SeisNoise.jl is designed for fast and easy ambient noise cross-correlation in Julia.
From the Julia command prompt:
- Press
]to enterpkg. - Type or copy:
add SeisNoise - Press backspace to exit
pkg. - Type or copy:
using SeisNoise
- Built upon SeisIO for easy and fast I/O.
- Custom types for saving Fourier Transforms of data and cross-correlations
- Array-based processing of raw data and cross-correlation.
- Methods for dv/v measurements.
- Coming soon: Dispersion analysis.
Once you have installed the package you can type using SeisNoise to start
cross-correlating. For example
using SeisNoise, SeisIO
fs = 40. # sampling frequency in Hz
freqmin,freqmax = 0.1,0.2 # min and max frequencies
cc_step, cc_len = 450, 1800 # corrleation step and length in S
maxlag = 60. # maximum lag time in correlation
s = "2019-02-03"
t = "2019-02-04"
S1 = get_data("FDSN","CI.SDD..BHZ",src="SCEDC",s=s,t=t)
S2 = get_data("FDSN","CI.PER..BHZ",src="SCEDC",s=s,t=t)
process_raw!(S1,fs)
process_raw!(S2,fs)
R = RawData.([S1,S2],cc_len,cc_step)
detrend!.(R)
taper!.(R)
bandpass!.(R,freqmin,freqmax,zerophase=true)
FFT = rfft.(R)
whiten!.(FFT,freqmin,freqmax)
C = correlate(FFT[1],FFT[2],maxlag)
clean_up!(C,freqmin,freqmax)
abs_max!(C)
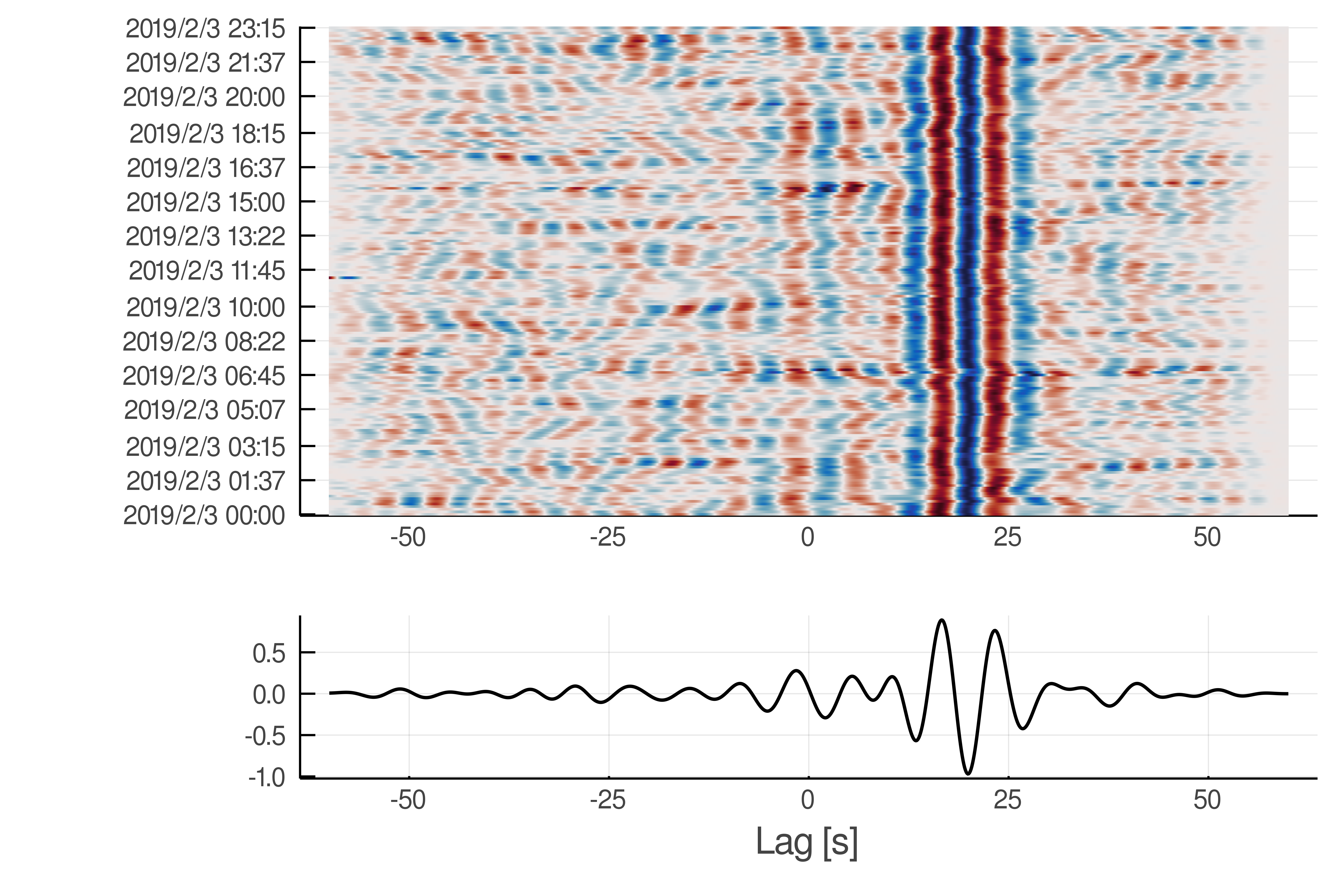
corrplot(C)will produce this figure:
SeisNoise can process data and compute cross-correlations on the GPU with CUDA. The JuliaGPU suite provides a high-level interface for CUDA programming through the CuArrays.jl and CUDAnative.jl packages. CuArrays.jl provides an array type for storing data on the GPU. Data in SeisNoise structures (R.x, F.fft, and C.corr fields, for RawData, FFTData, and CorrData, respectively) can move between an Array on the CPU to a CuArray on the GPU using the gpu and cpu functions, as shown below.
⚠️ Only Nvidia GPUs are suported at the moment. Hold in there for AMD/OpenCL support...
# create raw data and send to GPU
R = RawData(S1, cc_len, cc_step) |> gpu
R.x
72000×188 CuArrays.CuArray{Float32,2,Nothing}
# send data back to the CPU
R = R |> cpu
R.x
72000×188 Array{Float32,2}All basic processing remains the same on the GPU. Here is a complete cross-correlation routine on the GPU:
# send data to GPU
R1 = RawData(S1, cc_len, cc_step) |> gpu
R2 = RawData(S2, cc_len, cc_step) |> gpu
R = [R1,R2]
# preprocess on the GPU
detrend!.(R)
taper!.(R)
bandpass!.(R,freqmin,freqmax,zerophase=true)
# Real FFT on GPU
FFT = rfft.(R)
whiten!.(FFT,freqmin,freqmax)
# compute correlation and send to cpu
C = correlate(FFT[1],FFT[2],maxlag) |> cpu- Preprocessing:
detrend,demean,taper,onebit,smooth
- Filtering:
bandpass,bandstop,lowpass,highpass
- Fourier Domain:
whiten,rfft,irfft
- Cross-correlation:
correlate,cross-coherence,deconvolution
- Post-processing:
stack,filters, etc..