Hatuqway: Difference between revisions
Removed inaccurate photo Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{More citations needed|date=June 2022}} |
|||
{{Short description|Circassian tribe}} |
{{Short description|Circassian tribe}} |
||
{{Infobox ethnic group |
{{Infobox ethnic group |
||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
| native_name = Хьатыкъуайхэр, Хьатыкъоехэр |
| native_name = Хьатыкъуайхэр, Хьатыкъоехэр |
||
| native_name_lang = ady |
| native_name_lang = ady |
||
| flag = |
| flag = Hatuqwayfamilies.png |
||
| flag_caption = [[ |
| flag_caption = Family symbols ([[Tamga|tamigha]]) of some Hatuqway families |
||
| |
| image = Circassian_flag.svg |
||
| image_caption = [[Circassian flag]] |
|||
| population = 5,650 (estimate){{cn|date=June 2022}} |
|||
| region1 = {{flagcountry|Turkey}} |
| region1 = {{flagcountry|Turkey}} |
||
| pop1 = 5 |
| pop1 = ~5,000{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| region2 = {{flagcountry|Syria}} |
| region2 = {{flagcountry|Syria}} |
||
| pop2 = 200 |
| pop2 = ~200{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| region3 = {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
| region3 = {{flagcountry|Germany}} |
||
| pop3 = 200 (estimate) |
| pop3 = ~200 (estimate){{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| region4 = {{flagcountry|United States of America}} |
| region4 = {{flagcountry|United States of America}} |
||
| pop4 = 100 (estimate) |
| pop4 = ~100 (estimate){{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| region5 = {{flagcountry|Jordan}} |
| region5 = {{flagcountry|Jordan}} |
||
| pop5 = 100 |
| pop5 = ~100{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| region6 = {{flagcountry|Israel}} |
| region6 = {{flagcountry|Israel}} |
||
| pop6 = 50 |
| pop6 = ~50{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
||
| pop7 = |
| pop7 = |
||
| languages = [[Adyghe language|Adyghe]], [[Turkish language|Turkish]], [[English language|English]], [[Arabic]], [[Hebrew]] |
| languages = [[Adyghe language|Adyghe]], [[Turkish language|Turkish]], [[Russian language|Russian]], [[English language|English]], [[Arabic]], [[Hebrew]], [[German language|German]] |
||
| religions = [[Islam]] |
| religions = [[Islam]] |
||
| related_groups = [[Circassians|Other Adyghe tribes |
| related_groups = [[Circassians|Other Adyghe tribes]] |
||
}}{{Circassians}} |
}} |
||
{{Circassians}} |
|||
The '''Hatuqway'''<ref name="Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook 2017">{{cite book |title=Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-315-47540-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XpcuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA79 |access-date=20 July 2018 |page=79}}</ref> |
The '''Hatuqway'''<ref name="Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook 2017">{{cite book |title=Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=2017 |isbn=978-1-315-47540-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XpcuDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA79 |access-date=20 July 2018 |page=79}}</ref>{{efn|{{IPAc-en|ˈ|h|ɑː|t|ʊ|k|w|aɪ}}; {{langx|ady|Хьатыкъуай}}, {{IPA-all|ħaːtɘqʷaːj|}}; {{langx|tr|Hatukay}}; {{langx|ar|حتوقاي}}; {{Langx|de|Hatkoj}}; {{langx|ru|Хатукай}}}} are one of the twelve major [[Circassians|Circassian]] tribes, representing one of the twelve stars on the green-and-gold [[Flag of Adygea|Circassian flag]].<ref name="Cunningham 1977">{{cite book |last=Cunningham |first=B. |title=The New Jersey ethnic experience |publisher=W. H. Wise |year=1977 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_MYRAQAAIAAJ |access-date=20 July 2018 |page=108 |quote=... or Pontic branch, consisting of Abkhaz, Ubykh, and Circassian proper (or Adyghe). The Circassians themselves are divided into some fifteen different clans, including the Abadsakh, Besliney, Bjedoogh, Hatukay, Kabardey, Kamurggoi, Shapsoogh, and Ubykh.}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|date=2010|title=Circassians|url=https://www.adiga-home.net/Circassians.htm|url-status=unfit|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140820015838/https://www.adiga-home.net/Circassians.htm|archive-date=August 20, 2014|access-date=17 May 2016|website=Adiga-home.net|quote=The 12 Circassian tribes: Abadzeh Besleney Bzhedug Yegeruqay Zhaney Kabarday Mamheg Natuhay Temirgoy Ubyh Shapsug Hatukay. The twelve stars on the Adyghe Flag also refers to the twelve tribes.}}</ref> They were known for their art of war as a warrior tribe. After the [[Russo-Circassian War]], their presence in the Caucasus was destroyed during the [[Circassian genocide]], and their number was significantly decreased and today they exist only in small communities in various diasporas, and their names are not mentioned anymore in Circassian dialectology.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Papşu|first=Murat|date=2013-06-10|title=Çerkes dillerine genel bir bakış Kafkasya ve Türkiye|url=https://www.kafkasfederasyonu.org/kultursanat/anadil/cerkes_dilleri.htm|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130610062416/https://www.kafkasfederasyonu.org/kultursanat/anadil/cerkes_dilleri.htm|archive-date=2013-06-10|access-date=2021-01-17}}</ref> |
