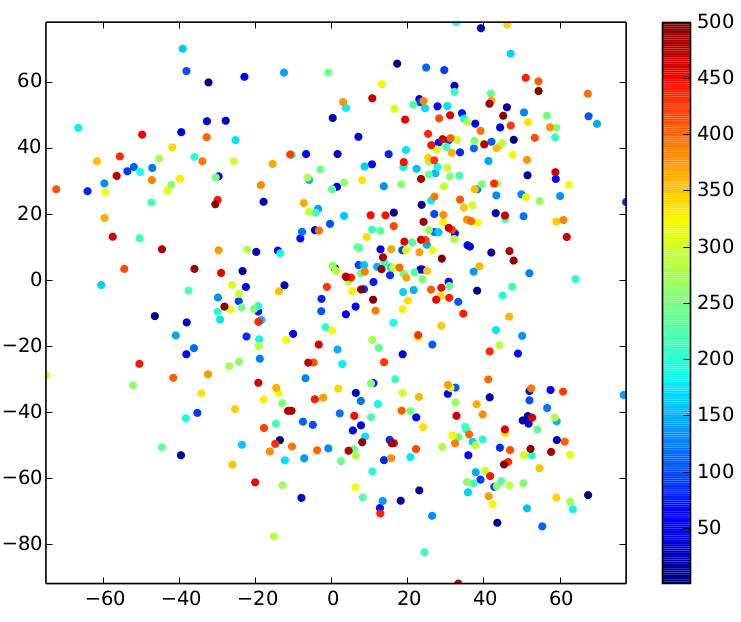 |
We are using the generated input data to run the clustering using a Flink job.
# go to the Flink-root directory
cd flink
# start Flink (use ./bin/start-cluster.sh if you're on a cluster)
./bin/start-local.sh
# Start Flink web client
./bin/start-webclient.sh
The Flink webclient allows to submit Flink programs using a graphical user interface.
2. Upload the file. {% highlight bash %} examples/flink-java-examples-0.6-incubating-KMeans.jar {% endhighlight %}
3. Select it in the left box to see how the operators in the plan are connected to each other.
4. Enter the arguments in the lower left box: {% highlight bash %} file:https://points file:https://centers file:https://result 10 {% endhighlight %} For example: {% highlight bash %} file:https:///tmp/flink/kmeans/points file:https:///tmp/flink/kmeans/centers file:https:///tmp/flink/kmeans/result 20 {% endhighlight %}
<div class="col-md-6">
1. Press the <b>RunJob</b> to see the optimzer plan. <br>
2. Inspect the operators and see the properties (input sizes, cost estimation) determined by the optimizer.
</div>
2. Open Flink's monitoring interface to see the job's progress.
3. Once the job has finished, you can analyize the runtime of the individual operators.
Use the Python Script again to visualize the result
python plotPoints.py result result result-pdfThe following three pictures show the results for the sample input above. Play around with the parameters (number of iterations, number of clusters) to see how they affect the result.
| relative stddev = 0.03 | relative stddev = 0.08 | relative stddev = 0.15 |
|---|---|---|
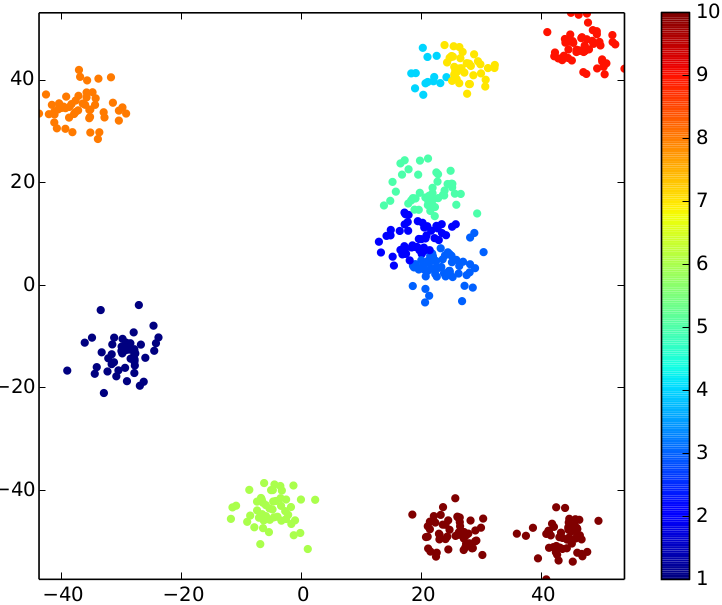 |
 |
 |


