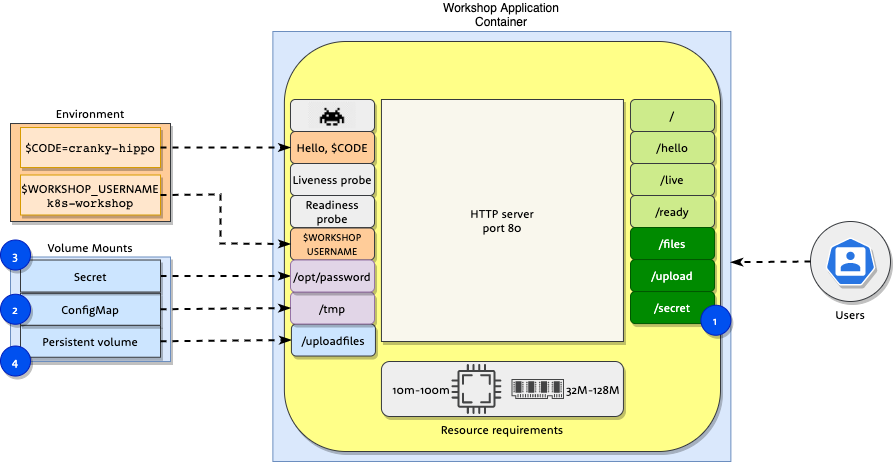
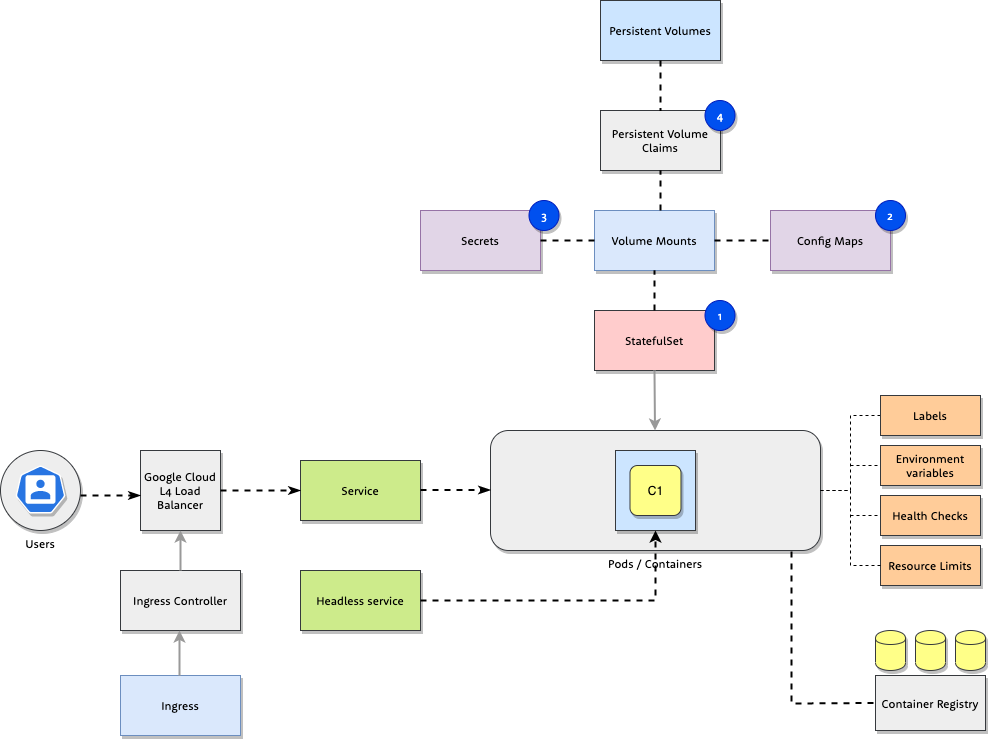
Workshop » Volumes
In this task you will learn how to configure pod deployments by using Secrets, ConfigMaps and Persistent volumes mounting them as volumes to Pod objects.