||
== |
== History == |
||
{{Refimprove-section|date=June 2022}} |
|||
=== History === |
|||
The Hatuqway were a western [[Circassians|Circassian]] tribal [[princedom]] whose homeland lay along the banks of the [[Kuban River]]. The Hatuqway people lived mostly in the mountains between the lower valleys of the [[Pshish River]] and the [[Belaya River (Kuban)|Belaya River]].<ref name="atlas">{{Cite web|url=https://linguarium.iling-ran.ru/publications/caucas/ACL-N_Cau.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060310231853/https://linguarium.iling-ran.ru/publications/caucas/ACL-N_Cau.pdf |url-status=dead |title=Atlas of Caucasian languages (a pdf file)|archive-date=March 10, 2006}}</ref> Due to their small size and closeness to [[Temirgoy]] tribe, they were considered as one of the subgroups of Temirgoy. Their neighbours were [[Bzhedug]] (West), [[Abzakhs|Abadzekhs]] (South) and, naturally, Temirgoys (East). |
The Hatuqway were a western [[Circassians|Circassian]] tribal [[princedom]] whose homeland lay along the banks of the [[Kuban River]]. The Hatuqway people lived mostly in the mountains between the lower valleys of the [[Pshish River]] and the [[Belaya River (Kuban)|Belaya River]].<ref name="atlas">{{Cite web|url=https://linguarium.iling-ran.ru/publications/caucas/ACL-N_Cau.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060310231853/https://linguarium.iling-ran.ru/publications/caucas/ACL-N_Cau.pdf |url-status=dead |title=Atlas of Caucasian languages (a pdf file)|archive-date=March 10, 2006}}</ref> Due to their small size and closeness to [[Temirgoy]] tribe, they were considered as one of the subgroups of Temirgoy. Their neighbours were [[Bzhedug]] (West), [[Abzakhs|Abadzekhs]] (South) and, naturally, Temirgoys (East). |
||
| Line 76: | Line 80: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Quote|text=Hatuqway province... The name of their prince is Jangiray, or Janbe Giray. This Hatuqway prince is rich, he owns many animals and eight thousand armed soldiers. Since this province was a large, fertile and beautiful homeland, its people slaughtered the son of the king of Moscow and bravely fought against the infidel Kalmyks. They are very loyal, savvy, armed and valiant soldiers. Even among the Circassian tribes, the villages are hostile to each other. So there is no shortage of constant internecine wars and strife. Nevertheless, they, communicate and trade with each other. And beyond the mountains live Abkhazians. In general, all the Abkhaz tribes are hostile towards these nomadic Circassian tribes. So, in the end, they do not have a single day free from battles and clashes |
{{Quote|text=Hatuqway province... The name of their prince is Jangiray, or Janbe Giray. This Hatuqway prince is rich, he owns many animals and eight thousand armed soldiers. Since this province was a large, fertile and beautiful homeland, its people slaughtered the son of the king of Moscow and bravely fought against the infidel Kalmyks. They are very loyal, savvy, armed and valiant soldiers. Even among the Circassian tribes, the villages are hostile to each other. So there is no shortage of constant internecine wars and strife. Nevertheless, they, communicate and trade with each other. And beyond the mountains live Abkhazians. In general, all the Abkhaz tribes are hostile towards these nomadic Circassian tribes. So, in the end, they do not have a single day free from battles and clashes – every day enemies come from different directions. |
||
In the whole world, there are no such beauties worthy of praise and love like this people. Also there are purebred Arabian horses here. They are famous in the mountains: martens, similar to sables, wild cats, wild chickens, partridges. |
In the whole world, there are no such beauties worthy of praise and love like this people. Also there are purebred Arabian horses here. They are famous in the mountains: martens, similar to sables, wild cats, wild chickens, partridges. |
||
| Line 86: | Line 90: | ||
Today, the Hatuqway have several villages in various diasporas. The Hatuqway dialect is one of the Circassian languages in big danger of extinction. |
Today, the Hatuqway have several villages in various diasporas. The Hatuqway dialect is one of the Circassian languages in big danger of extinction. |
||
== Etymology == |
|||
