This is a report server for reports created in R based on Renjin and Spring Boot. The name comes from the one of Odin's ravens who he sent out every day to scout the world and bring him back reports.
Munin is a reporting server that can run and display reports created in Renjin R on the web.
Currently, it supports R reports where the R code returns html, or the mdr format (markdown with support for r code, similar to rmd - more on that further down).
Creating html from R code can be done by using the htmlcreator package for Renjin, e.g:
library('se.alipsa:htmlcreator')
html.clear()
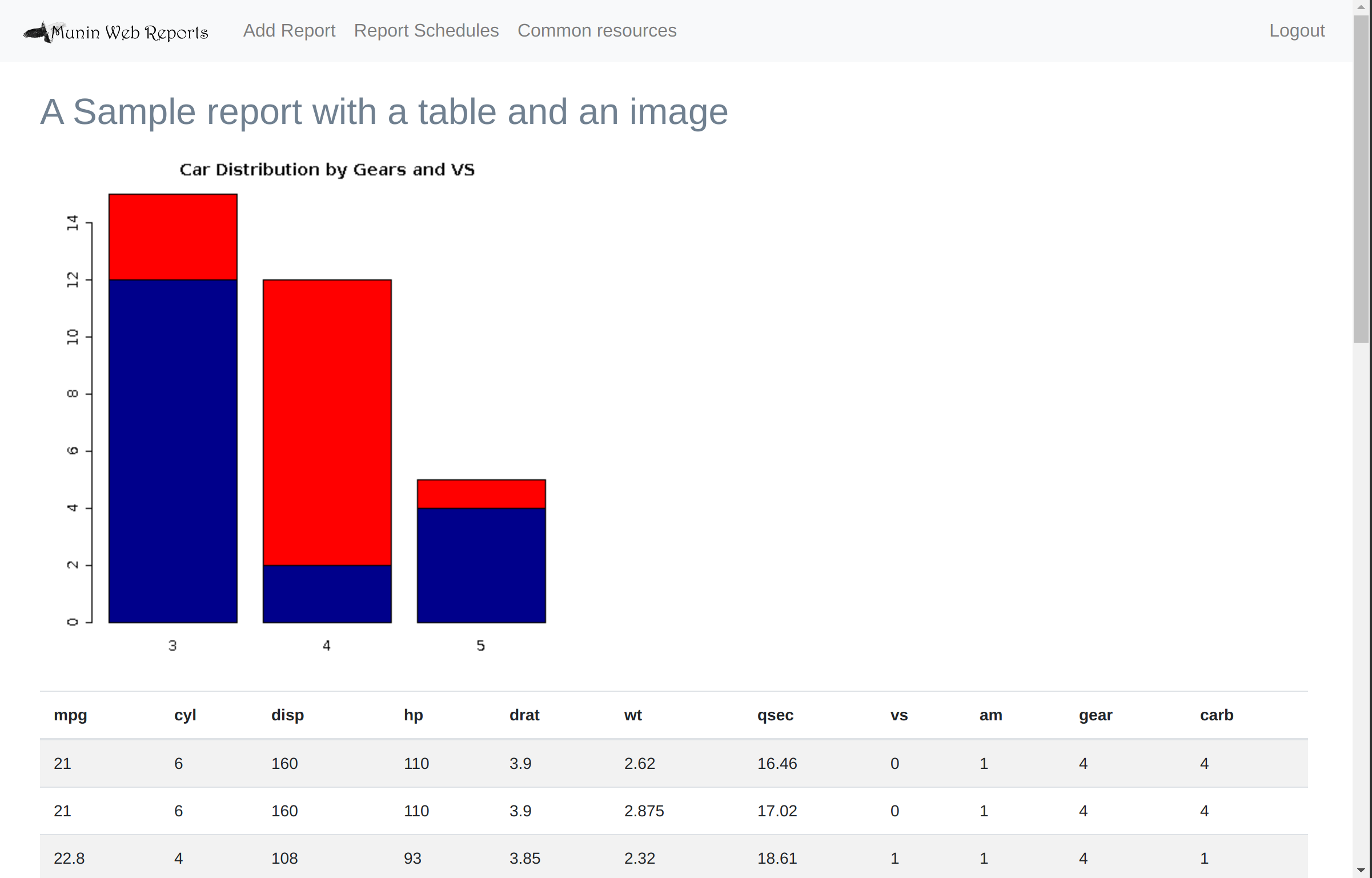
html.add("<h2>A Sample report with a table and an image<h2>")
html.addPlot(
{
barplot(
table(mtcars$vs, mtcars$gear),
main="Car Distribution by Gears and VS",
col=c("darkblue","red")
)
}
)
html.add("<div class='table'>")
html.add(mtcars)
html.add("</div>")
# Return the html
html.content()Any R code that returns html can be used however - you are not bound to use htmlcreator. This is why these type of reports are classified as "UNMANAGED" (as opposed to MDR) i.e. there is no magic to it (other than the magic of R).