Workshop application container also supports the following functionality:
- Additional http endpoints for
/files/uploadand/secret. - Application can be configured to display files, which are stored in
/tmp, when you openhttps://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/filesweb page. These files can be stored inConfigMapand mounted into the container. - Application can be configured to password protect Space Invaders when
environment variable
WORKSHOP_USERNAMEis set and/opt/passwordfile exists with password. Password protected Space Invaders are accessible onhttps://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/secret/. - Application supports uploading files and storing them permanently to
PersistentVolume. You can upload files usinghttps://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/uploadendpoint.
Objects:
StatefulSet- Object containing application definition. This is the file we will be editing in workshop tasks.ConfigMap- Config map containing files served at/filesendpoint.Secret- Secret for access to Space invaders game.Persistent Volume Claim- Volume to store uploaded files.
Your task is extension of the StatefulSet created in section Basic
Objects with ConfigMap, Secret and
PersistentVolume volumes.
See kubectl cheat sheet for full command reference.
kubectl get all
kubectl describe statefulset/workshop-example
kubectl describe pod/workshop-example-0
kubectl logs -f pod/workshop-example-0This task builds on resources deployed in Basic Objects. Before you start with the tasks deploy and inspect the deployed elements with:
kubectl get all
kubectl describe statefulset/workshop-example
kubectl describe pod/workshop-example-0In case you did not complete the Basic Objects task you can redeploy it using solutions:
kubectl apply -f ../01_basic_objects/solutions/04_statefulset.yaml
kubectl apply -f ../01_basic_objects/service.yaml
kubectl create -f /k8s.3fs.si-cert.yaml
kubectl apply -f ../01_basic_objects/solutions/01_ingress.yamlApplication container supports displaying files located in /tmp/ directory through /files endpoint.
Tasks:
- Create a
ConfigMapobject with files located infiles/sub-directory- use
kubectl create configmap workshop-configmap-filescommand with appropriate arguments.
- use
- Update
StatefulSetinstatefulset.yamlto mount the previously createdConfigMapin the/tmpdirectory:- add the
ConfigMapreference to.spec.template.spec.volumessection - add the reference to volume in
.spec.template.containers[0].volumeMountssection
- add the
After you have updated the statefulset.yaml, deploy the application with the following command.
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlAfter the successful deployment check https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/files. Webpage Cheat sheet - Kubectl should appear.
Inspect the deployed objects by using the following kubectl commands:
kubectl get all
kubectl describe configmap/workshop-configmap-files
kubectl describe statefulset/workshop-example
kubectl logs pod/workshop-example-0Show solution
Create a ConfigMap object using the following command:
$ kubectl create configmap workshop-configmap-files --from-file=files/
configmap/workshop-configmap-files createdYou can check the full ConfigMap file here.
Update statefulset.yaml with appropriate references in .spec.template.spec.volumes and .spec.template.containers[0].volumeMounts sections.
--- statefulset.yaml 2020-05-26 16:09:18.000000000 +0200
+++ solutions/01_statefulset.yaml 2020-05-26 16:09:32.000000000 +0200
@@ -47,5 +47,11 @@ spec:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 64Mi
- volumeMounts: []
- volumes: []
+ volumeMounts:
+ - name: workshop-files
+ mountPath: /tmp/
+ readOnly: true
+ volumes:
+ - name: workshop-files
+ configMap:
+ name: workshop-configmap-filesDeploy to cluster
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlYou can check the full statefulset.yaml here.
Application can be configured to password protect Space Invaders when
environment variable WORKSHOP_USERNAME is set and WORKSHOP_PASSWORD is set
to path of file containing password. By using Secret object we will mount a
file into a container, which will be used for authentication to Space Invaders
Tasks:
- Create a
Secretobject with keypasswordwith a value of random password- use
kubectl create secret generic workshop-example-secret --from-literal=password=supersecretcommand with appropriate arguments
- use
- Update
StatefulSetinstatefulset.yamlto mount the previously createdSecret, keypasswordto/opt/directory.- add the
Secretreference to.spec.template.spec.volumessection - add the reference to volume in
.spec.template.containers[0].volumemountssection
- add the
After you have updated the statefulset.yaml, deploy the application with the following command.