The widely accepted theory is that the names derives from [[Prince Inal]] the Great's son Temruk's son Hatko, who was prince of the Taman Peninsula. His principality is called Hatuqway (Place of Hatko) and the people of the principality are described as "From Hatuqway". Thus the name of the principality became the name of the tribe. |
The widely accepted theory is that the names derives from [[Prince Inal]] the Great's son Temruk's son Hatko, who was prince of the Taman Peninsula. His principality is called Hatuqway (Place of Hatko) and the people of the principality are described as "From Hatuqway". Thus the name of the principality became the name of the tribe. |
||
Another outdated theory about the origin of the name 'Hatuqway' is that it is from Хьаты ("Hatti") + Къуэ ("son"); meaning "Hattic son". 'Hatti' is an ancient name, originally referring to a non-Indo-European people of ancient Anatolia. Some researchers have claimed there may be links between Circassians and Indo-European-speaking communities,<ref>{{cite book|last=Serbes|first=Nahit|title=Yaşayan Efsane Xabze|publisher= |
Another outdated theory about the origin of the name 'Hatuqway' is that it is from Хьаты ("Hatti") + Къуэ ("son"); meaning "Hattic son". 'Hatti' is an ancient name, originally referring to a non-Indo-European people of ancient Anatolia. Some researchers have claimed there may be links between Circassians and Indo-European-speaking communities,<ref>{{cite book|last=Serbes|first=Nahit|title=Yaşayan Efsane Xabze|publisher=Phoenix Yayınları|year=2012|isbn=9786055738884}}</ref> and some have argued that there are connections between Circassians and [[Hattic language|Hatti]], who are from ancient Anatolian peoples,<ref>{{cite web|date=2003|title=Hititlerle Çerkezler Arasında Dil Benzerliği|url=https://bianet.org/bianet/kultur/27528-hititlerle-cerkezler-arasinda-dil-benzerligi|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181208170317/https://bianet.org/bianet/kultur/27528-hititlerle-cerkezler-arasinda-dil-benzerligi|archive-date=8 December 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Çurey|first=Ali|title=Hatti-Hititler ve Çerkesler|year=2011|publisher=Chiviyazıları Yayınevi|isbn=9786055708399}}</ref><ref>Prof.Dr. ĞIŞ Nuh (yazan), HAPİ Cevdet Yıldız (çeviren). [https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_4710_adigece_nin_temel_sorunlari.html Adigece'nin temel sorunları-1] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130420005356/https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_4710_adigece_nin_temel_sorunlari.html |date=2013-04-20 }}. Адыгэ макъ,12/13 Şubat 2009</ref> but these theories have not been addressed further and are not widely accepted. This Circassian tribe may preserve this name. This name also occurs elsewhere in the Caucasus in a [[Nart saga]] wherein the hero [[Batraz]] is said to speak in Hattic. |
||
== Culture |
== Culture == |
||
Traditional Hatuqway culture is part of greater Circassian culture. The Hatuqway were engaged in agriculture, cattle and horse breeding. Before Islam, the Hatuqways worshipped Jesus as well as the gods of Circassians such as Shibla (god of lightning and thunder), Sozeresh (god of fertility), Yamish, Ahin, and Hakustash.{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
|||
== Language == |
|||
{{Split section|Hatuqwai dialect|date=August 2024}} |
|||
Traditional Hatuqway culture is part of the Circassian culture. The Hatuqway were engaged in agriculture, cattle and horse breeding. Before Islam, the Hatuqways worshipped Jesus as well as the gods of Circassians such as Shibla (god of lightning and thunder), Sozeresh (god of fertility), Yamish, Ahin and Hakustash. |
|||
The Hatuqway speak the Hatuqway dialect of Adyghe, which is in the Circassian language branch of the Northwest Caucasian Languages. Nowadays, the number of speakers of this language has decreased considerably and it could not find a place in the literary language as there is no Hatuqway left in the Caucasus.{{cn|date=June 2022}} |
|||
== Hatuqway villages and families == |
|||
=== Language === |
|||
The Hatuqway speak the Hatuqway dialect of Adyghe, which is in the Circassian language branch of the Northwest Caucasian Languages. Nowadays, the number of speakers of this language has decreased considerably and it could not find a place in the literary language as there is no Hatuqway left in the Caucasus. |
|||
=== Villages === |
|||
== Hatuqway village and families == |
|||
Below are some of the Hatuqway villages in Turkey. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
=== Some Hatuqway villages in Turkey === |
|||
! Province |
|||
Some Hatuqway villages ({{Lang-ady|къуаджэ|translit=quadjə}}) in Turkey. |
|||
! Adyghe name |
|||
{| {{table}} |
|||
! Turkish name |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Province''' |
|||