Ride supports the Munin report formats natively, so you can use Ride to create and edit Munin reports.
If you use some other IDE to create reports then you can do a simple trick to detect the environment and display the report in the IDE or in Munin, i.e. just before the very end when you return the html content, you check if you are running in the IDE and display the report in Viewer tab, e.g:
# If we are using some IDE that defines an inout object), display the report in the IDE
if(exists("inout")) {
inout$viewHtml(html.content(), "SimpleExample")
}
html.content()Note that from ver 1.2.3 of Ride, there is built-in support for Munin reports, and you have a View button instead of the "normal" Run button than does this magic for you (and adds bootstrap etc. making the View look the same as when viewed from a browser when run from within Munin).
When publishing a report you can optionally add report parameters in the form of html form content, e.g:
<div class="form-group">
<label for="firstName">First name</label>
<input id="firstName" name="firstName">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<select name="dataSet">
<option value="mtcars">Motor Trend Car Road Tests</option>
<option value="iris">3 species of iris flowers</option>
</select>
</div>If you want numeric values, you need to convert the parameter to a number (e.g. by using as.numeric())
Note that, in order to be able to schedule a parameterized report, you must provide default parameters in the R code
e.g. by using exists(). Let's say the parameter is the name of the dataset to use i.e.
<div class="form-group">
<select name="dataSet">
<option value="mtcars">Motor Trend Car Road Tests</option>
<option value="iris">3 species of iris flowers</option>
</select>
</div>Then you can provide a default value for it as follows:
if (!exists("dataSet")) {
dataSet <- "iris"
}Bootstrap is available, so you can use bootstrap classes to style the form. If you are using the htmlcreator package, the html.add() functions takes a list of attributes as an optional parameter. This way you can add attributes such as id and class like this:
html.add(mtcars, htmlattr=list(id = "mtcars-table", class="table table-striped"))You can either upload a common stylesheet (using the "common resources" button) that you can reference in your reports e.g.
# import the uploaded stylesheet mystyle.css
html.add("<link rel='stylesheet' href='/common/resources/mystyle.css' />")or, to put it in the head section (should only be needed if your viewers have very old browsers):
# import the uploaded stylesheet mystyle.css
html.add('
<script>
const cssLink = document.createElement("link");
cssLink.href = "/common/resources/mystyle.css";
cssLink.rel="stylesheet";
document.head.appendChild(cssLink);
</script>
')...and you can of course also add stylesheets inline, e.g.
# add a style class to adjust the font size of table text:
html.add("
<style>
.table-font-size {
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
")
# reference the class together with some bootstrap classes when rendering a table:
html.add(mtcars, htmlattr=list(class="table table-striped table-font-size"))Mdr files is another supported report format. Support for mdr files is provided by the mdr package. Mdr files are similar to rmd files but gives you more control of the output of the r code parts. As a consequence it also pushes rendering responsibility over to you i.e. you need to make sure that your R code returns valid markdown syntax. Fortunately, the r2md package does just that. It is "built in" to the mdr package so no need to explicitly load it with "library(...)".
Set the "ReportType" to MDR to have Munin call mdr to render the report (mdr -> md -> html). If report type is set to UNMANAGED Munin assumes it is working R code that returns html (like in all the example above which is using the htmlcreator package) and will execute the code and render its result.
Here is a mdr example:
# MDR report example
This is a straight forward example of a mdr report.
This way of creating reports are useful when there are more text to write than actual R code to run.
I.e. you want the ease of markdown for your text, but the power of R for dynamic content.
There are two ways to add R content.
1. Inline, eg 2 + 5 * pi = `r 2 + 5 * pi` or `r x <- 2 + 5 * pi; x` which just evaluates and returns the result as markdown text
2. Code blocks, i.e. longer pieces of R code that returns Markdown text e.g.
```{r}
employee <- c('John Doe','Peter Smith','Jane Doe')
salary <- c(21000, 23400, 26800)
startdate <- as.Date(c('2013-11-1','2018-3-25','2017-3-14'))
endDate <- as.POSIXct(c('2020-01-10 00:00:00', '2020-04-12 12:10:13', '2020-10-06 10:00:05'), tz='UTC' )
df <- data.frame(employee, salary, startdate, endDate)
md.add(df, attr=list(class="table"))
```
We can also reference previous code in the document e.g:
```{r}
md.new(paste("As stated before, 2 + 5 * pi =", x))
```
Plots are supported, here is an example of a barplot:
```{r}
md.add("# Barplot")
md.add(
barplot,
table(mtcars$gear),
main="Car Distribution",
horiz=TRUE,
names.arg=c("3 Gears", "4 Gears", "5 Gears"),
col=c("darkblue","red", "green")
)
```
See the r2md [README](https://github.com/perNyfelt/r2md/blob/main/README.md) for more information.