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlAfter the successful deployment check https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/secret. The webpage should ask you for username and password. Use WORKSHOP_USERNAME and Secret value respectively.
Inspect the deployed objects by using the following kubectl commands:
kubectl get all
kubectl describe secret/workshop-example-secret
kubectl describe statefulset/workshop-example
kubectl logs pod/workshop-example-0Show solution
Create a Secret object using the following command:
$ kubectl create secret generic workshop-example-secret --from-literal=password=my-super-password
secret/workshop-example-secret createdYou can check the full Secret file here.
Update statefulset.yaml with appropriate references in .spec.template.spec.volumes and .spec.template.containers[0].volumeMounts sections.
--- 01_statefulset.yaml 2020-05-27 12:00:02.000000000 +0200
+++ 02_statefulset.yaml 2020-05-27 12:00:02.000000000 +0200
@@ -52,7 +52,16 @@ spec:
- name: workshop-files
mountPath: /tmp/
readOnly: true
+ - name: workshop-secret-password
+ mountPath: /opt/
+ readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: workshop-files
configMap:
name: workshop-configmap-files
+ - name: workshop-secret-password
+ secret:
+ secretName: workshop-example-secret
+ items:
+ - key: password
+ path: passwordDeploy updated StatefulSet to cluster
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlOpen webpage: https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/secret and password prompt should open.
You can check the whole statefulset.yaml file here.
Workshop application has the ability to store files uploaded through web interface by using /upload endpoint. Uploaded files are available on endpoint https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/uploadfiles/.
To allow persistence during Pod restarts, PersistentVolume and PersistentVolumeClaim must be created and mounted into container.
Tasks:
-
Add
PersistentVolumeClaim(size:128Mi) to existingStatefulSet:- create
.spec.volumeClaimTemplateskey with the following configuration
volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: pvc-uploadfiles spec: accessModes: - "ReadWriteOnce" resources: requests: storage: "128Mi"
- configure
volumeMountto mount configuredPersistentVolumeClaimin/uploadfilescontainer path.
- create
After you have updated the statefulset.yaml, deploy the application with the following command.
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlAfter the successful deployment check https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/upload and upload a file. You can check the list of uploaded files here: https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/uploadfiles/.
Inspect the deployed objects by using the following kubectl commands. These commands will show you information about newly created objects and its usage.
kubectl get all
kubectl describe pod/workshop-example-0
kubectl describe persistentvolumeclaims
kubectl describe persistentvolumesTo check persistence delete the running Pod by executing the following command. New Pod will be recreated and PersistentVolume will be mounted to the new container. Your previously uploaded files should be available again here: https://$CODE.k8s.3fs.si/uploadfiles.
kubectl delete pod/workshop-example-0Show solution
Update statefulset.yaml file with appropriate references in .spec.template.containers[0].volumeMounts and .spec.volumeClaimTemplates sections:
--- 02_statefulset.yaml 2020-05-26 18:49:03.000000000 +0200
+++ 03_statefulset.yaml 2020-05-26 18:51:49.000000000 +0200
@@ -55,6 +55,8 @@ spec:
- name: workshop-secret-password
mountPath: /opt/
readOnly: true
+ - name: pvc-uploadfiles
+ mountPath: /uploadfiles
volumes:
- name: workshop-files
configMap:
@@ -65,3 +67,12 @@ spec:
items:
- key: password
path: password
+ volumeClaimTemplates:
+ - metadata:
+ name: pvc-uploadfiles
+ spec:
+ accessModes:
+ - "ReadWriteOnce"
+ resources:
+ requests:
+ storage: "128Mi"Deploy updated StatefulSet to cluster
kubectl replace --force -f statefulset.yamlYou can check the whole statefulset.yaml file here.
To preserve the kubernetes resources remove all created object by executing:
kubectl delete statefulset workshop-example
kubectl delete service workshop-example
kubectl delete service workshop-example-headless
kubectl delete ingress workshop-example
kubectl delete secret workshop-example-secret
kubectl delete configmap workshop-configmap-files
kubectl delete pvc --all