! Source |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Adyghe name''' |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Romanisation''' |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Turkish name''' |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Source''' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Kayseri]] |
|[[Kayseri Province|Kayseri]] |
||
|Къэйнэр, ''Qəynər'' |
|||
|[[Kaynar, Pınarbaşı|Къэйнэр]] |
|||
|[[Kaynar, Pınarbaşı|Kaynar]] |
|||
|Qəynər |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_462_kaynarlilar_bir_araya_geliyor.html|title=Kaynarlılar bir araya geliyor|access-date=3 October 2018|date=|language=tr|work=Nart Ajans|publisher=|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130418103852/https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_462_kaynarlilar_bir_araya_geliyor.html|archive-date=18 April 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
|Kaynar |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_462_kaynarlilar_bir_araya_geliyor.html|title=Kaynarlılar bir araya geliyor|access-date=3 October 2018|date=|language=tr|work=Nart Ajans|publisher=|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130418103852/https://www.nartajans.net/site/haberler_462_kaynarlilar_bir_araya_geliyor.html|archive-date=18 April 2013|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Kaynar,_P%C4%B1narba%C5%9F%C4%B1&oldid=22299925|title=Kaynar, Pınarbaşı|access-date=3 October 2020|date=2 May 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Чэчэнэй, ''Çəçənəy'' |
|||
|[[Beserek, Pınarbaşı|Чэчэнэй]] |
|||
|[[Beserek, Pınarbaşı|Beserek]] |
|||
|Çəçənəy |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20163&haritasi=beserek|title=Beserek|access-date=|date= |work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Beserek |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Beserek,_P%C4%B1narba%C5%9F%C4%B1&oldid=23213509|title=Beserek, Pınarbaşı|access-date=3 October 2020|date=12 September 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nisanyanmap.com/?yer=20163&haritasi=beserek|title=Beserek|access-date=|date=April yanmap|publisher=|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Лакхьэблэ, ''Lakhəblə'' |
|||
|[[Tersakan, Pınarbaşı|Лакхьэблэ]] |
|||
|[[Tersakan, Pınarbaşı|Tersakan]] |
|||
|Lakhəblə |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20177&haritasi=tersakan|title=Tersakan|access-date=|date= |work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Tersakan |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Tersakan,_P%C4%B1narba%C5%9F%C4%B1&oldid=23219569|title=Tersakan, Pınarbaşı|access-date=3 October 2020|date=12 September 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Лыбыйхьэблэ, ''Lıbıyhəblə'' |
|||
|[[Kavakköy, Pınarbaşı|Лыбыйхьэблэ]] |
|||
|[[Kavakköy, Pınarbaşı|Kavak/Kavakkköy]] |
|||
|Lıbıyhəblə |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20170&haritasi=kavak|title=Kavak|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Kavak/Kavakkköy |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nisanyanmap.com/?y=Kavak&lv=&t=Pınarbaşı&u=1&ua=5|title=Kavak|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyanmap|publisher=|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Мэлак, ''Məlak'' |
|||
|[[Malakköy, Pınarbaşı|Мэлак]] |
|||
|[[Malakköy, Pınarbaşı|Malak/Malakköy]] |
|||
|Məlak |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20173&haritasi=malak|title=Malak|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Malak/Malakköy |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.nisanyanmap.com/?yer=20161&haritasi=akören|title=Akören|access-date=|date=|publisher=Nisanyanmap|url-status=live}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Пэдысэй, ''Pədısəy'' |
|||
|[[Akören, Pınarbaşı|Пэдысэй]] |
|||
|[[Akören, Pınarbaşı|Akören]] |
|||
|Pedısəy |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20161&haritasi=ak%C3%B6ren|title=Akören|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Akören |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ak%C3%B6ren,_P%C4%B1narba%C5%9F%C4%B1&oldid=22760079|title=Akören, Pınarbaşı|access-date=3 October 2020|date=21 June 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Kayseri |
||
|Хаджыисхьакъ, ''Xacıyishaq'' |
|||
|[[Demirciören, Pınarbaşı|Хаджыисхьакъ]] |
|||
|[[Demirciören, Pınarbaşı|Demirciören]] |
|||
|Xacıyishaq |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=20166&haritasi=demirci%C3%B6ren|title=Demirciören|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Demirciören |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Demirci%C3%B6ren,_P%C4%B1narba%C5%9F%C4%B1&oldid=23219311|title=Demirciören, Pınarbaşı|access-date=3 October 2020|date=12 September 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Bolu]] |
|[[Bolu Province|Bolu]] |
||
|Пэциехьэблэ, ''Pətsiyehəblə'' |
|||
|[[Elmalık, Bolu|Пэциехьэблэ]] |
