- Overview
- LowLevelAPI-s and HighLevelAPI-s
- Fours and eights in the API-s
- Zeros and ones in the API-s
- Recommended API-s
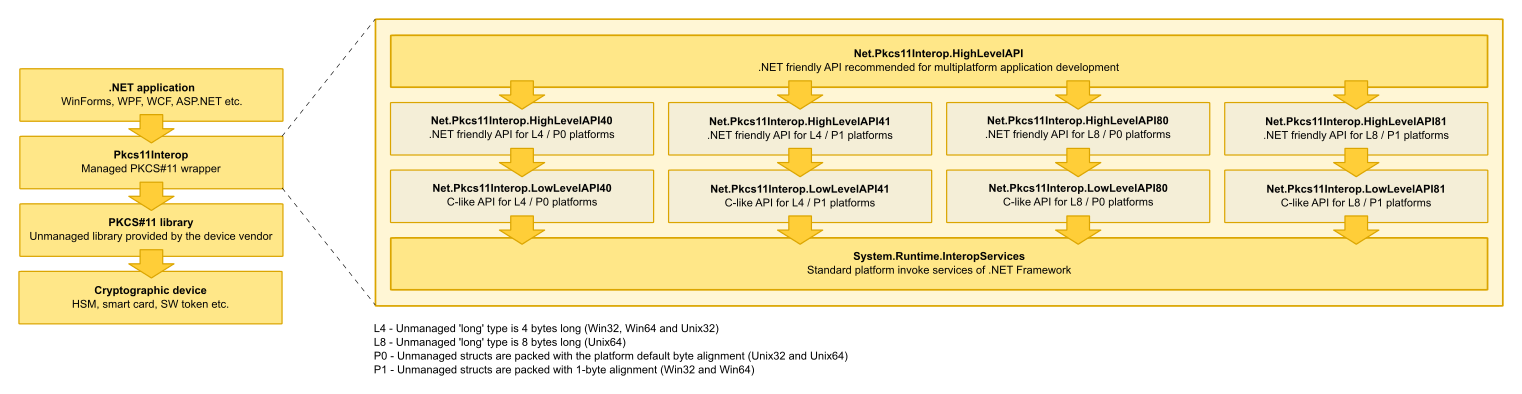
Pkcs11Interop forms a bridge between the unmanaged ANSI C and managed .NET worlds. It loads unmanaged PKCS#11 library provided by the cryptographic device vendor and makes its functions accessible to .NET application.
Pkcs11interop uses System.Runtime.InteropServices to define platform invoke methods for unmanaged PKCS#11 API and specifies how data is marshaled between managed and unmanaged memory.
Following figure presents the typical usage of Pkcs11Interop library in .NET application (left side) and internal architecture of Pkcs11Interop library (right side):
Note: Click on a picture for a larger image.
Pkcs11Interop API is logically divided into the set of LowLevelAPI-s and the set of HighLevelAPI-s.
In order to bring the full power of PKCS#11 API to the .NET environment LowLevelAPI-s follow ANSI C API defined by PKCS#11 specification as closely as possible and because of that require C-like coding style with a manual memory management.
On the other hand HighLevelAPI-s, which are built on top of LowLevelAPI-s, use garbage collector for automatic memory management and utilize developer friendly constructs such as collections or streams.
The C ulong type is extensively used throughout the PKCS#11 ANSI C API and unfortunately it is one of the most difficult types to marshal since there is no equivalent type in .NET that universally matches its size.
The problem is that the C ulong type can be 4 bytes long on some platforms (Win32, Win64 and Unix32) and in the same time it can be 8 bytes long on the other platforms (Unix64). In .NET there is uint type which is 4 bytes long regardless of platform and there is ulong type which is 8 bytes long regardless of platform.
Neither of .NET types can be used as a multiplatform alternative for C ulong type and the only option is to use and marshal two different sets of functions and structures:
- set with
uint.NET type for platforms where Culongtype is 4 bytes long
for LowLevelAPI40, LowLevelAPI41, HighLevelAPI40 and HighLevelAPI41 - set with
ulong.NET type for platforms where Culongtype is 8 bytes long
for LowLevelAPI80, LowLevelAPI81, HighLevelAPI80 and HighLevelAPI81
PKCS#11 specifications v2.01 - v2.30 all vaguely state:
Cryptoki structures are packed to occupy as little space as is possible. In particular, on the Win32 and Win16 platforms, Cryptoki structures should be packed with 1-byte alignment. In a UNIX environment, it may or may not be necessary (or even possible) to alter the byte-alignment of structures.
One could say that packing with 1-byte alignment should be preferred on all platforms but most of PKCS#11 libraries available for Unix platforms use the default byte alignment instead. Structure packing in .NET is controlled by the Pack field of System.Runtime.InteropServices.StructLayoutAttribute which cannot be modified in the runtime so the only option is to use and marshal two different sets of structures:
- set with
Packfield set to 1 to indicate 1-byte alignment
for LowLevelAPI41, LowLevelAPI81, HighLevelAPI41 and HighLevelAPI81 - set with
Packfield set to 0 to indicate the default byte alignment
for LowLevelAPI40, LowLevelAPI80, HighLevelAPI40 and HighLevelAPI80
Net.Pkcs11Interop.HighLevelAPI automagically uses correct set of platform dependent API-s and therefore is recommended API for most use cases.