Abstract
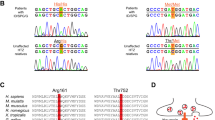
Lurcher (Lc) is a spontaneous, semidominant mouse neurological mutation1. Heterozygous Lurcher mice (Lc/+) display ataxia as a result of a selective, cell-autonomous and apoptotic death of cerebellar Purkinje cells during postnatal development2,3,4. Homozygous Lurcher mice (Lc/Lc) die shortly after birth because of a massive loss of mid- and hindbrain neurons during late embryogenesis5. We have used positional cloning to identify the mutations responsible for neurodegeneration in two independent Lc alleles as G-to-A transitions that change a highly conserved alanine to a threonine residue in transmembrane domain III of the mouse δ2 glutamate receptor gene (GluRδ2). Lc/+ Purkinje cells have a very high membrane conductance and a depolarized resting potential, indicating the presence of a large, constitutive inward current. Expression of the mutant GluRδ2Lc protein in Xenopus oocytes confirmed these results, demonstrating that Lc is inherited as a neurodegenerative disorder resulting from a gain-of-function mutation in a glutamate receptor gene. Thus the activation of apoptotic neuronal death in Lurcher mice may provide a physiologically relevant model for excitotoxic cell death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phillips, R. J. S. “Lurcher”, new gene in linkage group XI of the house mouse. J. Genet. 57, 35–42 (1960).
Caddy, K. W. & Biscoe, T. J. Structural and quantitative studies on the normal C3H and Lurcher mutant mouse. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 287, 167–201 (1979).
Wetts, R. & Herrup, K. Interaction of granule, Purkinje and inferior olivary neurons in Lurcher chimaeric mice. I. Qualitative studies. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 68, 87–98 (1982).
Normal, D. J.et al. The Lurcher gene induces apoptotic death in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Development 121, 1183–1193 (1995).
Cheng, S. S. & Heintz, N. Massive loss of mid- and hindbrain neurons during embryonic development of homozygous Lurcher mice. J. Neurosci. 17, 2400–2407 (1997).
Hollmann, M. & Heinemann, S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 31–108 (1994).
Lomeli, H.et al. The rat delta-1 and delta-2 subunits extend the excitatory amino acid receptor family. FEBS Lett. 315, 318–322 (1993).
Araki, K.et al. Selective expression of the glutamate receptor channel δ2 subunit in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197, 1267–1276 (1993).
Kashiwabuchi, N.et al. Impairment of motor coordination, Purkinje cell synapse formation, and cerebellar long-term depression in GluRδ2 mutant mice. Cell 81, 245–252 (1995).
Zuo, J., De Jager, P. L., Norman, D. J. & Heintz, N. Generation of a high-resolution genetic map and a YAC contig of the Lurcher locus on mouse chromosome 6. Genome Res. 5, 381–392 (1995).
De Jager, P. L., Zuo, J. & Heintz, N. An ∼1.2 Mb BAC contig refines the genetic and physical maps of the Lurcher locus on mouse chromosome 6. Genome Res. 7, 736–746 (1997).
De Jager, P. L., Zuo, J., Cook, S. A. & Heintz, N. Anew ataxic mouse mutant, NM1991, is new allele of the Lurcher gene, LcJ. Mamm. Genome(in the press).
Takayama, C., Nakagawa, S., Watanabe, M., Mishina, M. & Inoue, Y. Developmental changes in expression and distribution of the glutamate receptor channel δ2 subunit according to the Purkinje cell maturation. Dev. Brain Res. 92, 147–155 (1996).
Mayat, E., Petralia, R. S., Wang, Y. & Wenthold, R. J. Immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and immunocytochemistry studies suggest that glutamate receptor δ subunits form novel postsynaptic receptor complexes. J. Neurosci. 15, 2533–2546 (1995).
Takayama, C., Nakagawa, S., Watanabe, M., Mishina, M. & Inoue, Y. Light- and electron-microscopic localization of the glutamate receptor channel δ2 subunit in the mouse Purkinje cell. Neurosci. Lett. 188, 89–92 (1995).
Landsend, A. S.et al. Differential localization of δ glutamate receptors in the rat cerebellum: coexpression with AMPA receptors in parallel fiber-spine synapses and absence from climbing fiber-spine synapses. J. Neurosci. 17, 834–842 (1997).
Choi, D. W. Calcium: still center-stage in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Trends Neurosci. 18, 58–60 (1995).
Patel, N.et al. Apotassium channel mutation in weaver mice implicates membrane excitability in granule cell differentiation. Nature Genet. 11, 126–129 (1995).
Burgess, D. L.et al. Mutation of a new sodium channel gene, Scn8a, in the mouse mutant ‘motor endplate disease’. Nature Genet. 10, 461–465 (1995).
Fletcher, C. F.et al. Absence epilepsy in tottering mutant mice is associated with calcium channel defects. Cell 87, 607–617 (1996).
Burgess, D. L., Jones, J. M., Meisler, M. H. & Noebels, J. L. Mutation of the Ca2+ channel β subunit gene Cchb4 is associated with ataxia and seizures in the Lethargic (lh) mouse. Cell 88, 385–392 (1997).
Ho, S. N., Hunt, H. D., Horton, R. M., Pullen, J. K. & Pease, L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77, 51–59 (1989).
Quick, M. W. & Lester, H. A. Methods for expression of excitability proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Methods Neurosci. 19, 261–279 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank W. Hu for technical assistance; R. MacKinnon and J. Imredy for advice and help with oocyte physiology experiments; colleagues of the Heintz and Linden laboratories for discussion and support; and C. Desplan, R. Duvoisin, J. Friedman, A. Hirano, A. J. Hudspeth, A. S. Peterson, N. Segil and Z. P. Sun for critical reading of the manuscript. J.Z., W.J. and N.H. are supported by HHMI; P.L.D. is supported by NIH/NIGMS; D.J.L. is supported by PHS MH51106, the McKnight Foundation, the Develbiss Fund, and the National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, J., De Jager, P., Takahashi, K. et al. Neurodegeneration in Lurcher mice caused by mutation in δ2 glutamate receptor gene. Nature 388, 769–773 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/42009
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/42009
This article is cited by
-
Two gates mediate NMDA receptor activity and are under subunit-specific regulation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Amelioration of a neurodevelopmental disorder by carbamazepine in a case having a gain-of-function GRIA3 variant
Human Genetics (2022)
-
Consensus Paper: Strengths and Weaknesses of Animal Models of Spinocerebellar Ataxias and Their Clinical Implications
The Cerebellum (2022)