|||
|[[Elmalık, Bolu|Elmalık]] |
|||
|Pətsiyeheblə |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.circassiancenter.com/cc-turkiye/arastirma/0500-cerkeskoyleri.htm|title=TÜRKİYE'DEKİ ÇERKES KÖYLERİ|access-date=3 October 2020|date=|work=www.circassiancenter.com|publisher=|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120924052906/https://www.circassiancenter.com/cc-turkiye/arastirma/0500-cerkeskoyleri.htm|archive-date=24 September 2012|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=7139&haritasi=elmal%C4%B1k|title=Elmalık|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Elmalık |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.circassiancenter.com/cc-turkiye/arastirma/0500-cerkeskoyleri.htm|title=TÜRKİYE'DEKİ ÇERKES KÖYLERİ|access-date=3 October 2020|date=|work=www.circassiancenter.com|publisher=|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120924052906/https://www.circassiancenter.com/cc-turkiye/arastirma/0500-cerkeskoyleri.htm|archive-date=24 September 2012|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Elmal%C4%B1k,_Bolu&oldid=21968912|title=Elmalık, Bolu|access-date=3 October 2020|date=4 April 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Bilecik]] |
|[[Bilecik Province|Bilecik]] |
||
|Хьатыкъуае, ''Hatıquaye'' |
|||
|[[Poyra, Bozüyük|Хьатыкъуае]] |
|||
|[[Poyra, Bozüyük|Poyra]] |
|||
|Hatıquaye |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=5809&haritasi=poyra|title=Poyra|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Poyra |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Poyra,_Boz%C3%BCy%C3%BCk&oldid=23139520|title=Poyra, Bozüyük|access-date=3 October 2020|date=31 August 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|Bilecik |
||
|Адыгэчэпни, ''Adıgəçəpni'' |
|||
|[[Yeniçepni, Bozüyük|Адыгэчэпни]] |
|||
|[[Yeniçepni, Bozüyük|Çerkesçepni/Yeniçepni]] |
|||
|Adıgəçəpni |
|||
|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nisanyanyeradlari.com/?yer=5812&haritasi=yeni%C3%A7epni|title=Yeniçepni|access-date=|date=|work=Nisanyan Yeradları}}</ref> |
|||
|Çerkesçepni/Yeniçepni |
|||
|<ref>{{citation|url=https://tr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Yeni%C3%A7epni,_Boz%C3%BCy%C3%BCk&oldid=22113069|title=Yeniçepni, Bozüyük|access-date=3 October 2020|date=18 April 2020|language=tr|work=Vikipedi}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|} |
||
=== |
=== Clans === |
||
{{Unreferenced section|date=June 2022}} |
|||
Some of the Hatuqway clans ({{Lang-ady|лъакӀо|translit=tlak'o}}) in Turkey. |
|||
Below are some of the Hatuqway clans in Turkey. |
|||
{| {{table}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Adyghe name''' |
|||
! Adyghe name |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Turkized''' |
|||
! Turkish name |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Englishised''' |
|||
! Russian name |
|||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;" |'''Russianized''' |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Бзадж |
|Бзадж |
||
|Bzac |
|Bzac |
||
|Бзаджов |
|||
|Bzaj |
|||
|Бзаджов (Bzadzhov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Джэндар |
|Джэндар |
||
|Candar |
|Candar |
||
|Джандаров |
|||
|Jandar |
|||
|Джандаров (Jandarov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Иуаныкъу |
|Иуаныкъу |
||
|Yivanuk |
|Yivanuk |
||
|Иваников |
|||
|Yiwaneqo |
|||
|Иваников (Ivanikov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Къокӏасэ |
|Къокӏасэ |
||
|Koçase |
|Koçase |
||
|Кочесеко |
|||
|Kochase |
|||
|Кочесеко (Kocheseko) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|ЛӀымафэкъо |
|ЛӀымафэкъо |
||
|Lımafko |
|Lımafko |
||
|Тлимафов |
|||
|Lmafqo |
|||
|Тлимафов (Tlimafov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|МэфэшIукъо |
|МэфэшIукъо |
||
|Mafeşuko |
|Mafeşuko |
||
|Мафошов |
|||
|Mafeshuqo |
|||
|Мафошов (Mafoshov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Пэдыс |
|Пэдыс |
||
|Pedıs |
|Pedıs |
||
|Падисов |
|||
|Padis |
|||
|Падисов (Padisov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Такъырыкъо |
|Такъырыкъо |
||
|Takırıko |
|Takırıko |
||
|Такириков |
|||
|Taqereqo |
|||
|Такириков (Takirikov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Шэджэрыкъо |
|Шэджэрыкъо |
||
|Şacerıko |
|Şacerıko |
||
|Шегероков |
|||
|Shajereqo |
|||
|Шегероков (Shegerokov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Жьанэ |
|Жьанэ |
||
|Jane |
|Jane |
||
|Жанев |
|||
|Zhaney |
|||
|Жанев (Žanev) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Мастыр |
|Мастыр |
||
|Mastır |
|Mastır |
||
|Мастиров |
|||
|Mastir |
|||
|Мастиров (Mastirov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Шъобае |
|Шъобае |
||
|Şobaye |
|Şobaye |
||
|Собаев |
|||
|Shobaye |
|||
|Собаев (Sobaev) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Хьатыкъо |