Which will result in the following report output:

Rmd requires knitr which depends on the Markdown package. The Markdown packages has some C code that the Renjin GCC bridge cannot make sense of. Hence, knitr and thus the rmd file format does not (currently) work in Renjin. As soon as that is fixed, I plan to support rmd files in Munin as well.
There are a few different ways to install Munin.
-
Simple:
- Download the munin-[version].jar file from https://github.com/perNyfelt/munin/releases/latest
- Copy the jar to a directory of your choice
- create an application-prod.properties file and override whatever default config you need
- run the application with
java -Dspring.profiles.active=prod -jar munin-[version]-exec.jarSee production config for info on how to make it a service.
-
Customized: This is appropriate if you want to do more involved customization.
- Create a new maven (of Gradle or whatever) project and set munin as the parent project:
<parent> <artifactId>munin</artifactId> <groupId>se.alipsa</groupId> <version>1.1.7</version> </parent>
-
Customized alternative: Fork the project on github and make any changes you want. Create the executable jar with
mvn clean packageand copy it from your target dir.
The release jar is in "demo" mode meaning it comes with a few user accounts preinstalled, and uses
a file base h2 database for persistence.
You start it by simply doing java -jar munin-[version]-exec.jar.
The application will be available on https://localhost:8088
See here for some screenshots.
The default admin user name / password is admin / adminpwd. If you log in as admin you will see an "Administration" button on the main page (https://localhost:8088). There are three predefined roles:
- Viewer: someone who can only view reports. There is one predefined: test / testpwd
- Analyst: someone who can view / add / edit and schedule reports. There is one predefined: analyst /analystpwd
- Admin: someone who can do user/role administration. There is one predefined: admin / adminpwd
There a few example reports that might help you get going which you can download/copy and publish to the Munin server:
-
Simple: This is a Simple report with a barplot and a table with some styling.
-
Parameterized: This is report that show how to do parameterized reports. The parameters form provides the input variables used in the report.
-
Pie Chart with External Image: This reports requires you to upload an external image first (this is to show the use of common content). Download the iris.jpg and upload the content using the "common resources" button you can see if you are logged in as admin or analyst. Then you can upload the pieChartWithExternalImage.R script and publish the report.
-
Table with external CSS: This report requires you to upload an external css (another typical us of common content). Download the [mystyle.css]((https://github.com/perNyfelt/munin/raw/main/src/test/resources/mystyle.css) and upload the content using the "common resources" as described above. You can then create the report based on the tableWithExternalCss.R script.
-
Example mdr report This report is an example of a mdr report, which is the other report format supported in Munin and described briefly above.
-
MDR code snippets Another very simple mdr report that show the mixing of formatted blocks styled for a specific language and the r code blocks which will be executed
You can do any customization by adding an application-prod.properties file next to the jar.
Then start the server with -Dspring.profiles.active=prod set e.g.
java -Dspring.profiles.active=prod -jar munin-[version]-exec.jar
This will override any default config with your specific config.
See application.properties for settings to override. Typically, you will change the following
Set the property server.port to something else e.g. server.port=8080 to listen for
web requests on port 8080 instead of the default 8088.
The database stores the reports and user config.
Default config is a file based H2 database (jdbc:h2:file:./munindb;DATABASE_TO_LOWER=TRUE)
To change the underlying database config, set the spring.datasource.xxx parameters
as you see fit.
There is a braking change between the h2 database used prior to munin version 1.2.0 (i.e. h2 1.4.x) and the h2 version used in version from 1.20 and later (h2 version 2.1.x). TO upgrade the database you need to export the old database to SQL and then import in the new version. Essentially you need to the following steps
- Download the 1.4.200 h2 from https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/h2database/h2/1.4.200/h2-1.4.200.jar
- Backup using
java -cp h2-1.4.200.jar org.h2.tools.Script -url jdbc:h2:file:./munindb -user sa -script test.zip -options compression zip - rename ./munindb.* to ./oldmunindb.*
- Download 2.210 from https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/h2database/h2/2.1.210/h2-2.1.210.jar
- Restore using
java -cp h2-2.1.210.jar org.h2.tools.RunScript -url jdbc:h2:file:./munindb -user sa -script test.zip -options compression zip FROM_1X
See the Upgrade, Backup, and Restore section of the h2 documentation for details. There is also a simple database migration script you can use (edit credentials etc. appropriately first).
