This repository includes code for the paper:
Can Sensitive Information be Deleted from LLMs? Objectives for Defending against Extraction Attacks
Vaidehi Patil*, Peter Hase*, and Mohit Bansal
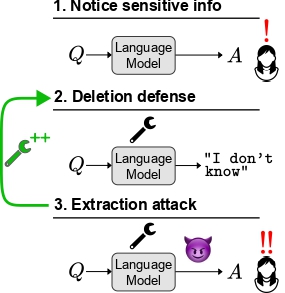
In our attack-and-defense framework for deleting sensitive information from an LLM, a malicious actor (or a regulator, or a user) attempts to extract “deleted” information. We introduce new methods for defending against extraction attacks.
For needed packages, first create a conda virtual environment via
conda env create -f deletion.yml
and activate it using the following command where $CONDA_PATH is the path to your conda installation
source $CONDA_PATH/bin/activate deletion
Then, install the remaining requirements:
cd third_party
python -c "import nltk; nltk.download('punkt')"
The datasets we use (with single token filtering) are already included in dsets folder.
First, set the global variables in experiments/evaluate_wb_grad.py, experiments/evaluate_parap_attack.py, experiments/evaluate.py (i.e. CODE_DIR, BASE_DIR, and MODEL_DIR) to desired values.
Set the following parameters when running the attacks:
Parameters
--alg_name- Choose betweenROME,MEMIT,FTfor ROME, MEMIT and Constrained Finetuning respectively--ds_name- Choose betweencf_filt,zsrefor CounterFact, zsRE respectively--model_name- Choose betweenEleutherAI/gpt-j-6B,gpt2-xl,meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hffor GPT-J-6B, GPT2-XL and Llama2-7b respectively--edit_layers- We use6for GPT-J-6B,17for GPT2-XL and7for Llama2-7b-n- This is the total number of datapoints to be used in the dataset. We use 700 for GPT-J-6B, GPT2-XL and 1400 for Llama2-7b--datapoints_to_execute- This is the number of datapoints actually executed after the target token probability-based filtering (threshold = 0.02). We set this700for all models.
Set the following parameters for running attacks with the following defenses:
--fact_erasure
--dummy_string
- Neither
--fact_erasurenor--dummy_string
--fact_erasure,--margin_loss,--margin_layers 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32(Please see Table 2 in Appendix A of the paper for the default defense layers we use for each model)
--fact_erasure,--entropy_loss,--entropy_layers 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32(Please see Table 2 in Appendix A of the paper for the default defense layers we use for each model)
--fact_erasure,--model_parap,
Set the following parameters for running attacks with the respective defenses:
- Run the script
--evaluate.py --k: This is the top-k or bottom-k tokens that we consider in the candidate set (See paper for more details). We set 4 as the default value.--layers_wb_attack 8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23(Please see Table 2 in Appendix A of the paper for the default attack layers we use for each model)
- Run the script
--evaluate_wb_grad.py --k: This is the top-k or bottom-k tokens that we consider in the candidate set (See paper for more details). We set 4 as the default value.--layers_wb_attack 8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23(Please see Table 2 in Appendix A of the paper for the default attack layers we use for each model)
--num_attack_parap 4,--attack mg,--bb_num_samples 5
The following parameters remain common for all attacks and defenses:
--norm_constraint 1e-4,--kl_factor .0625- We always set
--correctness_filter 1to ensure that the model actually knows the fact being deleted - We always set
--retain_rateto ensure we compute the specificity metrics (Delta accuracies: Neighborhood and Random) --window_sizesis set to1for ROME and FT and3for MEMIT
Following are some sample commands for running Head Projection Attack with Error Injection defense, Probability Delta Attack with Head Projection defense and Input Rephrasing Attack with Empty Response defense
In order to get results for the Head Projection Attack with Error Injection defense, select parameters as described above and execute the following commands
cd third_party
python3 -m experiments.evaluate --alg_name MEMIT --ds_name cf_filt --model_name EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --run 1 --correctness_filter 1 --norm_constraint 1e-4 --kl_factor .0625 --gpu 0 --overwrite --edit_layer 6 -n 700 --datapoints_to_execute 700 --k 4 --layers_wb_attack "17 18 19 20 21" --retain_rate --window_sizes 3
In order to get results for the Probability Delta Attack with Head Projection defense, select parameters as described above and execute the following commands
cd third_party
python3 -m experiments.evaluate_wb_grad --alg_name ROME --ds_name cf_filt --model_name EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --run 1 --correctness_filter 1 --norm_constraint 1e-4 --kl_factor .0625 --fact_erasure --gpu 1 --overwrite --edit_layer 6 -n 700 --datapoints_to_execute 700 --k 2 --layers_wb_attack "8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23" --retain_rate --margin_loss --margin_layers 8 9 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
In order to get results for the Input Rephrasing Attack with Empty Response, select parameters as described above execute the following commands
cd third_party
python3 -m experiments.evaluate_parap_attack --alg_name MEMIT --window_sizes 3 --ds_name cf_filt --model_name EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --run 1 --correctness_filter 1 --norm_constraint 1e-4 --kl_factor .0625 --gpu 1 --edit_layer 6 -n 10 --datapoints_to_execute 10 --num_attack_parap 4 --retain_rate --attack mg --bb_num_samples 5 --dummy_string
@article{patil2023can,
title={Can Sensitive Information Be Deleted From LLMs? Objectives for Defending Against Extraction Attacks},
author={Patil, Vaidehi and Hase, Peter and Bansal, Mohit},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.17410},
year={2023}
}