|Хьатыкъо |
||
|Hatıko |
|Hatıko |
||
|Хатиков |
|||
|Khateqo |
|||
|Хатиков (Khatikov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Хьапае |
|Хьапае |
||
|Hapaye |
|Hapaye |
||
|Хапаев |
|||
|Khapaye |
|||
|Хапаев (Khapaev) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Утыж |
|Утыж |
||
|Vutıj |
|Vutıj |
||
|Утижов |
|||
|Wutij |
|||
|Утижов (Utijov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Еутых |
|Еутых |
||
|Yevtıh |
|Yevtıh |
||
|Еутыхов |
|||
|Yewtekh |
|||
|Еутыхов (Eutykhov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Брыдж |
|Брыдж |
||
|Brıc |
|Brıc |
||
|Бриджов |
|||
|Brej |
|||
|Бриджов (Bridzhov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Чыназыр |
|Чыназыр |
||
|Çınazır |
|Çınazır |
||
|Чиназиров |
|||
|Chinazir |
|||
|Чиназиров (Chinazirov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Нэжъ |
|Нэжъ |
||
|Nej |
|Nej |
||
|Нажев |
|||
|Nazh |
|||
|Нажев (Nazhev) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|ЛIышъхьакъо |
|ЛIышъхьакъо |
||
|Lışhako |
|Lışhako |
||
|Тлишхаков |
|||
|Lshaqo |
|||
|Тлишхаков (Tlishkhakov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|ЦIэгъош |
|ЦIэгъош |
||
|Tseğoş |
|Tseğoş |
||
|Цегошов |
|||
|Tsaghosh |
|||
|Цегошов (Tsegoshov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Дэбракъыкъо |
|Дэбракъыкъо |
||
|Debrakıko |
|Debrakıko |
||
|Дебракиков |
|||
|Dabraqiqo |
|||
|Дебракиков (Debrakikov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Бэрзэдж |
|Бэрзэдж |
||
|Berzec |
|Berzec |
||
|Берзеков |
|||
|Barzej |
|||
|Берзеков (Berzekov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Иуныхь |
|Иуныхь |
||
|Yivnıh |
|Yivnıh |
||
|Юнихов |
|||
|Yiwnih |
|||
|Юнихов (Yunikhov) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Къалэбатэ |
|Къалэбатэ |
||
|Kalebate |
|Kalebate |
||
|Калибатов |
|||
|Qalebate |
|||
|- |
|||
|Калибатов (Kalibatov) |
|||
|Хьэбатыр |
|||
|Hebatır |
|||
|Хабатыров |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 318: | Line 289: | ||
* [[Temirgoy people|Temirgoy]] |
* [[Temirgoy people|Temirgoy]] |
||
* [[Besleney]] |
* [[Besleney]] |
||
== Notes == |
|||
{{Notelist}} |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 323: | Line 297: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [https:// |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/19991006144359/https://www.geocities.com/Eureka/Enterprises/2493/hatuqwai.html The Hatuqway nation] |
||
{{authority control}} |
{{authority control}} |
||
| Line 330: | Line 304: | ||
[[Category:History of Kuban]] |
[[Category:History of Kuban]] |
||
[[Category:Circassian tribes]] |
[[Category:Circassian tribes]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Circassians in Turkey]] |
||
[[Category:Adygea]] |
[[Category:Adygea]] |
||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 23 October 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2022) |
Хьатыкъуайхэр, Хьатыкъоехэр | |
|---|---|
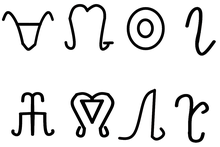 Family symbols (tamigha) of some Hatuqway families | |
 | |
| Total population | |
| 5,650 (estimate)[citation needed] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| ~5,000[citation needed] | |
| ~200[citation needed] | |
| ~200 (estimate)[citation needed] | |
| ~100 (estimate)[citation needed] | |
| ~100[citation needed] | |
| ~50[citation needed] | |
| Languages | |
| Adyghe, Turkish, Russian, English, Arabic, Hebrew, German | |
| Religion | |
| Islam | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Adyghe tribes | |
| Part of a series on the |
| Circassians Адыгэхэр |
|---|
 List of notable Circassians Circassian genocide |
| Circassian diaspora |
| Circassian tribes |
|
Surviving Destroyed or barely existing |
| Religion |
|
Religion in Circassia |
| Languages and dialects |
|
| History |
|
Show |
| Culture |
The Hatuqway[1][a] are one of the twelve major Circassian tribes, representing one of the twelve stars on the green-and-gold Circassian flag.[2][3] They were known for their art of war as a warrior tribe. After the Russo-Circassian War, their presence in the Caucasus was destroyed during the Circassian genocide, and their number was significantly decreased and today they exist only in small communities in various diasporas, and their names are not mentioned anymore in Circassian dialectology.[4]
History
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (June 2022) |
The Hatuqway were a western Circassian tribal princedom whose homeland lay along the banks of the Kuban River. The Hatuqway people lived mostly in the mountains between the lower valleys of the Pshish River and the Belaya River.[5] Due to their small size and closeness to Temirgoy tribe, they were considered as one of the subgroups of Temirgoy. Their neighbours were Bzhedug (West), Abadzekhs (South) and, naturally, Temirgoys (East).