Note that if you want another database other than H2, you need to make sure spring boot can access the jdbc driver jar. This can be done by setting the loader.path, e.g:
- create a lib folder where your spring boot jar resides
- copy the additional jar to the lib folder
- add the path to the folder when starting spring boot:
java -Dloader.path=file:lib/ -Dspring.profiles.active=prod -jar munin-[version]-exec.jar
Mail is used to email passwords when users are created as well as mailing out scheduled reports.
Set spring.mail.xxx properties as suitable for your mail server
The "from" address is controlled by the property munin.email.from
Perhaps not something you would typically override, but you likely want to set up some kind of integration with whatever health monitoring tool you are using at your business.
Actuator is included with default settings which means that a network monitoring tool can
check for availability by querying https://your-host-name:8088/actuator/health which will return the
json string {"status":"UP"} if everything is normal.
To run munin as a service, create a service starter script and make it run as a Linux service. Essentially:
- Edit the service starter script
- Copy the script to /etc/systemd/system
- start the service
sudo systemctl start munin.service - Make sure the service is running
systemctl is-active munin.service
For a Windows service see winsw. Essentially you do:
- Take WinSW.NET4.exe (or WinSW.NETCore31.x64.exe if you do not have .NET installed) from the distribution, and rename it to munin-windows.exe.
- Edit munin-windows.xml to match your file locations.
- Place those two files side by side.
- Run
munin-windows.exe installto install the service. - Run
munin-windows.exe startto start the service.
See the Spring documentation for more info.
The first thing you should probably do after setting up a database and providing the necessary config overrides is to change / remove the three predefined users using the admin interface mentioned in the demo section above. If you want to keep the admin user, begin by assigning your email to it and then log out and reset the password - a new password will then be emailed to you.
Munin provides a REST api for integration with other application. It is described here.
You might notice that you have code snippets that you want to centralize and reuse. The standard approach to that is to formulate those code snippets into functions that you include in a package.
An alternative way is to upload the R code into the common resource area and source it from the report e.g.
source(paste0(muninBaseUrl, "/common/resources/utils.R"))- Upgrade the h2 version from 1.4.200 to 2.1.210 due to security vulnerability issues with the previous versions. Migration is needed.
- Added a migrateDb.sh script to facilitate h2 migration
- Upgrade liquibase core from 4.7.0 to 4.7.1
- upgrade spring boot, mdr, plugins etc.
- Add some example to docs
- Add breadcrumbs for improved navigation
- Cleanup alignments and fix some bootstrap 4 to 5 changes
- Add info dialog for report types
- upgrade spring-boot, liquibase, junit, htmlcreator, mdr2html
- Bump versions for jquery, spring boot, cronutils, liquibase, spotbugs-annotations, junit, commons-collections bootstrap, webjars-locator
- Load javascripts at the end of the body instead of in the header - should give a slight perceived speed increase
- Add preview to common files section
Fix regression bug introduced in 1.1.3 where jquery update was not handled properly in the header.
- Allow public access to shared resources (/common)
- Add muninBaseUrl variable to the global R env so it can be referred to in reports.
- Upgrade jquery
- add docs on how to add external css (two ways, in body or in head using js)
- cleanup some link tags in the headers (use xhtml style)
- Add mdr output to the mdr example in the README.md
- Add restapi for integration with other tools (mainly to be able to add built in support for creating/editing Munin reports in Ride).
- convert unmanaged R reports to character vector if it returned something else.
- upgrade dependencies for junit, liquibase, mdr2html, and spotbugs, htmlcreator, spring-boot, bootstrap
- Add syntax highlighting for code blocks in mdr reports.
- Fix bug that prevented "normal" syntax highlighted blocks from working properly
- Go to group page instead of back to index after edit report
- Change to deploy the original jar to central instead of the repackaged one.
- Improve documentation
- Add support for the mdr (markdown with r) format
- Add report groups (folders that go one level deep only)
Add support for adding/removing external content (e.g. images and css) which can be referenced from the reports.
Basic functionality for admin and view/add/edit/delete/schedule reports.
- R interpreter for the JVM; used to execute reports
- License: GNU General Public License v2.0
- The application server framework providing most of the functionality
- License: Apache License 2.0
- Integration of Renjin with Spring boot
- License: MIT
- renjin extension (package) to create html from R objects (data.frames, images etc)
- License: MIT
- renjin extension (package) to create html from mdr files / content
- License: MIT
- Various IO stuff
- License: Apache License 2.0
- Used to handle various collection transformations
- License: Apache License 2.0
- Used to parse cron expressions to provide "plain english" descriptions for them.
- License: Apache License 2.0
- Simplifies web resource locations
- License: MIT
- Pretty web pages
- License: Apache License 2.0
- More convenient javascripts
- License: MIT
- Syntax highlighting for R and html code
- License: MIT
- Syntax highlighting for mdr reports
- License: BSD 3-Clause
See the pom.xml for more details...