In the time before the Russian invasion, the Hatuqway were known as a powerful and warlike tribe that fought many wars mostly against the Crimean Tatars.
Turkish explorer Evliya Çelebi compiled the oldest detailed description of the Hatuqway tribe, he wrote:
Hatuqway province... The name of their prince is Jangiray, or Janbe Giray. This Hatuqway prince is rich, he owns many animals and eight thousand armed soldiers. Since this province was a large, fertile and beautiful homeland, its people slaughtered the son of the king of Moscow and bravely fought against the infidel Kalmyks. They are very loyal, savvy, armed and valiant soldiers. Even among the Circassian tribes, the villages are hostile to each other. So there is no shortage of constant internecine wars and strife. Nevertheless, they, communicate and trade with each other. And beyond the mountains live Abkhazians. In general, all the Abkhaz tribes are hostile towards these nomadic Circassian tribes. So, in the end, they do not have a single day free from battles and clashes – every day enemies come from different directions.
In the whole world, there are no such beauties worthy of praise and love like this people. Also there are purebred Arabian horses here. They are famous in the mountains: martens, similar to sables, wild cats, wild chickens, partridges.
They have no temples, no shopping malls and bazaars, no inns and baths. All wanderers and travelers stay with them for the night. And if you are staying as a guest in someone else's home, you will not be harmed. No matter how enemy you are for the owners, all the same, the owner of the camp, together with the neighbors living nearby, will do everything only for your well-being. You will not be blamed for a single mistake. If you ask your owner of the camp or the owner of the house for a chicken, he will show diligence, take a loan; if only he realizes that you need something, he will certainly do everything for you. If you are going to leave feeling embarrassed in something, he will give you, as if the whole world is in his hands.
I wrote and spoke very well in all one hundred and forty-seven languages, but I could not write this Circassian language, which is like a magpie shout.
— Evliya Çelebi, the Seyahatnâme
After Imperial Russia's conquest of the Caucasus in the 1860s the tribe's homeland was occupied, and its members were scattered among the other Circassian tribes, resulting in the Hatuqway effectively ceasing to exist as a separate entity.
Today, the Hatuqway have several villages in various diasporas. The Hatuqway dialect is one of the Circassian languages in big danger of extinction.
Etymology
[edit]The widely accepted theory is that the names derives from Prince Inal the Great's son Temruk's son Hatko, who was prince of the Taman Peninsula. His principality is called Hatuqway (Place of Hatko) and the people of the principality are described as "From Hatuqway". Thus the name of the principality became the name of the tribe.
Another outdated theory about the origin of the name 'Hatuqway' is that it is from Хьаты ("Hatti") + Къуэ ("son"); meaning "Hattic son". 'Hatti' is an ancient name, originally referring to a non-Indo-European people of ancient Anatolia. Some researchers have claimed there may be links between Circassians and Indo-European-speaking communities,[6] and some have argued that there are connections between Circassians and Hatti, who are from ancient Anatolian peoples,[7][8][9] but these theories have not been addressed further and are not widely accepted. This Circassian tribe may preserve this name. This name also occurs elsewhere in the Caucasus in a Nart saga wherein the hero Batraz is said to speak in Hattic.
Culture
[edit]Traditional Hatuqway culture is part of greater Circassian culture. The Hatuqway were engaged in agriculture, cattle and horse breeding. Before Islam, the Hatuqways worshipped Jesus as well as the gods of Circassians such as Shibla (god of lightning and thunder), Sozeresh (god of fertility), Yamish, Ahin, and Hakustash.[citation needed]
Language
[edit]It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled Hatuqwai dialect. (Discuss) (August 2024) |
The Hatuqway speak the Hatuqway dialect of Adyghe, which is in the Circassian language branch of the Northwest Caucasian Languages. Nowadays, the number of speakers of this language has decreased considerably and it could not find a place in the literary language as there is no Hatuqway left in the Caucasus.[citation needed]
Hatuqway villages and families
[edit]Villages
[edit]Below are some of the Hatuqway villages in Turkey.
| Province | Adyghe name | Turkish name | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kayseri | Къэйнэр, Qəynər | Kaynar | [10] |
| Kayseri | Чэчэнэй, Çəçənəy | Beserek | [11] |
| Kayseri | Лакхьэблэ, Lakhəblə | Tersakan | [12] |
| Kayseri | Лыбыйхьэблэ, Lıbıyhəblə | Kavak/Kavakkköy | [13] |
| Kayseri | Мэлак, Məlak | Malak/Malakköy | [14] |
| Kayseri | Пэдысэй, Pədısəy | Akören | [15] |
| Kayseri | Хаджыисхьакъ, Xacıyishaq | Demirciören | [16] |
| Bolu | Пэциехьэблэ, Pətsiyehəblə | Elmalık | [17][18] |
| Bilecik | Хьатыкъуае, Hatıquaye | Poyra | [19] |
| Bilecik | Адыгэчэпни, Adıgəçəpni | Çerkesçepni/Yeniçepni | [20] |
Clans
[edit]Below are some of the Hatuqway clans in Turkey.
| Adyghe name | Turkish name | Russian name |
|---|---|---|
| Бзадж | Bzac | Бзаджов |
| Джэндар | Candar | Джандаров |
| Иуаныкъу | Yivanuk | Иваников |
| Къокӏасэ | Koçase | Кочесеко |
| ЛӀымафэкъо | Lımafko | Тлимафов |
| МэфэшIукъо | Mafeşuko | Мафошов |
| Пэдыс | Pedıs | Падисов |
| Такъырыкъо | Takırıko | Такириков |
| Шэджэрыкъо | Şacerıko | Шегероков |
| Жьанэ | Jane | Жанев |
| Мастыр | Mastır | Мастиров |
| Шъобае | Şobaye | Собаев |
| Хьатыкъо | Hatıko | Хатиков |
| Хьапае | Hapaye | Хапаев |
| Утыж | Vutıj | Утижов |
| Еутых | Yevtıh | Еутыхов |
| Брыдж | Brıc | Бриджов |
| Чыназыр | Çınazır | Чиназиров |
| Нэжъ | Nej | Нажев |
| ЛIышъхьакъо | Lışhako | Тлишхаков |
| ЦIэгъош | Tseğoş | Цегошов |
| Дэбракъыкъо | Debrakıko | Дебракиков |
| Бэрзэдж | Berzec | Берзеков |
| Иуныхь | Yivnıh | Юнихов |
| Къалэбатэ | Kalebate | Калибатов |
| Хьэбатыр | Hebatır | Хабатыров |
See also
[edit]- Circassians#Tribes
- Ethnic cleansing of Circassians
- Shapsugs
- Bzhedug
- Abzakhs
- Zhaney
- Mamkhegh
- Natukhai
- Temirgoy
- Besleney
Notes
[edit]- ^ /ˈhɑːtʊkwaɪ/; Adyghe: Хьатыкъуай, [ħaːtɘqʷaːj]; Turkish: Hatukay; Arabic: حتوقاي; German: Hatkoj; Russian: Хатукай
References
[edit]- ^ Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook. Taylor & Francis. 2017. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-315-47540-0. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- ^ Cunningham, B. (1977). The New Jersey ethnic experience. W. H. Wise. p. 108. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
... or Pontic branch, consisting of Abkhaz, Ubykh, and Circassian proper (or Adyghe). The Circassians themselves are divided into some fifteen different clans, including the Abadsakh, Besliney, Bjedoogh, Hatukay, Kabardey, Kamurggoi, Shapsoogh, and Ubykh.
- ^ "Circassians". Adiga-home.net. 2010. Archived from the original on August 20, 2014. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
The 12 Circassian tribes: Abadzeh Besleney Bzhedug Yegeruqay Zhaney Kabarday Mamheg Natuhay Temirgoy Ubyh Shapsug Hatukay. The twelve stars on the Adyghe Flag also refers to the twelve tribes.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Papşu, Murat (2013-06-10). "Çerkes dillerine genel bir bakış Kafkasya ve Türkiye". Archived from the original on 2013-06-10. Retrieved 2021-01-17.
- ^ "Atlas of Caucasian languages (a pdf file)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 10, 2006.
- ^ Serbes, Nahit (2012). Yaşayan Efsane Xabze. Phoenix Yayınları. ISBN 9786055738884.
- ^ "Hititlerle Çerkezler Arasında Dil Benzerliği". 2003. Archived from the original on 8 December 2018.
- ^ Çurey, Ali (2011). Hatti-Hititler ve Çerkesler. Chiviyazıları Yayınevi. ISBN 9786055708399.
- ^ Prof.Dr. ĞIŞ Nuh (yazan), HAPİ Cevdet Yıldız (çeviren). Adigece'nin temel sorunları-1 Archived 2013-04-20 at the Wayback Machine. Адыгэ макъ,12/13 Şubat 2009
- ^ "Kaynarlılar bir araya geliyor". Nart Ajans (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 18 April 2013. Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- ^ "Beserek". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Tersakan". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Kavak". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Malak". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Akören". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Demirciören". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "TÜRKİYE'DEKİ ÇERKES KÖYLERİ". www.circassiancenter.com. Archived from the original on 24 September 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- ^ "Elmalık". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Poyra". Nisanyan Yeradları.
- ^ "Yeniçepni". Nisanyan Yeradları.

